Tumor Diagnosis-Applied Exosomes
Tumor-derived exosomes are small vesicles secreted by tumor cells into bodily fluids like blood, urine, or saliva. These exosomes carry molecular information, including proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, that reflect the status and activity of the tumor from which they originated. They offer a non-invasive and highly sensitive means to detect cancer, making them an invaluable tool for early diagnosis and monitoring disease progression. MtoZ Biolabs has developed cutting-edge Tumor Diagnosis-Applied Exosomes services for the isolation, characterization, and biomarker discovery of tumor-derived exosomes to support non-invasive cancer diagnostics and personalized treatment strategies.
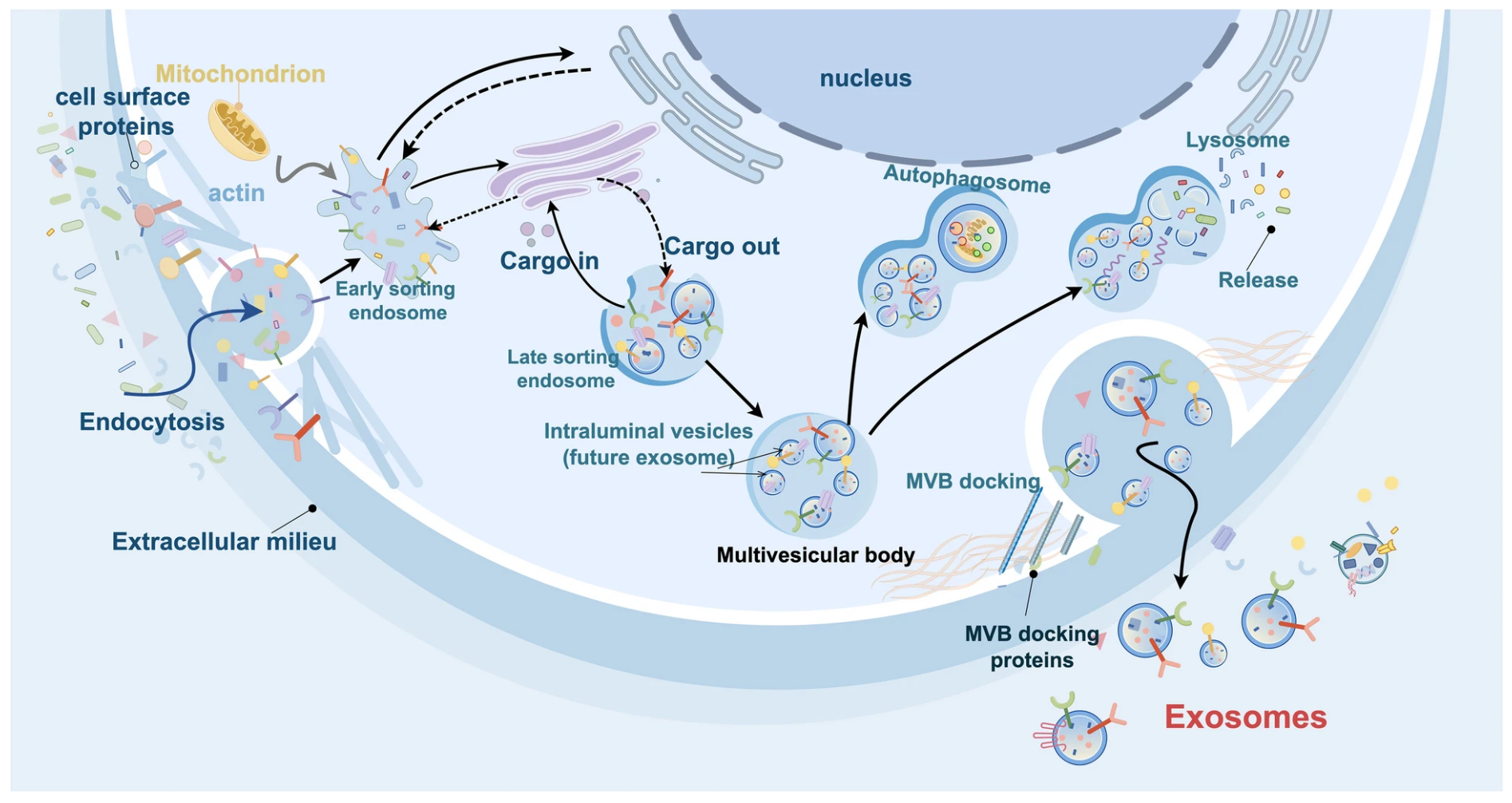
Figure 1. The Biological Roles of Tumor-derived Exosomes in Gastrointestinal Cancer
Key Features of Tumor Diagnosis-Applied Exosomes:
1️⃣Tumor-Specific Biomarkers: Tumor-derived exosomes contain unique molecular signatures from their originating tumor, making them highly specific for cancer diagnosis.
