Aptamer-Based Exosome Targeting Service
- Covalent coupling (e.g., click chemistry): Provides high stability, ideal for in vivo applications.
- Non-covalent binding (e.g., electrostatic interaction, strand hybridization): Offers flexibility, suitable for high-throughput screening.
- Lipid-anchor insertion (e.g., DSPE-PEG-Aptamer): Balances targeting efficiency and membrane integration, widely used in drug delivery systems.
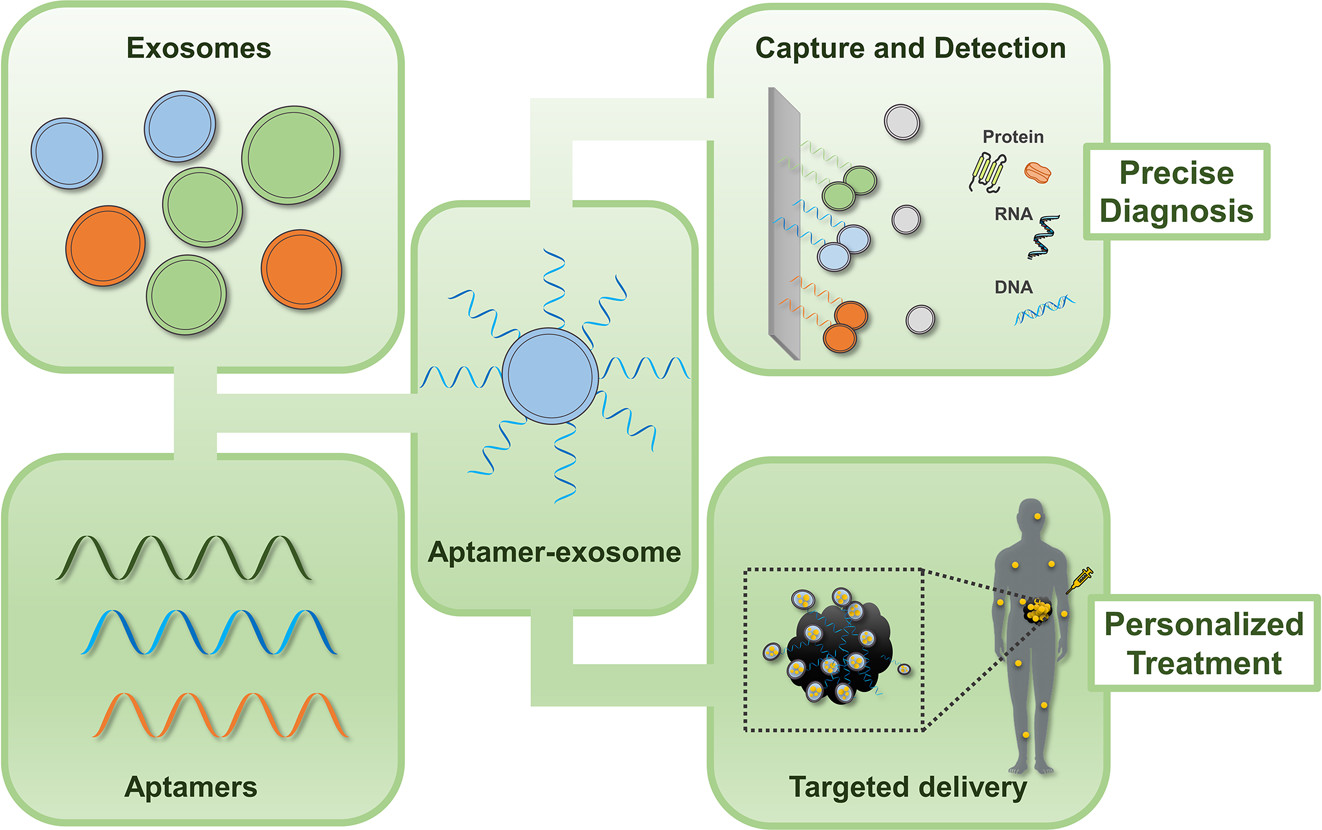
Aptamer-Based Exosome Targeting Service is designed to endow exosomes with the ability to recognize specific target cells or microenvironments by integrating specific aptamers onto their surface, thereby enabling precise delivery, therapy, or imaging functions.
