2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation Proteomics Analysis Service
2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation Proteomics Analysis Service offers identification and quantification of 2-hydroxyisobutyrylated proteins at the omics level, facilitating the in-depth study of this modification’s biological functions. 2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation (khib) refers to the covalent attachment of a 2-hydroxyisobutyryl group (2-HIBA) to lysine residues in proteins, forming 2-hydroxyisobutyrylated proteins. Research has shown that 2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation modifications are widespread among metabolic enzymes, histones, signal transduction proteins, and other cellular function-related proteins, and are closely associated with energy metabolism, protein stability, gene expression regulation, and more. By leveraging advanced mass spectrometry platforms, MtoZ Biolabs provides 2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation Proteomics Analysis Service to identify and quantify 2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation proteins in samples, providing researchers with high-quality analysis results to facilitate in-depth exploration in the fields of cell biology, epigenetics, and disease research.
Analysis Workflow
Bo F. et al. Scientific Reports. 2021.
Figure 1. Systematic analysis of Khib in wheat roots.
1. Sample Preparation
Extract proteins and perform preprocessing.
2. 2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation Modification Enrichment
Enrich 2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation proteins using antibody enrichment (Immunoprecipitation, IP) or affinity chromatography methods.
3. Enzymatic Digestion
Digest the enriched proteins with trypsin to generate peptides suitable for mass spectrometry analysis.
4. Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) Analysis
Perform LC-MS/MS analysis using nano-LC coupled with high-resolution mass spectrometry to analyze the peptides.
5. Data Analysis and Interpretation
Process the obtained mass spectrometry data using data analysis software to identify modified peptides and quantify the modification levels.
Use Gene Ontology (GO) and KEGG pathway analysis to uncover the functional roles of 2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation modification in biological processes.
Applications
Metabolic Research
2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation Proteomics Analysis Service can be used to study the role of 2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation modification in cellular energy metabolism, particularly in the regulation of metabolic enzymes and adaptive responses.
Epigenetics
Detect 2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation modification on histones, clarify its role in chromatin remodeling, gene expression regulation and cell differentiation, and promote in-depth research on epigenetic regulatory mechanisms.
Disease Mechanisms
Reveal the relationship between 2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation modifications and diseases such as cancer, metabolic diseases (e.g., diabetes, obesity), and neurodegenerative diseases, helping to identify potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
Protein Function and Interactions
2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation Proteomics Analysis can help explore the role of 2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation modifications in regulating protein stability, interactions, and enzyme activity, providing support for research into key regulatory pathways and biological functions.
Service Advantages
1. Advanced Analysis Platform: MtoZ Biolabs established an advanced 2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation Proteomics Analysis Service platform, guaranteeing reliable, fast, and highly accurate analysis service.
2. One-Time-Charge: Our pricing is transparent, no hidden fees or additional costs.
3. High-Data-Quality: Deep data coverage with strict data quality control. AI-powered bioinformatics platform integrates all 2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation Proteomics Analysis data, providing clients with a comprehensive data report.
4. Customized Service: Based on the specific needs of clients, we optimize experimental design and data analysis strategies to ensure the reliability and practicality of the results.
FAQ
Q. How to Optimize Mass Spectrometry Sensitivity to Detect Low Abundance 2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation Modified Peptides?
Optimizing the sensitivity of mass spectrometry for detecting low-abundance 2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation modified peptides involves improving both sample preparation and mass spectrometry parameters. First, using efficient enrichment methods (such as high-specificity antibody enrichment or optimized affinity chromatography techniques) can significantly increase the relative abundance of 2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation modified peptides and reduce background noise. Second, adjusting the liquid chromatography gradient and flow rate, combined with high-resolution mass spectrometers (such as Orbitrap or Q-Exactive series) and optimized fragmentation modes (like HCD or EThcD), can improve signal-to-noise ratio and peak intensity when detecting low-abundance modified peptides. Additionally, employing Data Independent Acquisition (DIA) mode can further enhance the detection coverage of low-abundance modified peptides.
Q. How to Confirm the Specific Impact of 2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation Modifications on Protein Function?
To confirm the functional impact of 2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation modifications on protein function, a combination of biological experiments and functional analysis is required. Point mutation experiments can be performed to mutate the modification site to a residue that cannot be modified (e.g., substituting lysine with arginine or alanine) and observing its effects on protein activity, stability, or subcellular localization. Using recombinant proteins in vitro, differences in enzymatic activity between unmodified and 2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation modified proteins can further validate the functional significance of the modification. Additionally, protein interaction experiments (such as Co-IP or pull-down) and mass spectrometry detection can clarify whether 2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation modifications affect protein-protein interactions. These combined experiments can systematically reveal the specific roles of 2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation modifications in regulating protein function.