2️⃣Non-Invasive Sampling: Exosomes can be isolated from blood, plasma, urine, or other bodily fluids, eliminating the need for invasive procedures like biopsies.
3️⃣Real-Time Molecular Profiling: Exosomes provide a snapshot of the tumor's molecular profile, offering insights into tumor composition, mutations, and therapeutic targets.
4️⃣Rich Source of Information: Exosomes contain a wide range of biomolecules, including tumor-associated proteins, miRNAs, and lncRNAs, which can be leveraged for comprehensive diagnostics.
Tumor diagnosis often requires invasive methods such as tissue biopsies, which can be challenging, especially for inaccessible tumors or in patients with multiple sites of disease. The combination of Tumor Diagnosis-Applied Exosomes analysis and liquid biopsy enables real-time assessment of tumor progression, therapeutic response, and minimal residual disease, overcoming limitations of traditional tissue biopsies. This synergy enhances early cancer detection, longitudinal monitoring, and personalized treatment planning with high specificity and sensitivity.
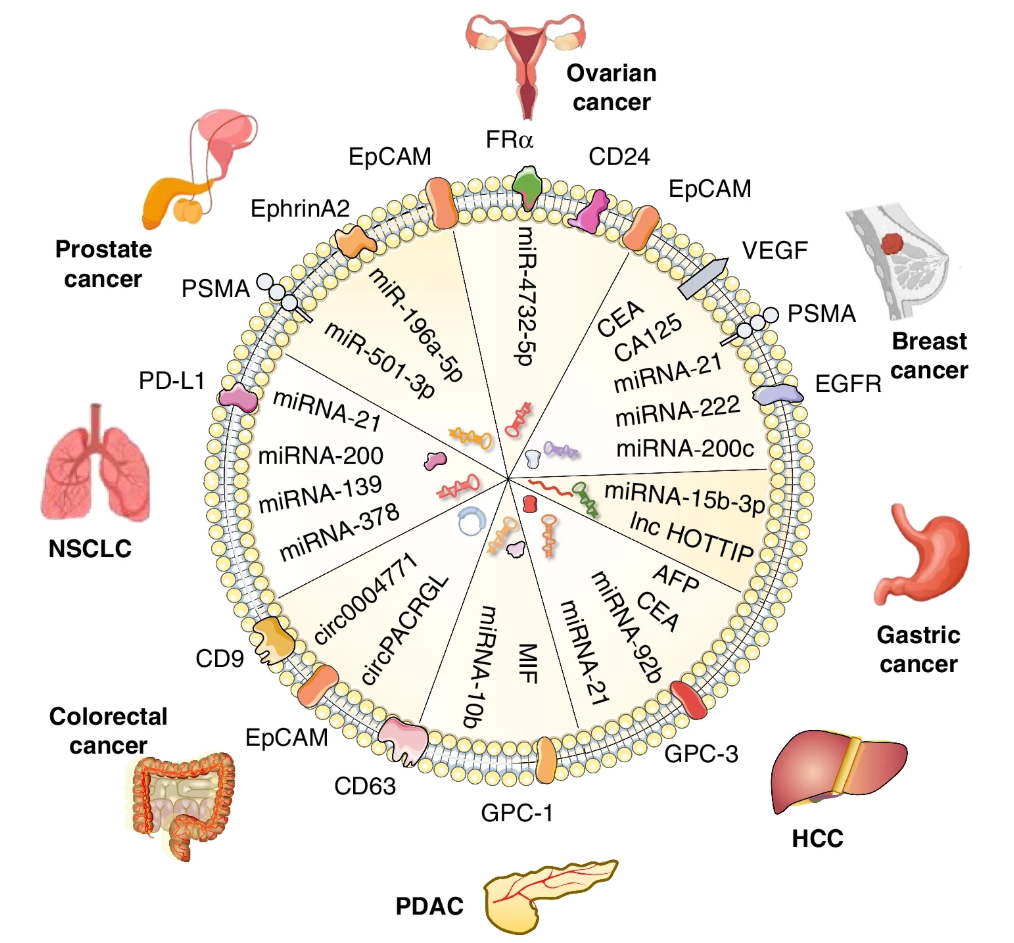
Figure 2. The Application of Exosomes in Cancer Liquid Biopsy
Service at MtoZ Biolabs
MtoZ Biolabs offers a comprehensive Tumor Diagnosis-Applied Exosomes service, integrating advanced exosome isolation, characterization, and molecular profiling technologies to support cancer biomarker discovery and clinical research. Utilizing state-of-the-art methods such as ultracentrifugation, size exclusion chromatography (SEC), immunoaffinity capture, and microfluidics-based platforms, MtoZ Biolabs ensures high-purity isolation of tumor-derived exosomes from diverse body fluids. Comprehensive characterization techniques, including flow cytometry, mass spectrometry, and next-generation sequencing (NGS), are employed to analyze exosomal proteins, lipids, DNA, and RNA, including miRNA and lncRNA.