In modern biomedical research, exosomes—nano-sized vesicles secreted by cells—have attracted significant attention due to their potential applications in drug delivery, gene therapy, and disease diagnostics. However, native exosomes have certain limitations in targeting specific cells or tissues. To overcome this challenge, aptamer-modified exosome targeting technology has emerged. By decorating the surface of exosomes with specific aptamers, this approach aims to achieve precise delivery to designated cells or tissues.
Yi K. et al. ACS Sensors. 2021.
Aptamers are single-stranded DNA or RNA molecules, typically 20–100 nucleotides in length, that fold into unique three-dimensional structures capable of binding target molecules—such as small molecules, biomacromolecules, or cell surface receptors—with high specificity and affinity. Their molecular recognition capability is comparable to that of monoclonal antibodies, while offering advantages such as easier synthesis, chemical modification, and engineering. By modifying the surface of exosomes with aptamers, these vesicles can be endowed with the ability to target specific antigens or receptors, enabling precise delivery to desired sites.
MtoZ Biolabs offers Aptamer-Based Exosome Targeting Service by leveraging the high specificity and affinity of aptamers to empower exosomes with the ability to precisely recognize and bind to target cells or tissues. This enhances the efficacy of drug delivery and gene therapy, supporting the development of more precise and efficient therapeutic strategies and advancing the progress of personalized medicine.
Technical Workflow
The technical process of Aptamer-Based Exosome Targeting Service is as follows:
1. Aptamer Selection and Optimization
High-affinity aptamers specific to target cells or tissues are selected and further optimized to improve their stability and specificity.
2. Exosome Isolation and Purification
Exosomes are extracted from donor cells and purified using techniques such as ultracentrifugation and size exclusion chromatography (SEC), ensuring high purity and structural integrity.
3. Aptamer-Exosome Conjugation
Aptamers are conjugated to the surface of exosomes via chemical coupling or non-covalent interactions, forming aptamer-modified exosome complexes.
4. Characterization of Modified Exosomes
The modified exosomes are thoroughly characterized using transmission electron microscopy (TEM), nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA), dynamic light scattering (DLS), and Western blotting to evaluate particle size, morphology, surface charge, and aptamer display efficiency.
5. Functional Validation (Optional)
In vitro and in vivo models can be used to assess the biological functions of the aptamer-modified exosomes, such as targeting specificity and drug delivery efficiency.
Applications
Aptamer-Based Exosome Targeting Service has broad applications, including but not limited to:
Targeted Drug Delivery
Aptamer-modified exosomes can deliver chemotherapeutic drugs or gene-editing tools specifically to target cells such as cancer cells, enhancing therapeutic efficacy while minimizing off-target effects.
Gene Therapy
Exosomes loaded with specific genes or siRNA can be directed to target cells using aptamer modifications, enabling gene expression regulation for the treatment of genetic disorders or viral infections.
Disease Diagnosis
Aptamer-modified exosomes can selectively capture or detect biomarkers in body fluids, providing a powerful tool for early disease diagnosis and real-time monitoring.
Service Advantages
1. High Specificity: Aptamers offer high affinity and specificity, ensuring that exosomes can accurately recognize and bind to their target cells or tissues, significantly improving delivery efficiency.
2. Enhanced Efficiency: Exosomes possess a small particle size and long circulation half-life, facilitating efficient membrane penetration and targeted delivery. Their high cargo capacity also enables co-loading of multiple therapeutic agents.
3. Excellent Biocompatibility: As naturally derived nanocarriers, exosomes exhibit low immunogenicity and good biocompatibility, reducing the risk of adverse immune reactions and toxicity.
4. Customized Solutions: We offer end-to-end services including aptamer screening, exosome modification, and functional validation tailored to your specific research needs.
FAQ
Q. How are Aptamers Conjugated to Exosomes? What are the Differences in Coupling Efficiency Among Methods?
Aptamers can be loaded onto exosomes using several methods, including:
Q. Can Cargo be Simultaneously Loaded into the Exosome? Will Aptamer Modification Affect Cargo Encapsulation or Release?
Yes, we support co-loading of cargo such as siRNA, miRNA, proteins, or small-molecule drugs. Common methods include electroporation, co-incubation, sonication, or membrane permeabilization. Since aptamer modification is primarily surface-based, it generally does not interfere with cargo encapsulation. We also optimize the loading sequence, buffer system, and encapsulation method based on cargo type to ensure efficient, stable delivery.
