CD24-Expressed Exosome Modification Service
CD24-Expressed Exosome Modification Service involves the surface modification of exosomes with CD24 to reduce their uptake by macrophages, enhance their stability in circulation, and improve their delivery efficiency to target tissues—ultimately increasing the efficacy of therapeutic or nucleic acid cargos.
As exosomes gain increasing traction in drug delivery, immunotherapy, and targeted tissue research, enhancing their in vivo stability and immune evasion capabilities has become a major challenge. Once introduced into the circulatory system, exosomes are highly susceptible to rapid recognition and clearance by the mononuclear phagocyte system (MPS), limiting their bioavailability and therapeutic potential.
CD24 is a highly glycosylated adhesion protein that is anchored to the cell membrane through glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI). It can release anti-phagocytic signals and inhibit excessive immune responses. Studies have shown that in many malignant tumors (such as ovarian cancer and breast cancer), high expression of CD24 is closely related to the immune escape of tumor cells. CD24 can act as an anti-phagocytic signaling molecule by binding to the macrophage surface receptor Siglec-10 to inhibit phagocytic function, thereby helping tumor cells evade immune clearance. Taking advantage of this property, CD24 can be modified on the surface of exosomes to inhibit the phagocytosis of exosomes by macrophages, prolong the circulation time of exosomes in the body, and improve their effectiveness as drug delivery carriers.
Using genetic engineering or chemical conjugation methods, MtoZ Biolabs offers CD24-Expressed Exosome Modification Service enabling the customization of CD24-modified exosomes to inhibit phagocytic clearance, extend in vivo half-life, and enhance delivery efficacy.
Analysis Workflow
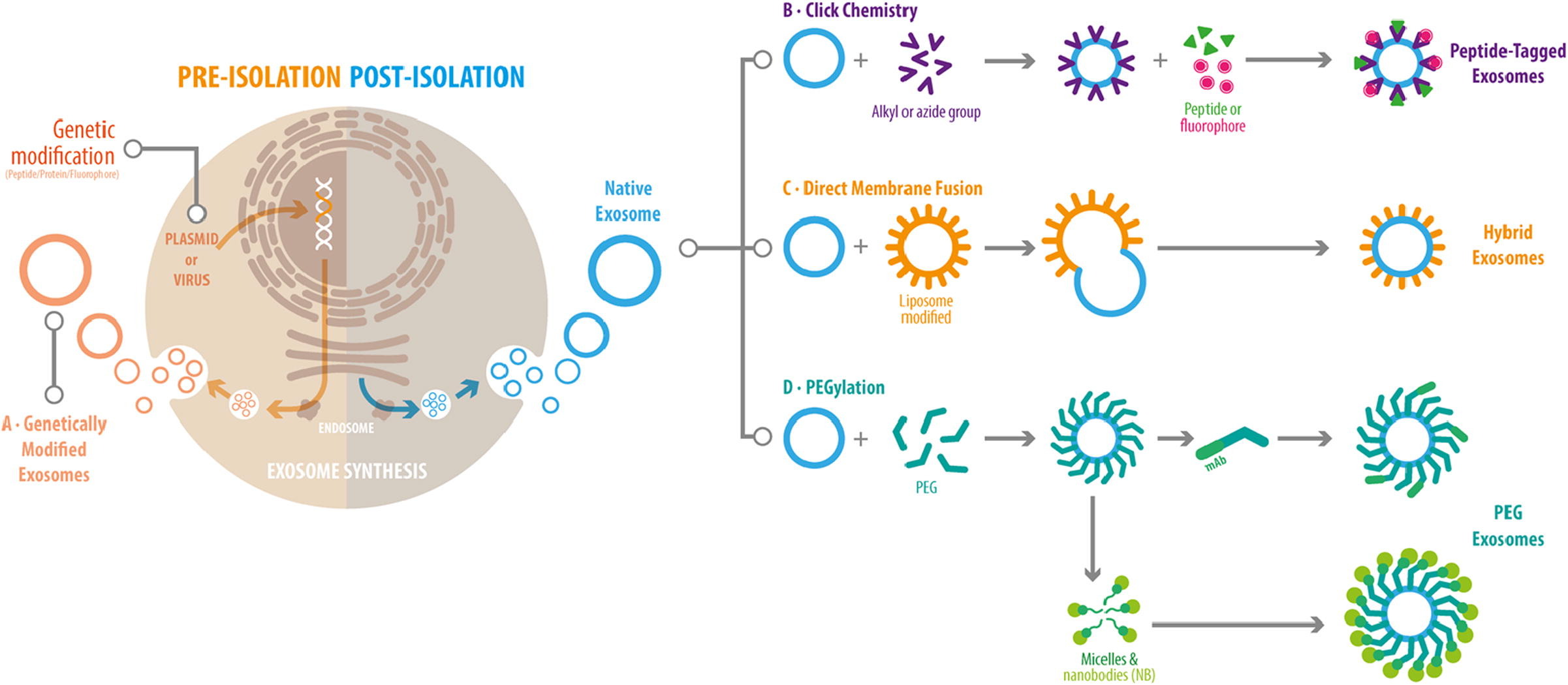
Parada N. et al. Journal of Advanced Research. 2021.
CD24-Expressed Exosome Modification Service provides a variety of methods for exosome CD24 modification. The following outlines the core process of the fusion protein expression approach:
1. Fusion Protein Expression Design
Design a fusion construct combining CD24 with an exosomal membrane protein to ensure correct localization of CD24 on the exosome surface.
2. Stable Cell Line Construction and Exosome Production
