Viral Infection Mechanisms Research Service
-
High-Throughput Host Receptor Screening: Utilizing an array of over 1,000 human membrane proteins to identify viral binding targets;
-
Functional Validation Services: Including receptor expression regulation, cell infection models, blocking experiments, etc.;
-
Structural Modeling and Target Analysis: Assisting in elucidating binding mechanisms and recommending potential neutralization strategies;
-
Customized Analysis Reports: Providing experimental data, heatmap analyses, binding strength assessments, and literature support.
-
Identifying specific binding sites between viral surface proteins (e.g., Spike, E proteins) and host receptors;
-
Analyzing variations in receptor recognition capabilities among different viral strains;
-
Uncovering co-receptors or auxiliary factors essential for viral cell entry;
-
Providing foundational receptor target information for the development of vaccines, blocking antibodies, or viral inhibitors.
-
Hypothesis-free screening: Enables panoramic discovery without relying on predefined target assumptions;
-
Native protein expression: Preserves functional domains such as transmembrane and extracellular regions;
-
High throughput and sensitivity: Ideal for dissecting complex viral infection mechanisms;
-
Compatible with various viral sample types: Including RVPs, VLPs, and recombinant proteins.
-
Reporter Virus Particles (RVPs): Recommended format due to their safety, stability, and compatibility with protein array-based screening;
-
Virus-Like Particles (VLPs) or recombinant viral surface proteins (e.g., S protein, HA protein): Also accepted;
-
Live viruses: Due to biosafety concerns, we currently do not accept live virus samples. However, we can assist clients in constructing expression systems to produce the required proteins or virus-like particles.
Viral infections are the initiating events of numerous significant diseases, involving complex and precise interactions between viruses and host cells. From the recognition of target cells and entry into the host to the release of the genome and completion of replication and assembly, each step critically depends on the molecular pairing between the virus and the host, particularly during the initial viral adsorption phase. Research indicates that the success of viral infection hinges on the specific binding between viral surface adsorption proteins and receptors on the host cell membrane.
In the current era of frequent emergence and rapid mutation of new viruses, traditional methods for studying viral mechanisms struggle to meet the demands for quick responses and precise mechanistic elucidation. Key challenges in virology research, vaccine development, and antiviral drug discovery include comprehensively identifying the essential receptors utilized by viruses during invasion and elucidating the virus-host interaction network.
The advent of Human Membrane Protein Array (HMPA) technology offers robust technical support for analyzing viral infection mechanisms. By constructing large-scale arrays of human-derived membrane proteins that mimic the host cell membrane environment, this technology precisely screens for receptor-ligand binding events between viruses and hosts, representing a cutting-edge approach in current viral receptor screening and mechanistic studies.
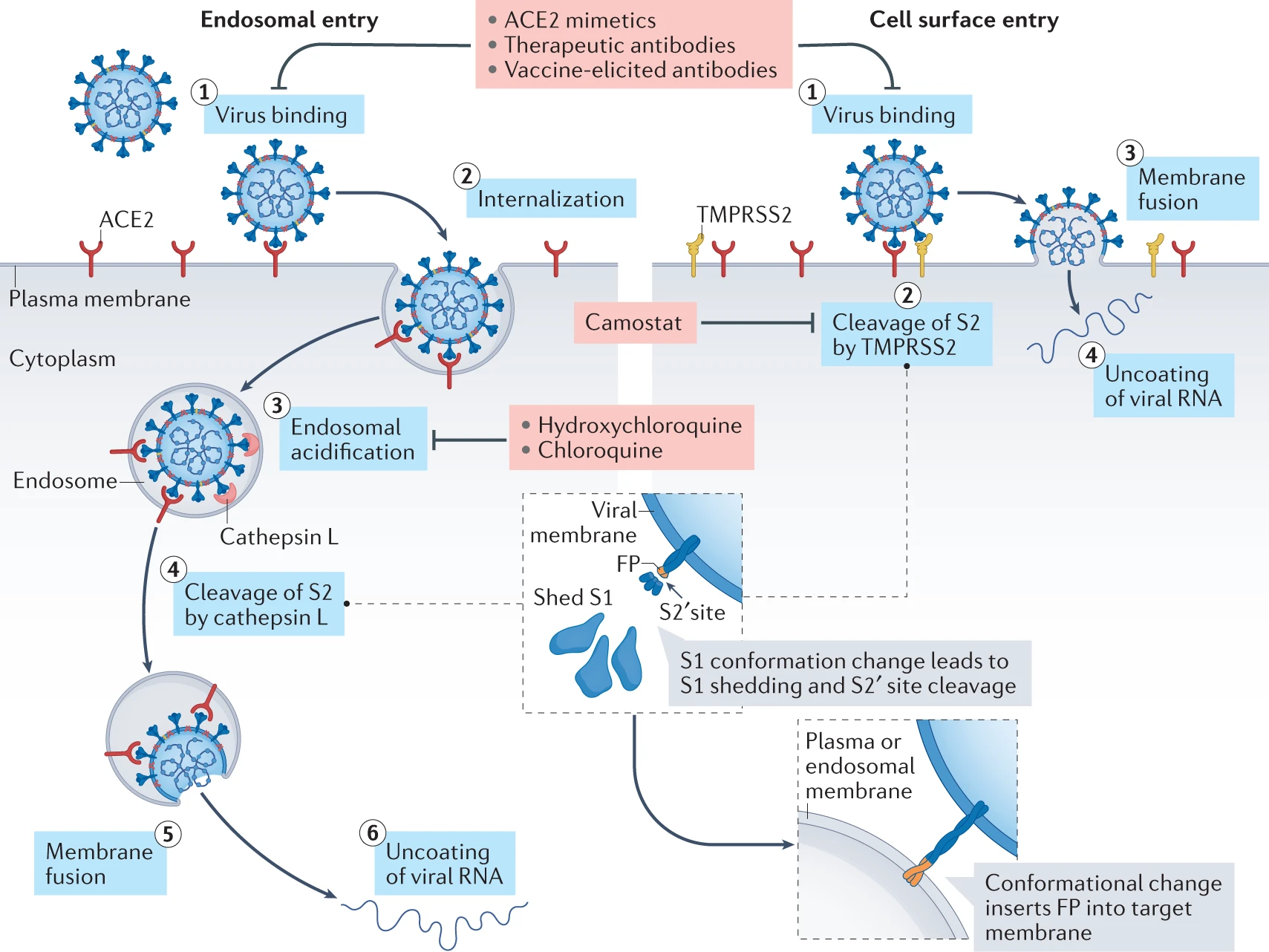
Jackson, C. B. et al. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2022.