Case Study
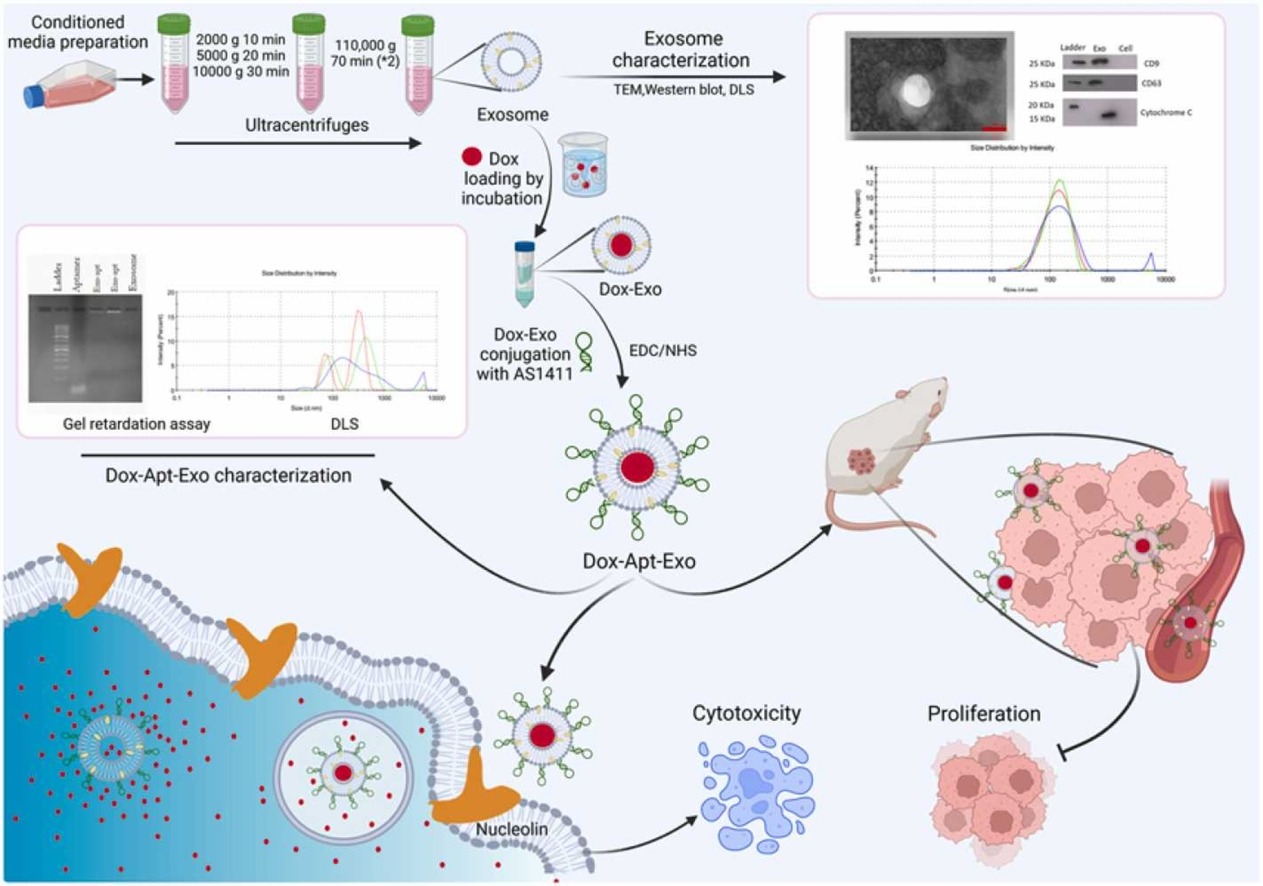
In this study, the anti-nucleolin aptamer AS1411 was covalently conjugated to the surface of exosomes derived from HEK293 cells, and the chemotherapeutic drug doxorubicin (DOX) was encapsulated within the exosomes to construct a tumor-targeting delivery system, referred to as DOX-Apt-Exo. The results demonstrated that aptamer modification significantly enhanced the exosomes’ specificity in recognizing and being internalized by colorectal cancer cells. In vitro assays confirmed the system’s increased cytotoxicity, while in vivo experiments in mouse models showed that the modified exosomes efficiently accumulated at tumor sites and markedly inhibited tumor growth, highlighting their strong targeting capability and antitumor efficacy.
Hosseini NF. et al. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022.
How to order?







