Extracellular Vesicle Characterization and Quantification Service
Extracellular vesicle characterization and quantification is a technical service for comprehensive analysis of extracellular vesicles (EVs), including particle size, morphology, concentration, and surface markers, aiming to assess the quality and characteristics of EVs in a given sample. This service is based on multiple platforms such as nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), dynamic light scattering (DLS), and flow cytometry (FACS), and is combined with protein quantification and Western blot methods to achieve precise quantification and molecular-level characterization of vesicles.
Extracellular vesicle characterization and quantification service is widely applied in fields such as tumor biology, immune regulation, drug delivery, stem cell research, and biomarker development. It is a critical step to ensure the reliability and comparability of experimental data in exosome research. Accurate characterization and quantification not only help standardize research workflows but also lay the foundation for subsequent functional validation, mechanistic studies, and clinical translation.
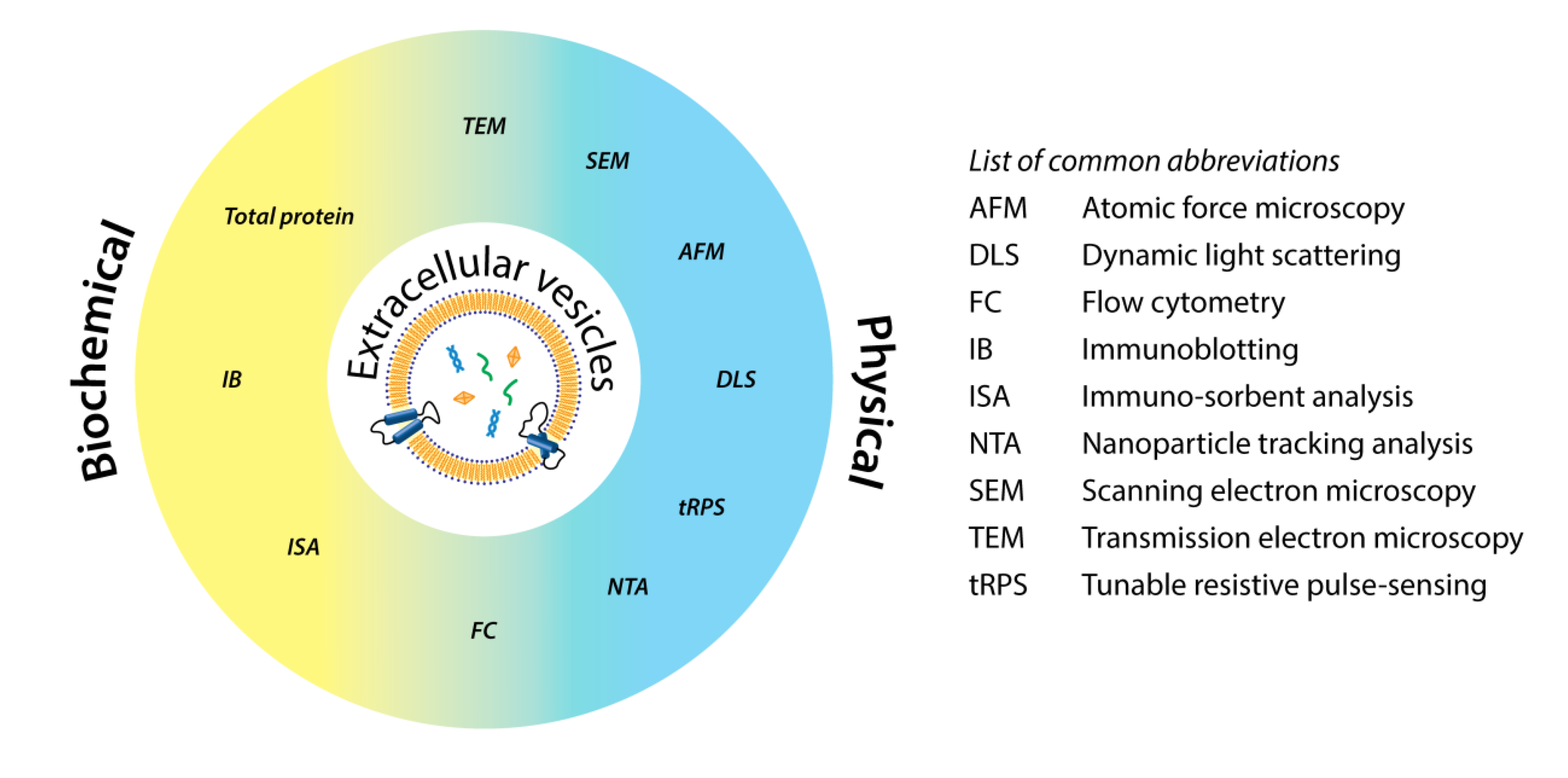
Hartjes, T A. et al. Bioengineering, 2019.
