X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Services
X-ray diffraction (XRD) is an analytical technique used to study the crystal structure and phase composition of materials. By emitting X-rays onto a sample and analyzing the diffraction pattern of the rays in the crystal, the crystal structure, molecular arrangement, and composition of the sample can be determined. The X-rays interact with the atoms in the sample, forming a characteristic diffraction pattern that reveals important information such as lattice constants, interplanar spacing, symmetry, and other crucial details. XRD technology is non-destructive, highly accurate, and widely applicable, often used for both qualitative and quantitative analysis of materials.

Bijelic, A. et al. ChemTexts, 2018.
Figure 1. X-ray Diffraction Experiment.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Based on advanced X-ray diffraction instruments, MtoZ Biolabs' X-ray diffraction (XRD) services can precisely analyze the crystal structure, phase composition, grain size, and crystal defects of samples. When the sample is irradiated with X-rays, diffraction patterns are generated. By analyzing these patterns, researchers can obtain detailed information on the lattice constants, interplanar spacing, crystal form, and more. The final data includes the phase composition, crystal structure, and grain size distribution of the sample, helping clients gain in-depth insights into the physical and chemical properties of the material and its application potential.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Types
Suitable for powder, thin film, or single crystal samples. The samples should be uniform and representative to ensure accurate and reproducible analysis results.
2. Sample Purity
It is recommended that the sample purity be no less than 90%, with impurities removed to minimize interference with the diffraction pattern and ensure accurate structural analysis.
3. Sample Transportation
Samples should be sealed properly to prevent moisture or contamination. During transportation, the samples should be protected from extreme vibrations to avoid damage or alteration of their structure.
Advantages and Limitations
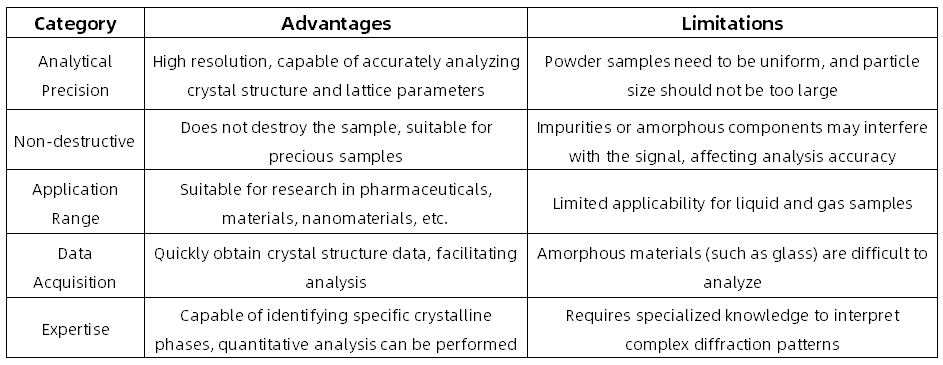
Applications
1. Drug Polymorph Research
XRD can be used to analyze how the crystal structure affects drug stability, solubility, and bioavailability, aiding in the optimization of drug formulations and improving the effectiveness of dosage forms.
2. Biomaterial Analysis
X-ray diffraction (XRD) services are used to analyze the crystal structure of materials, evaluating their compatibility and stability with biological systems, supporting the development of implants, bone repair materials, and other products.
3. Protein Crystallography
XRD is widely used in the analysis of protein crystal structures, providing essential support for drug design and functional studies.
4. Vaccine Development
X-ray diffraction (XRD) services can be used to analyze the crystal structure and physical stability of vaccine components, aiding in the optimization of vaccine formulations and enhancing immunological efficacy.
5. Nanomedicine Research
XRD is used to assess the particle size, stability, and biocompatibility of nanomedicines, promoting the application of nanotechnology in drug delivery systems.
FAQ
Q1: Can XRD detect amorphous substances?
A1: XRD is primarily used to analyze crystalline materials. For amorphous substances, their signals are weak, and sufficient structural information may not be available. However, with appropriate techniques such as small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS), some information can still be obtained.
Q2: How is XRD data interpreted?
A2: The interpretation of XRD data involves comparing the position, intensity, and shape of diffraction peaks to determine the crystal structure, molecular composition, and polymorph of the sample. MtoZ Biolabs provides professional data analysis to help clients accurately interpret the experimental results.
How to order?