Figure1. Two Distinct SARS-CoV-2 Entry Pathways
Service at MtoZ Biolabs
As a biotechnology company focused on protein interactions and antibody specificity, MtoZ Biolabs utilizes advanced proteomics platforms and HMPA technology to deliver comprehensive viral infection mechanism research solutions encompassing everything from high-throughput virus-host interaction screening to functional validation and mechanistic studies, supporting basic research, drug discovery, and vaccine development with high-value data.
Our viral infection mechanism research service offers:
Technical Principles
MtoZ Biolabs offers a viral mechanism research service based on HMPA technology. Viral infection mechanisms research service involves immobilizing hundreds of naturally conformed human membrane proteins onto microplates or chips to simulate the structure of host cell receptors. These arrays are then incubated with viral particles (Virus or Reporter Virus Particles, RVPs) to identify the binding targets of viral surface proteins.
HMPA technology centers on functionally expressed membrane proteins, combined with highly sensitive fluorescence labeling, immunodetection, and high-throughput screening systems, enabling high-resolution analysis of viral adsorption mechanisms, including but not limited to:
Analysis Workflow
MtoZ Biolabs has established a standardized and customizable technical workflow for viral mechanism research, ensuring experimental reproducibility, accuracy, and scientific rigor:
1. Preparation of Viral Particles or Recombinant Proteins
Clients may provide live viruses, Virus-Like Particles (VLPs), Reporter Virus Particles (RVPs), or recombinantly expressed viral surface proteins (e.g., S, E, HA proteins). Alternatively, MtoZ Biolabs can construct expression systems for production.
2. Construction of Human Membrane Protein Array
Utilizing a human membrane protein expression library derived from HEK293 cells, approximately 1,000+ membrane proteins are expressed in their native conformations, including receptors, co-receptors, adhesion molecules, ion channels, enzymes, etc., ensuring high coverage and functional integrity.
3. Detection of Virus-Protein Interactions
Labeled viral particles or recombinant proteins are incubated with the array. Binding signals are detected using immunofluorescence labeling or biotin-streptavidin systems to obtain the binding profile between the virus and host membrane proteins.
4. Data Analysis and Receptor Screening
Combining protein expression level normalization, high-affinity binding targets are identified and evaluated for their functional roles in viral adsorption and entry processes. Bioinformatics annotations are provided based on literature and databases.
5. Subsequent Validation and Functional Studies (Optional)
Additional validation services are available, including receptor knockout/overexpression cell infection models, co-localization analysis, binding affinity measurements (SPR/BLI), and functional blocking experiments.
Applications
MtoZ Biolabs' Viral infection mechanism research service has been widely applied across various research and industrial fields, assisting researchers and enterprises in accelerating virology studies and formulating antiviral strategies:
1. Screening Receptors and Analyzing Entry Mechanisms of Emerging Viruses
Applicable to new viruses or mutant strains such as SARS-CoV-2, influenza virus, dengue virus, monkeypox virus, HIV, etc., to identify key receptors involved in infection and guide vaccine target design.
2. Antiviral Drug Screening and Target Identification
By validating virus-host receptor interactions, assessing the impact of drug interventions on binding events, optimizing candidate compound screening strategies, and clarifying drug targeting pathways.
3. Validation of Vaccine Antigens and Blocking Antibodies
Assisting in evaluating whether neutralizing antibodies induced by vaccines can block virus-receptor interactions, providing experimental evidence for vaccine protective mechanisms.
4. Assessment of Infectivity of Viral Variants
Analyzing changes in host receptor binding capabilities among different strains (e.g., Alpha, Delta, Omicron), evaluating differences in transmissibility and pathogenicity.
5. Research on Cross-Species Transmission Mechanisms of Viruses
Exploring whether viruses can bind to membrane proteins from various species to assess potential cross-species transmission risks.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What are the advantages of Human Membrane Protein Array technology compared to traditional receptor screening methods?
The HMPA technology constructs a high-throughput library of functionally expressed human membrane proteins, displayed on microplates or chips in near-native conformations, effectively simulating the authentic host cell membrane environment. Compared to conventional receptor prediction or single-target validation methods, this approach offers the following key advantages:
2. What types of samples are required for the Viral Mechanism Research Service? Do you accept live viruses?
We support multiple sample formats, and clients can select the most suitable option based on their research goals:
Before initiating the project, we communicate with each client to confirm sample type, preparation methods, and label design strategies to ensure experimental feasibility and data reliability.
How to order?