MtoZ Biolabs' Tumor Diagnosis-Applied Exosomes services cover biomarker identification, exosomal nucleic acid and protein profiling, validation of tumor-specific exosome markers, and custom assay development for liquid biopsy applications. By offering end-to-end solutions from exosome isolation to multi-omics analysis, MtoZ Biolabs helps researchers and clinicians overcome challenges such as tumor heterogeneity, early-stage detection, and real-time monitoring of cancer progression, thereby facilitating accurate, minimally invasive tumor diagnostics and personalized oncology strategies.
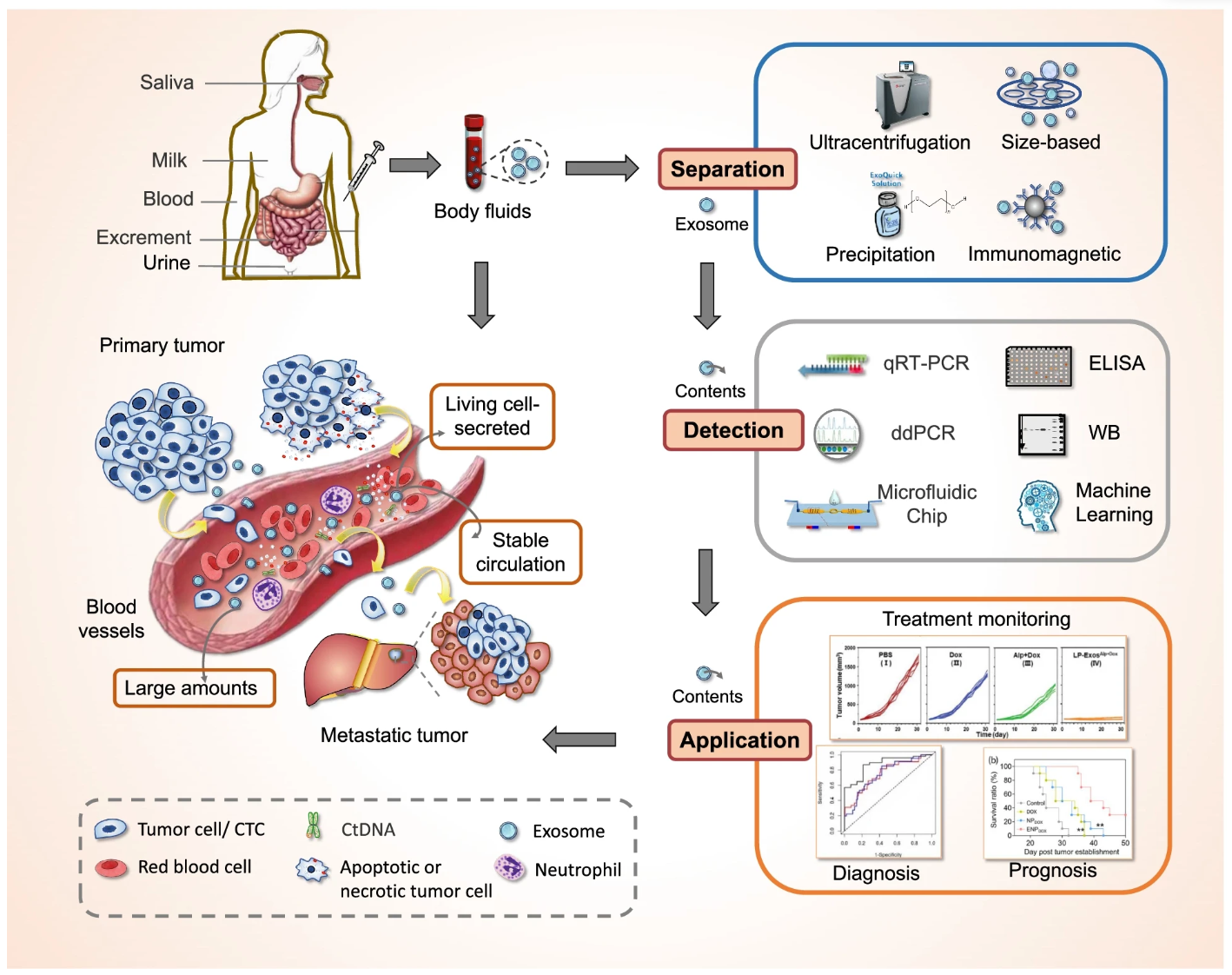
Figure 3. Workflow for Tumor Diagnosis-Applied Exosomes Analysis
Service Advantages
1. Advanced Platform: MtoZ Biolabs established an advanced exosome analysis platform for tumor diagnosis, guaranteeing reliable, fast, and highly accurate analysis service.
2. Expert Team: Our team of experienced scientists and researchers specializes in exosome isolation, characterization, and analysis, ensuring reliable, high-quality results with expertise in oncology and biomarker discovery.
3. End-to-End Service: We provide a comprehensive, seamless workflow from exosome isolation and characterization to biomarker identification, analysis, and reporting, offering a complete solution for tumor diagnostics.
4. Transparent Pricing: Our service comes with clear, all-inclusive pricing, ensuring no hidden costs and making it easier for clients to plan and budget effectively.
Applications
