Time Resolved Emission Spectroscopy (TRES) Analytical Service
Time resolved emission spectroscopy (TRES) is an analytical method that studies the dynamics of excited states and energy transfer processes by recording changes in the emission spectra of samples at different time scales. Its basic principle is that when a sample is excited by a short light pulse, molecules undergo relaxation and emission processes from the excited state to the ground state. By collecting emission spectra at different time delays, it is possible to reveal fluorescence lifetime, energy transfer efficiency, and intermolecular interactions. TRES technology, due to its high sensitivity and dynamic monitoring capability, is widely used to analyze molecular excited-state dynamics and energy transfer processes, supporting protein conformational changes, drug–target binding, and functional material performance characterization.
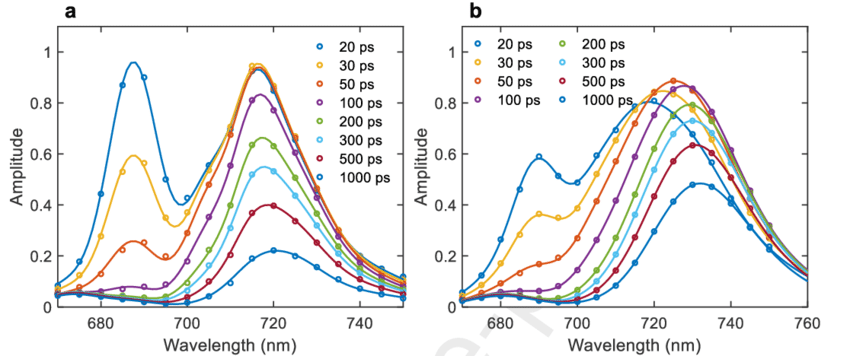
Akhtar, P. et al. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Bioenergetics, 2020.
Figure 1. TRES at Selected Times Reconstructed from the DAES and Fitted Spectra from Gaussian Decomposition Analysis
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Based on an advanced time-resolved emission spectroscopy platform, MtoZ Biolabs offers time resolved emission spectroscopy (TRES) analytical service that can capture the dynamic changes of sample emission spectra under precise time-resolved conditions. This service can analyze excited-state energy relaxation pathways, emission lifetime distributions, and intermolecular energy transfer characteristics, thereby revealing the dynamic behavior of complex systems. The results include time-dependent emission spectra, lifetime parameters, and kinetic curves, providing systematic data support for studying protein folding processes, molecular interaction characteristics, and the optical properties of novel materials.
Analysis Workflow
1. Sample Preparation
Pretreat the sample according to research requirements to ensure uniformity and representativeness, avoiding interference from impurities on emission signals.
2. Pulse Excitation
Use a pulsed light source to excite the sample molecules, bringing them into an excited state and generating emission signals that change over time.
3. Time-Resolved Acquisition
Record the emission spectra of the sample at different delay times to capture excited-state relaxation and energy transfer processes.
4. Data Processing
Perform peak identification and background correction on the time-series spectra, extracting lifetime distributions and kinetic parameters.
5. Result Output
Generate time-dependent emission spectra, decay curves, and quantitative parameters to visually present the dynamic characteristics of molecular conformations and interactions.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Type
Applicable to samples such as proteins, peptides, cell solutions, and functional materials. Samples must be representative and uniform to obtain stable time-resolved emission signals.
2. Sample Purity
It is recommended to minimize impurities or fluorescent contaminants to avoid interference with emission signals and lifetime measurements, ensuring the accuracy of data analysis.
3. Sample Storage
Samples should be stored under low-temperature and dark conditions to prevent structural or fluorescence property changes caused by light exposure or high temperature.
4. Sample Transport
Samples must be transported in sealed containers, and cold-chain conditions should be applied if necessary, to ensure stability and integrity before reaching the analytical platform.
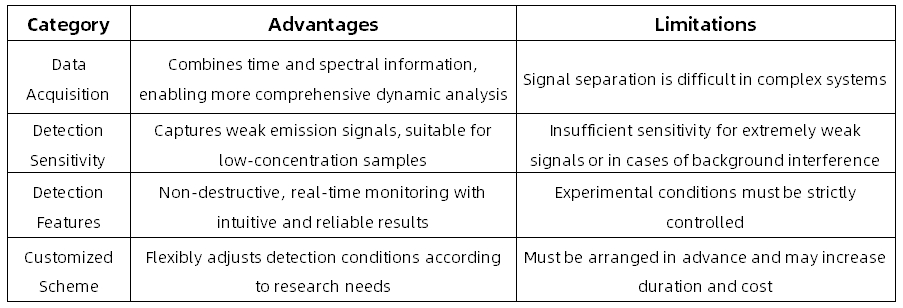
Advantages and Limitations
Applications
1. Protein and Peptide Conformation Studies
Time resolved emission spectroscopy (TRES) analytical Service can be used to monitor protein folding, denaturation, and peptide conformational changes, revealing their dynamic characteristics.
2. Molecular Interaction Analysis
Molecular energy transfer and binding kinetics can be evaluated through time-resolved spectra to assess interaction properties.
3. Biomaterial Performance Characterization
Time resolved emission spectroscopy (TRES) analytical service is applied to the excited-state dynamics of biodegradable biomaterials and functional materials, supporting performance optimization.
4. Optical Function Verification
By analyzing emission lifetimes and energy transfer characteristics of novel nanoprobes and photosensitive materials, their applicability in biological systems can be evaluated.
FAQs
Q1: What Advantages Does TRES Have Compared with Conventional Fluorescence Spectroscopy?
A1: Conventional fluorescence spectroscopy can only provide overall emission intensity and wavelength information, while TRES can record emission changes at different time scales, revealing dynamic processes such as excited-state lifetime, energy transfer, and molecular interactions.
Q2: Is TRES Suitable for Quantitative Research?
A2: TRES is more suitable for qualitative and semi-quantitative studies. It can compare the characteristics of different samples through lifetime distributions and decay curves, but precise quantification usually requires the combination of other methods.
Q3: What Factors May Affect the Reliability of the Results?
A3: Sample concentration being too high or too low, impurity interference, improper laser power settings, and unstable experimental conditions can all affect signal quality and data analysis.
How to order?