Transfect or infect HEK293T, MSCs, or client-provided cell lines with the fusion construct. Collect the culture supernatant and isolate exosomes using ultracentrifugation, size exclusion chromatography (SEC), or nanofiltration.
3. CD24 Modification Validation
Confirm CD24 surface expression on exosomes via Western blotting, flow cytometry, and immunogold TEM. Evaluate exosome particle size, concentration, and integrity using NTA and TEM.
Applications
Specific application examples of CD24-Expressed Exosome Modification Service:
Development of immune-evasive drug delivery platforms
Improve delivery efficiency of RNA, proteins, or small molecules for applications in tumor therapy and chronic inflammatory disease models.
Prolonged in vivo half-life and enhanced stability
Reduce hepatic and splenic uptake to improve systemic circulation time of exosomes.
Assisted physiological barrier penetration
Enhance drug delivery efficiency to the nervous system when combined with targeting strategies.
FAQ
Q. How is CD24 Modified onto Exosomes? Which Membrane Proteins are Used for Fusion Expression?
CD24 is typically fused with exosomal membrane proteins such as CD63, LAMP2B, or VSVG to achieve stable membrane localization. We recommend using CD63-CD24 or LAMP2B-CD24 fusion constructs, which enable outward-facing CD24 expression on the exosome surface during biogenesis. Fusion site (N-/C-terminal) and linker design can be optimized based on the cargo type and cell background to ensure both expression stability and functional activity.
Q. Does CD24 Modification Affect Cargo Encapsulation or Delivery Efficiency?
No. CD24 is localized on the exosomal membrane surface, while the cargo—such as siRNA, proteins, or small-molecule drugs—is encapsulated within the lumen. These regions are spatially distinct and functionally complementary. CD24 modification not only preserves cargo loading efficiency but also enhances overall delivery performance by reducing immune clearance and increasing tissue accumulation.
Case Study
In this study, engineered CD24-overexpressing exosomes (EXO-CD24) were delivered via inhalation to patients with mild to moderate COVID-19-associated ARDS. The modified exosomes demonstrated excellent safety and significantly improved inflammatory markers such as CRP and ferritin. These findings suggest that EXO-CD24 can suppress excessive immune responses via the CD24–Siglec-10 axis, offering promising therapeutic potential for controlling cytokine storms and mitigating disease progression.
