What Is Edman Sequencing? A Key Technology in Protein Sequencing Explained
-
High accuracy: Amino acids are identified sequentially, yielding high fidelity in sequence determination.
-
No external labeling required: The method does not require isotopic or fluorescent labeling of the target protein.
-
Effective for purified proteins: Well-suited for sequence analysis of single, highly purified protein samples.
-
Blocked N-termini: Proteins with modified N-termini (e.g., acetylation or formylation) are not amenable to Edman degradation.
-
Ineffective for complex mixtures: The method is only applicable to individual peptides or proteins of high purity.
-
Limited sequencing range: Typically, only 20–30 amino acid residues can be determined, which is insufficient for full-length protein sequences.
-
Sample quantity requirement: A minimum of approximately 1 pmol of purified protein is generally required for reliable analysis.
Proteins play essential roles in virtually all biological processes, and their primary structure—the linear sequence of amino acids—determines their function. To investigate protein structure and function, it is essential to first understand their amino acid composition and sequence. As such, protein sequencing represents a critical step in modern life science research and biopharmaceutical development. Among various sequencing methods, Edman sequencing is widely recognized as a classical approach for resolving protein primary structure.
What Is Edman Sequencing?
Edman sequencing is a chemical method for determining the N-terminal amino acid sequence of proteins, developed by Australian chemist Pehr Edman in 1950. The core principle involves selectively labeling the N-terminal amino acid of a peptide with phenyl isothiocyanate (PITC). Under mild conditions, this labeled residue is cleaved to yield a detectable phenylthiohydantoin (PTH)-amino acid derivative, while the remaining peptide chain is preserved for subsequent cycles. Through this stepwise removal of amino acids, the N-terminal sequence of a protein can be determined sequentially.
Reaction Process of Edman Sequencing
1. Labeling: PITC reacts with the free amino group at the peptide’s N-terminus, forming a cyclic phenylthiocarbamoyl intermediate.
2. Cleavage: Under acidic conditions, the N-terminal amino acid is selectively cleaved and converted into a stable PTH-amino acid.
3. Identification: The resulting PTH-amino acid is identified using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) or comparable analytical techniques.
4. Repetition: The above steps are repeated iteratively to remove and identify amino acids one by one, typically up to a maximum of 30 residues.
Advantages and Limitations of Edman Sequencing
1. Advantages
2. Limitations
Applications of Edman Sequencing in Scientific Research
Although modern mass spectrometry (MS) technologies have become increasingly mainstream, Edman sequencing continues to offer unique advantages in the following scenarios:
1. N-Terminal Validation of Proteins
Following the expression and purification of recombinant proteins, researchers often employ Edman sequencing to determine whether the target protein has undergone N-terminal truncation or modification, and to verify whether translation initiates correctly at the intended start codon.
2. Epitope Sequencing in Antibody Development
Edman degradation is well-suited for determining the sequence of individual peptides, such as antigenic peptides or B-cell epitopes, which is particularly valuable during the development of both polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies.
3. Cross-Validation with Mass Spectrometry
In critical applications—such as the development of clinical-grade protein therapeutics or protein engineering studies—researchers often perform Edman degradation in parallel with LC-MS/MS to cross-validate protein sequences and ensure data accuracy.
Edman Sequencing vs. Mass Spectrometry: Complementary Techniques
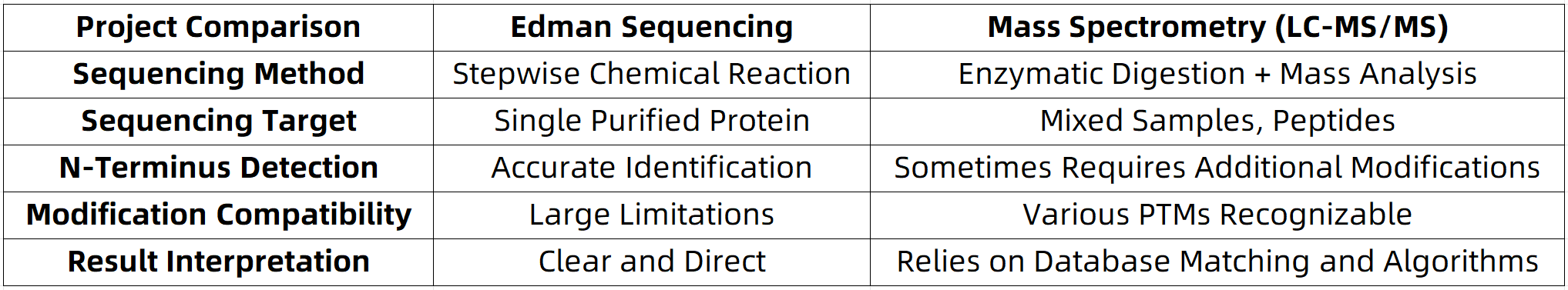
Empirical evidence suggests that combining Edman degradation with mass spectrometry achieves optimal outcomes in areas such as N-terminal sequencing, pharmaceutical quality control, and the development of quantitative reference standards.
As a foundational technique in protein sequencing, Edman sequencing remains indispensable in specific applications due to its high precision and interpretability. MtoZ Biolabs is committed to a research-oriented approach, delivering high-quality, reliable protein sequencing solutions and technical support to academic research groups, scientific institutions, and biopharmaceutical R&D teams.
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
How to order?







