CEPCs-Targeted Exosome Modification Service
CEPCs-Targeted Exosome Modification Service enables the engineering of exosomes to specifically recognize and deliver therapeutic molecules to circulating endothelial progenitor cells (CEPCs), offering a novel, efficient, and precise delivery platform for vascular repair, regenerative therapy, and targeted drug delivery.
CEPCs are a cell population with vascular regenerative potential and have been widely applied in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases, vascular repair, and regenerative medicine research. However, conventional delivery methods often fail to achieve precise targeting and efficient delivery, limiting their clinical utility.
Exosomes, nanoscale vesicles secreted by cells, exhibit excellent biocompatibility, stability, and delivery capability. By modifying the exosomal membrane with specific targeting peptides, antibodies, or aptamers, exosomes can be endowed with targeting specificity toward CEPCs. These engineered exosomes can bind to receptors on the CEPC surface, enter the cells via endocytosis, and release their therapeutic cargo, thereby modulating CEPC function and promoting vascular repair and regeneration.
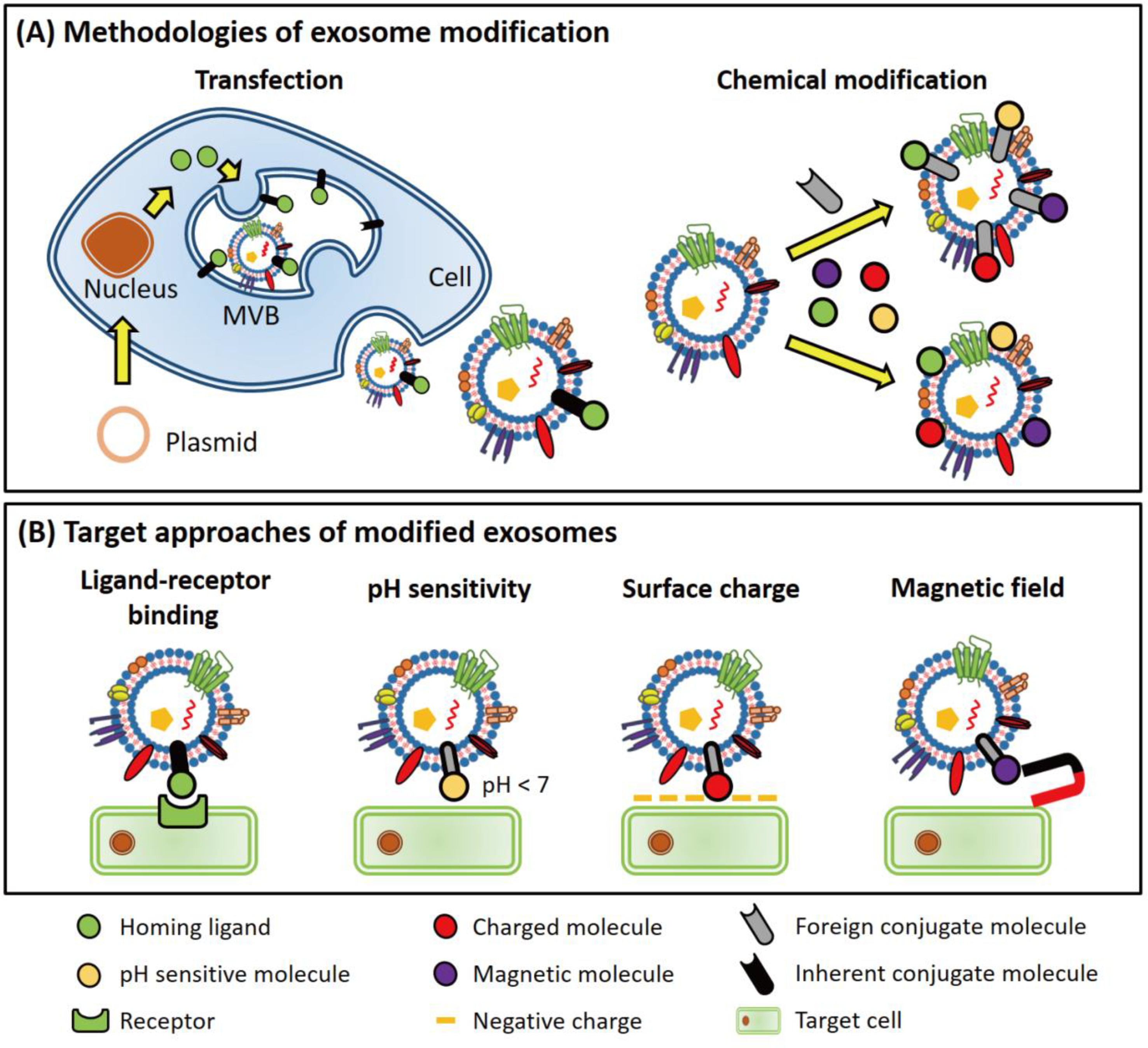
Fu S. et al. NanoImpact. 2020.