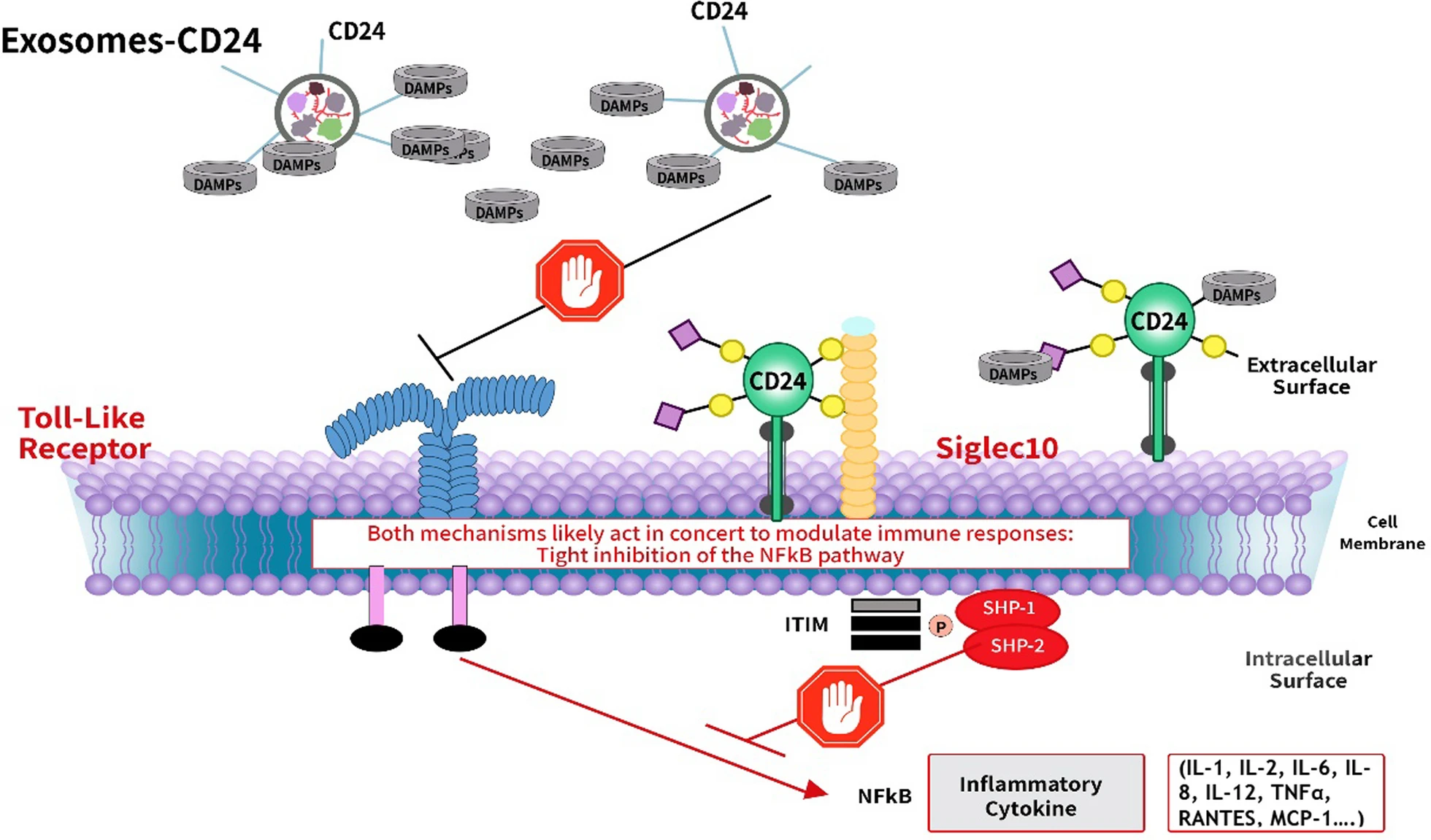
Grigoropoulos I. et al. Respir Res. 2024.
How to order?