☑️Cancer Screening: Tumor-derived exosomes can be used for routine screening in high-risk populations, enabling early intervention.
☑️Therapeutic Monitoring: Analyze exosome profiles to track how tumors respond to therapies, helping clinicians adjust treatments as needed.
☑️Prognosis Prediction: By identifying specific biomarkers in exosomes, we can predict patient prognosis and tailor individualized treatment plans.
☑️Biomarker Discovery: Our exosome analysis helps uncover new biomarkers that could serve as targets for novel therapeutic approaches, advancing cancer research.
FAQ
Q1: What analytical techniques are used to characterize tumor-derived exosomes and identify diagnostic biomarkers?
Characterization of tumor-derived exosomes and identification of diagnostic biomarkers rely on advanced analytical techniques, including transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) for morphology and size profiling, flow cytometry and Western blotting for surface marker validation, and mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) and next-generation sequencing (NGS) for comprehensive proteomic, lipidomic, and RNA profiling, enabling precise biomarker discovery.
Q2: How does MtoZ Biolabs ensure reproducibility and clinical relevance in exosome-based cancer diagnostics?
MtoZ Biolabs ensures reproducibility and clinical relevance in exosome-based cancer diagnostics through standardized isolation protocols, batch-to-batch consistency checks, and comprehensive quality control.
Our Tumor Diagnosis-Applied Exosomes services enable early detection of a wide range of cancers, from solid tumors like breast, lung, and colorectal cancers to specific tumor subtypes. Free project evaluation, welcome to learn more details.
How to order?







