Why Is Shotgun Proteomics the Preferred Strategy for Comprehensive Proteome Profiling?
-
Label-free quantification: Suitable for large-scale studies with high experimental flexibility.
-
TMT/iTRAQ: Enables multiplexed sample analysis with high quantitative precision.
-
DIA: Offers improved reproducibility and consistency, making it well suited for translational and clinical studies.
-
Identification of disease-related biomarkers
-
Elucidation of drug mechanisms of action
-
Differential proteomic analysis during development and aging
-
Integration with transcriptomic and metabolomic data to construct regulatory networks
-
Analysis of dynamic changes in time-series samples
-
Mechanistic modeling based on protein–protein interactions and GO/KEGG pathway analyses
-
Data Independent Acquisition (DIA): Substantially enhances reproducibility and data completeness, enabling robust large-cohort studies.
-
Single-Cell Proteomics: Shotgun-based analysis of trace-level samples has emerged as a frontier in proteomics research.
-
AI-Driven Spectral Interpretation: Improves peptide identification rates and quantitative accuracy.
In proteomics research, the efficient characterization of protein composition and dynamic changes in complex biological samples remains a fundamental challenge. Owing to its high throughput, broad proteome coverage, and superior analytical sensitivity, shotgun proteomics has emerged as the most widely adopted strategy for comprehensive proteome profiling. It has been extensively applied in studies of disease mechanisms, biomarker discovery, and integrative multi-omics analyses.
What Is Shotgun Proteomics?
Shotgun proteomics, also referred to as bottom-up proteomics, is an analytical strategy in which proteins are enzymatically digested into peptides prior to identification and quantification by mass spectrometry. The term “shotgun” reflects an untargeted, large-scale analytical concept, whereby information on the original proteins is computationally reconstructed from the collective identification of numerous peptide fragments.
Overview of the technical workflow:
1. Protein Extraction: Total proteins are isolated from cells, tissues, or biological fluids.
2. Enzymatic Digestion: Proteins are commonly digested into peptides using trypsin.
3. Liquid Chromatography Separation (LC): Complex peptide mixtures are fractionated.
4. Mass Spectrometry Analysis (MS/MS): Peptides are identified and quantified using high-resolution mass spectrometers.
5. Database Searching: Fragment ion spectra are matched against protein databases to infer protein identities and relative abundances.
Why Has Shotgun Proteomics Become the Dominant Approach?
1. High-Throughput and Broad Proteome Coverage
Shotgun proteomics enables the simultaneous detection of thousands to tens of thousands of proteins in a single experiment. Compared with traditional gel-based methods (e.g., two-dimensional electrophoresis, 2-DE), it provides substantially improved proteome coverage and is particularly well suited for complex biological samples such as tumor tissues, brain tissues, and serum.
2. High Analytical Sensitivity for Low-Abundance Proteins
Continuous advances in mass spectrometry technologies, including data-dependent acquisition (DDA) and data-independent acquisition (DIA), have markedly enhanced the ability of shotgun proteomics to detect low-abundance proteins. This makes the approach especially valuable for investigating key regulatory components such as signaling pathway nodes, transcription factors, and cytokines.
3. High Data Depth Supporting Functional Enrichment and Bioinformatics Analyses
Shotgun proteomics datasets are frequently integrated with downstream analyses such as Gene Ontology (GO), KEGG pathway analysis, and protein–protein interaction (PPI) networks, enabling systematic investigation of disease mechanisms, biological processes, and cellular functions.
4. Compatibility with Multiple Quantitative Strategies(Label-free, TMT, iTRAQ, etc.)
Shotgun proteomics is inherently compatible with a variety of quantitative approaches, including:
Comparative Advantages over Other Proteomic Approaches
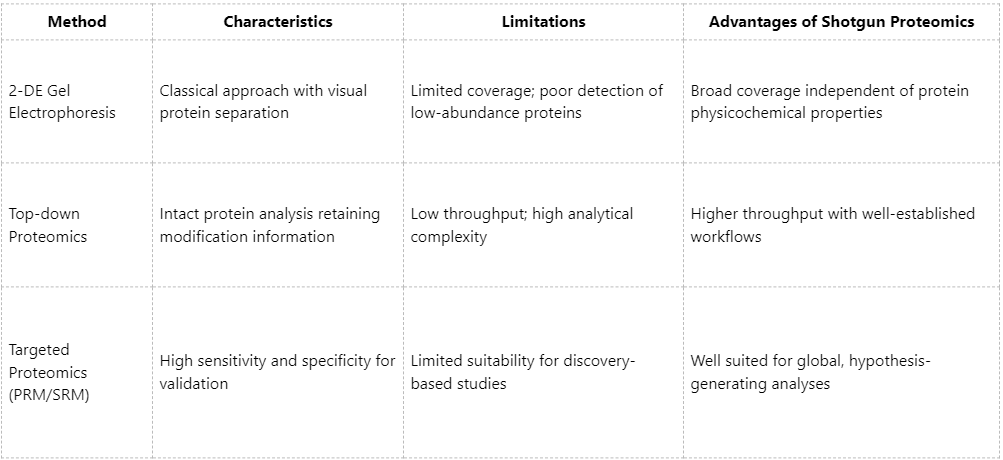
Research Applications Best Suited for Shotgun Proteomics
1. Discovery-Oriented Studies
2. Integrative Multi-Omics Analyses
3. Biological Pathway and Network Reconstruction
Technological Advances and Future Directions
Shotgun proteomics is transitioning from primarily high-throughput qualitative profiling toward precise quantitative analysis and clinical translation:
In summary, owing to its comprehensive coverage, high sensitivity, scalability, and strong compatibility with advanced analytical platforms, shotgun proteomics has become the preferred approach for whole-proteome analysis. Its advantages are particularly pronounced during the exploratory phase of scientific research. For researchers seeking high-reliability and high-depth proteomics studies, MtoZ Biolabs offers integrated services based on state-of-the-art instrumentation and extensive experience in omics research, encompassing experimental design, sample preparation, mass spectrometry analysis, and bioinformatics interpretation to support in-depth biological discovery.
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
How to order?







