What Is Acylation Proteomics?
- Comprehensive identification of acylation sites
- Robust quantitative analyses (supporting TMT, iTRAQ, SILAC, and DIA strategies)
- Flexible project design (single or multiple modification studies)
- Full-scale bioinformatics support suitable for SCI publication
Acylation proteomics refers to the systematic identification and quantification of protein acylation sites and their dynamic alterations in cells or tissues using high-throughput mass spectrometry. As an important branch of proteomics, it focuses on the comprehensive characterization of acyl-type post-translational modifications (PTMs).
Definition of Protein Acylation
Protein acylation is a class of post-translational modifications in which diverse acyl groups are covalently attached to specific residues, typically lysine (Lys), on target proteins. These modifications profoundly influence protein structure, stability, subcellular localization, and biological function.
Common types of protein acylation include:
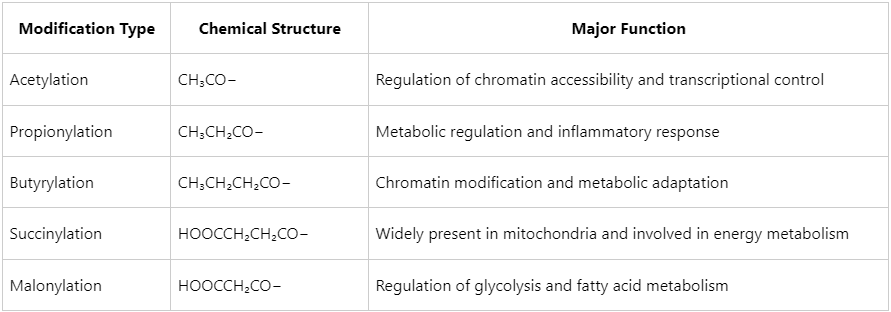
Through modulating the charge state, conformation, or binding affinity of proteins, these modifications play critical roles in various biological processes such as transcriptional regulation, signal transduction, metabolic control, and cell-cycle progression.
Research Workflow of Acylation Proteomics
The core methodology of acylation proteomics relies on high-resolution liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS), coupled with efficient enrichment approaches and bioinformatics analysis.
1. Sample Preparation and Proteolytic Digestion
Total proteins are first extracted from cells or tissues and subsequently digested into peptides using trypsin.
2. Specific Enrichment of Acylated Peptides
Given the typically low abundance of acylated peptides, targeted enrichment is essential. Common strategies include:
(1) Antibody-based affinity enrichment (e.g., anti-acetyl-lysine beads)
(2) Chemical derivatization-based enrichment (e.g., biotin labeling followed by streptavidin magnetic bead capture)
3. Mass Spectrometry Analysis
LC–MS/MS is performed on high-resolution instruments such as Orbitrap or TOF systems, employing either data-dependent acquisition (DDA) or data-independent acquisition (DIA) modes.
4. Bioinformatics Analysis
(1) Software tools such as MaxQuant and Proteome Discoverer are used to identify modified sites
(2) Annotate protein functions, and perform pathway enrichment analyses (GO/KEGG)
(3) Quantitative comparisons are conducted to examine dynamic acylation changes across different conditions or time points.
Applications and Research Significance
Acylation proteomics has become an indispensable tool across several cutting-edge fields of life science:
1. Epigenetic Regulation
Histone acylations (e.g., H3K9ac) modulate chromatin structure and gene transcription, constituting an essential mechanism in cancer and stem cell research.
2. Metabolic Disease Studies
Acylation is intricately linked to cellular metabolic pathways. Modifications such as succinylation and propionylation exhibit marked alterations in models of diabetes and hepatic steatosis.
3. Inflammation and Immune Regulation
Emerging acylations, including malonylation, have been shown to regulate the NF-κB signaling pathway and macrophage activation.
4. Cancer Research
Aberrant acylation patterns observed in various malignancies represent potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
Technological Strengths of MtoZ Biolabs in Acylation Proteomics
MtoZ Biolabs integrates the high-sensitivity Orbitrap Exploris mass spectrometry platform with proprietary acylation enrichment technologies, offering:
As a rapidly evolving frontier within the PTM landscape, systematic investigations of protein acylation continue to unveil the intricate regulatory networks underlying biological systems. With ongoing advancements in mass spectrometry and the expansion of proteomic databases, acylation proteomics is poised to become a pivotal tool for studying metabolic reprogramming, epigenetic regulation, and disease mechanisms. Researchers exploring protein acylation-related topics are encouraged to collaborate with MtoZ Biolabs for professional analytical support and high-quality scientific solutions.
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
How to order?