Deliverables
1. Comprehensive Experimental Details
2. Materials, Instruments, and Methods
3. Total Ion Chromatogram & Quality Control Assessment (project-dependent)
4. Data Analysis, Preprocessing, and Estimation (project-dependent)
5. Bioinformatics Analysis
6. Raw Data Files
Case Study
This study used 2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation Proteomics Analysis to systematically identify lysine 2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation modification sites in Fusarium oxysporum, discovering a significant number of modifications on metabolic enzymes, chromatin proteins, and signal transduction proteins. The results suggest that 2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation modifications might play an important role in regulating fungal metabolic pathways, energy production, and gene expression, which are crucial in the host infection and pathogenic process. This research not only expands the understanding of fungal post-translational modifications but also provides foundational data for further studies on the role of 2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation modifications in plant pathogens, with significant theoretical implications and potential application value.
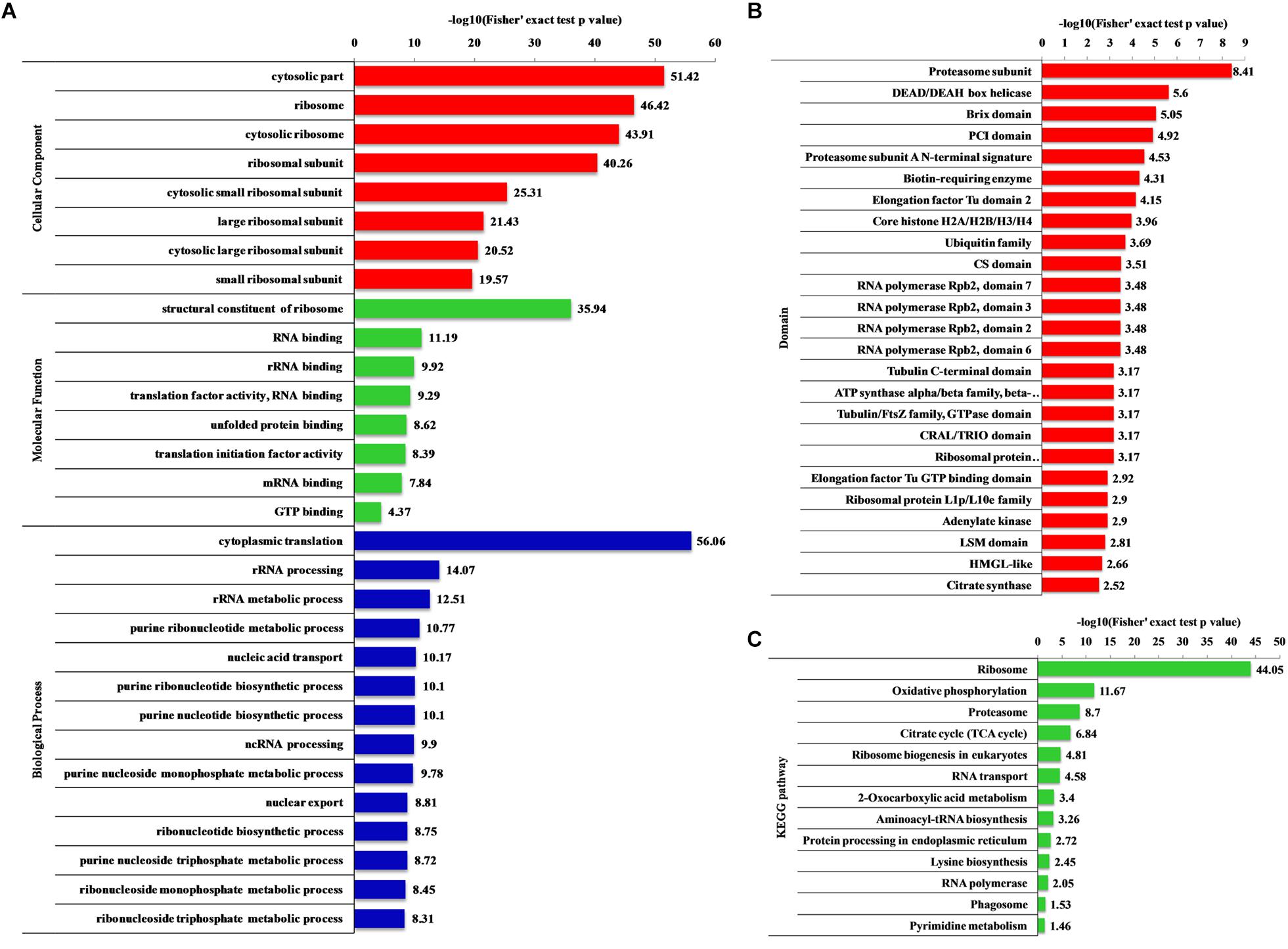
Qian H. et al. Frontiers in Microbiology. 2021.
Figure 2. Enrichment analysis of the 2-hydroxyisobutyrylated proteins in Fusarium oxysporum.
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
Post-Translational Modifications Proteomics Service
Histone 2-Hydroxyisobutyrylation Analysis
Lysine 2-hydroxyisobutyrylation Quantitative Analysis Service
How to order?