Figure 1. Schematic Classification of Common Technologies for EV Analysis.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Based on advanced platforms such as nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA), flow cytometry, and transmission electron microscopy (TEM), the extracellular vesicle characterization and quantification service offered by MtoZ Biolabs enables comprehensive analysis of EVs in terms of particle size distribution, concentration, morphological structure, and surface markers. The service covers key aspects including particle size and concentration detection, morphological observation, and surface protein marker analysis, ensuring high-resolution and reproducible quantitative and characterization data. This supports in-depth research on exosomes in areas such as biomarker development, disease studies, and drug delivery. MtoZ Biolabs provides a variety of optional methods to meet diverse research needs for comprehensive characterization and precise quantification of extracellular vesicles, including the following categories:
1. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)
Used to measure the particle size distribution and concentration of EVs, NTA features high resolution and high throughput, making it suitable for basic characterization of most EV samples.
2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
Directly visualizes the morphology and membrane structure of EVs, confirming their typical vesicular appearance. TEM is an essential tool for morphological validation of EVs.
3. Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting (FACS)
Combined with fluorescent antibody labeling, FACS is used to analyze surface markers of EVs (such as CD9, CD63, and CD81), enabling subpopulation typing and origin analysis. It is particularly suitable for larger EV particles or systems using antibody-conjugated beads.
4. Western Blot
Used to detect characteristic EV-associated proteins such as Alix, TSG101, and CD63, Western blot serves to verify the molecular features and purity of EV samples.
5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
Applied to quantitatively detect specific protein markers within EVs, ELISA offers high sensitivity and is well-suited for targeted quantitative analysis.
Service Advantages
1. Multi-Platform Integration for Comprehensive Characterization
By combining technologies such as NTA, TEM, FACS, Western blot, and ELISA, MtoZ Biolabs enables multidimensional and precise analysis of EVs, covering particle size, concentration, and surface markers.
2. High Sensitivity and High Resolution
Utilizing advanced instrumentation, this service ensures accurate and reliable results, making it suitable for quantitative studies involving low-abundance vesicles and limited sample volumes.
3. Standardized Workflow and High Reproducibility
A rigorous experimental protocol and quality control system are established to ensure data consistency across different sample batches.
4. Experienced Team and Customized Solutions
Supported by a skilled technical team, MtoZ Biolabs offers flexible and tailored analytical strategies and data interpretation services to meet diverse research needs.
Applications
1. Disease Biomarker Discovery
By analyzing the characteristics of EVs derived from body fluids, this service supports the identification of diagnostic or prognostic biomarkers associated with conditions such as cancer and neurodegenerative diseases.
2. Drug Delivery System Development
The extracellular vesicle characterization and quantification service can be used to evaluate the size, purity, and surface modifications of engineered EVs, helping to optimize their stability and targeting efficiency as nanoscale delivery vehicles.
3. Exosome Product Quality Control
Characterization of exosomes provides structural, compositional, and purity-related quality control support for the research and industrialization of exosome-based products.
4. Intercellular Communication Mechanism Studies
The extracellular vesicle characterization and quantification service can be used to elucidate the roles of EVs in cellular signaling, immune regulation, and pathological processes.
Case Study
1. Diversity of Extracellular Vesicles in Human Follicular Fluid: Morphological Analysis and Quantification
This study aimed to investigate the types and characteristics of extracellular vesicles (EVs) in human follicular fluid, analyze their morphological diversity, and conduct quantitative assessment. Human follicular fluid samples were used as research subjects. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was employed to observe the morphology of EVs, while nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) was used to measure particle size distribution and concentration. The results showed that multiple types of EVs, including exosomes and microvesicles, were present in follicular fluid, with a broad size range from 30 nm to 1000 nm. Additionally, the concentration of EVs in follicular fluid was significantly higher than in other body fluids, and variations in EV size and concentration were observed among samples from different patients. The study concluded that EVs in follicular fluid exhibit diverse morphological and concentration characteristics, suggesting a potential role in the ovarian microenvironment. These EVs may contribute to follicle development, oocyte maturation, and infertility research, and serve as a promising tool for further exploration of ovarian physiology and pathology.