Figure 1. The strategies for preparing targeted exosomes.
Utilizing genetic engineering and other biotechnological approaches, MtoZ Biolabs offers the CEPCs-Targeted Exosome Modification Service enabling exosomes to specifically target CEPCs through surface modification. This service supports precise drug delivery, gene therapy, and vascular repair, providing innovative solutions for cardiovascular disease treatment and regenerative medicine research.
Analysis Workflow
1. Targeting Ligand Design and Screening
Design and screen peptides, antibodies, or aptamers targeting CEPCs based on research needs, ensuring high affinity and specificity.
2. Construction of Modified Expression System
Fuse the targeting ligand to exosomal membrane proteins (e.g., Lamp2b, CD63), and establish engineered cell lines for the secretion of targeted exosomes.
3. Exosome Isolation and Purification
Exosomes are isolated from the engineered cell culture supernatant using methods such as ultracentrifugation, size-exclusion chromatography (SEC), or immunomagnetic bead separation.
4. Functional Molecule Loading (Optional)
Load miRNA, siRNA, proteins, or small-molecule drugs into the exosome interior using electroporation, sonication, or other methods to enhance therapeutic potential.
5. Targeting Validation
Evaluate whether the modified exosomes can specifically bind to and be taken up by CEPCs.
6. Delivery and Reporting
Provide a comprehensive experimental data report, including modification methods and targeting performance.
Applications
Examples of applications for CEPCs-Targeted Exosome Modification Service include:
Vascular Repair and Regenerative Medicine
Deliver pro-angiogenic factors or miRNAs to CEPCs via engineered exosomes to stimulate proliferation, migration, and tube formation, supporting research in ischemic heart disease, peripheral vascular disease, and diabetic vascular complications.
Gene Regulation and RNA Interference Studies
Deliver regulatory molecules such as siRNA, miRNA, or mRNA to CEPCs to modulate gene expression, investigate signaling pathways, and explore disease mechanisms.
Preclinical Cardiovascular Research
Apply exosome delivery systems in animal models to evaluate CEPC function and therapeutic efficacy in cardiovascular disease, providing theoretical support for clinical applications.
Service Advantages
1. High-Standard Technical Platform: A stable platform for exosome production and modification, supporting the design and optimization of various targeting molecules (peptides, antibodies, aptamers).
2. Comprehensive Services: A full-process solution for CEPCs-Targeted Exosome Modification, from exosome preparation and targeting modification to final data reporting.
3. Expert Technical Support: A team of experienced professionals offers customized experimental design and academic guidance to ensure project success.
FAQ
Q. How to select the right targeting molecule to ensure specific recognition and binding to CEPCs?
Targeting molecules for exosomes are typically ligands that bind specifically to receptors expressed on the surface of CEPCs, such as anti-CD34 antibodies or CXCR4 peptides. These ligands must have high affinity and specificity, and their targeting performance should be validated via flow cytometry, co-culture assays, and other techniques. Selection is based on surface marker profiles of CEPCs, ensuring the exosomes can efficiently recognize and bind to the target cells, thereby enhancing delivery precision.
Q. How do I know if this service fits my research needs?
Our expert team is available to discuss your research objectives and offer tailored recommendations. Whether you're studying cardiovascular diseases, angiogenesis, or tissue regeneration, we can help you design a customized exosome modification strategy to meet your specific requirements.
How to order?