Neyroud, A S. et al. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022.
Figure 2. Cryo-TEM Images of the 10 Subcategories of EVs.
2. Comparing Approaches to Normalize, Quantify, and Characterize Urinary Extracellular Vesicles
This study aimed to compare various methods for normalization, quantification, and characterization of extracellular vesicles (EVs) in urine in order to optimize the analytical workflow for urinary EVs. Urine samples from healthy donors were used as research subjects. EVs were isolated using multiple separation techniques, including ultracentrifugation, polymer-based precipitation, and column chromatography. Nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA), protein quantification, Western blot, and flow cytometry were employed to assess EV particle size, concentration, and marker expression. The results indicated that different isolation and normalization strategies significantly affected EV recovery and detection sensitivity. Notably, normalization based on urinary creatinine concentration or total protein content improved data comparability across samples. The study concluded that selecting appropriate combinations of normalization and detection methods is essential for obtaining consistent and reproducible data, providing a technical foundation for the application of urinary EVs in disease biomarker discovery and urological research.
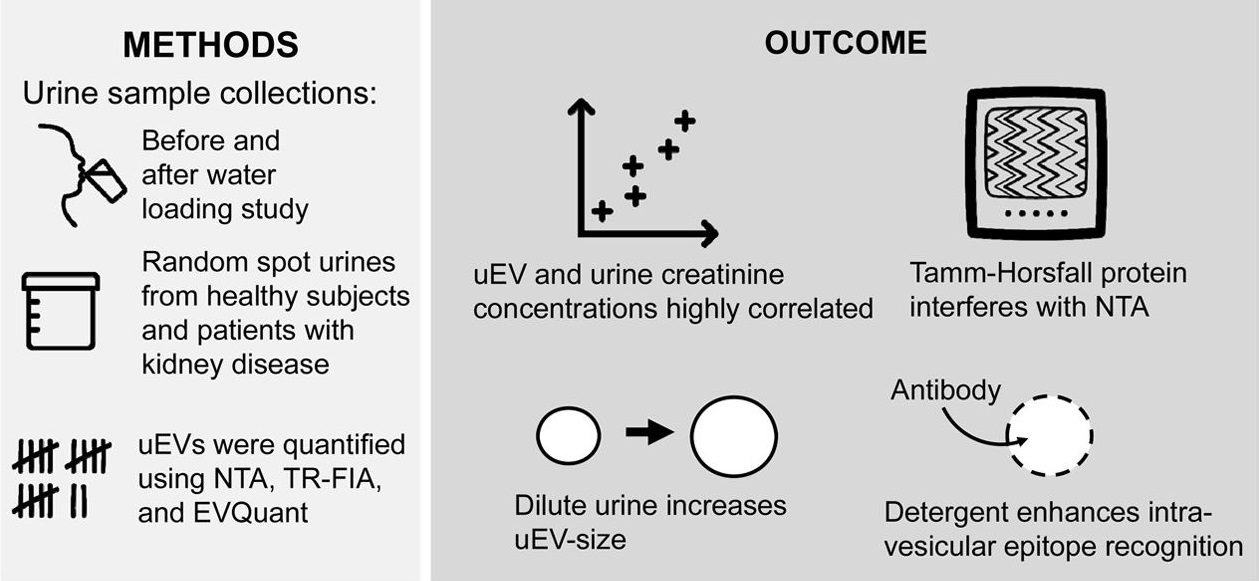
Blijdorp, C J. et al. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology: JASN, 2021.
Figure 3. The Visual Abstract of the Study.
FAQ
Q1: What Types of Samples Are Typically Required for Extracellular Vesicle Characterization? Are there Any Specific Requirements?
A1: We accept a variety of biological samples including serum, plasma, cell culture supernatant, urine, saliva, and cerebrospinal fluid. We recommend that clients provide sterile, non-thawed samples that have been subjected to low-speed centrifugation to remove cell debris. Samples should be stored frozen and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles to ensure EV integrity. For detailed guidelines, please contact us.
Q2: Is it Possible to Select Only One or a Few Detection Methods?
A2: Absolutely. Our service supports modular selection, allowing clients to choose individual assays or a combination based on their research goals. We also provide technical consultation to help recommend the most suitable analysis strategy.
How to order?







