RNA Circular Dichroism Assay Service
RNA molecules play a central role in gene regulation, protein synthesis, and drug action mechanisms, with their secondary and higher-order structures directly determining biological activity. Circular Dichroism spectroscopy (CD) detects differences in the absorption of left- and right-circularly polarized light by chiral molecules, enabling rapid, label-free assessment of RNA conformation, folding dynamics, and ligand binding under near-physiological conditions.
Leveraging a highly stable CD platform equipped with temperature control and titration accessories, MtoZ Biolabs offers the RNA Circular Dichroism Assay Service for both basic research and drug development. This end-to-end solution spans method design, data acquisition, and result interpretation, covering key applications such as RNA secondary structure determination, folding kinetics, thermal stability, and the evaluation of RNA-ligand or RNA-protein interactions.
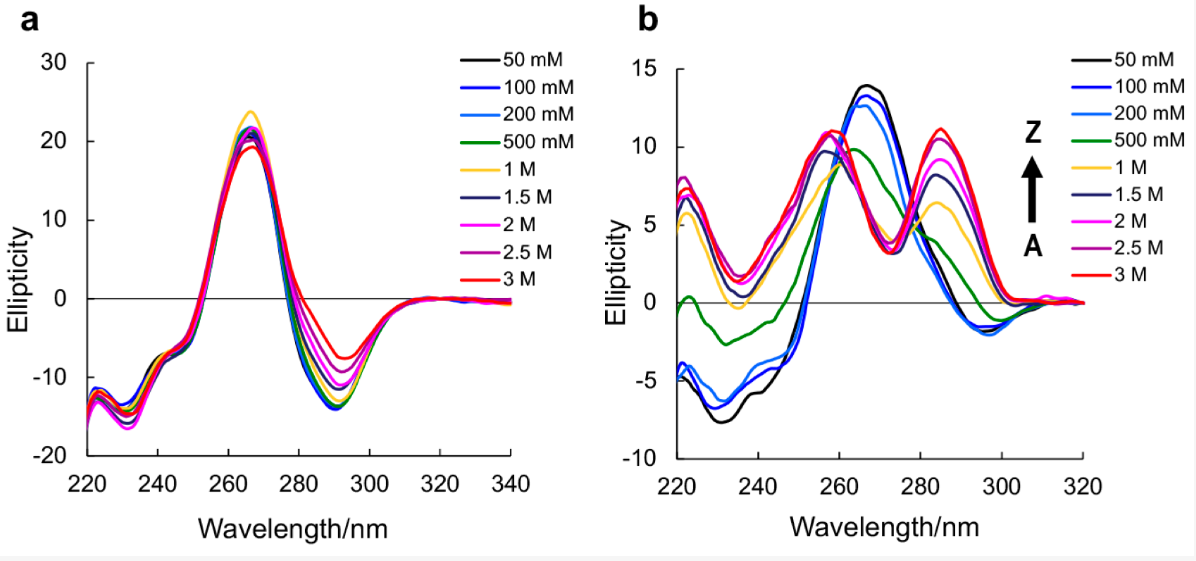
Balasubramaniyam, T. et al. Molecules. 2018.
Figure1. CD Spectra of Native RNA r(CGCGCG)₂ and m⁸Gm-contained r(CGC[m⁸Gm]CG)₂
Technical Principle
Circular Dichroism (CD) measures the minute differential absorption (ΔA) of left- and right-circularly polarized light, with spectral patterns determined by base stacking, helical chirality, and the local environment. For RNA, this enables:
Secondary Structure Identification: Distinct spectral profiles and characteristic extrema in position and intensity can differentiate A-form double helices, hairpins, stem-loop structures, and G-quadruplexes. These patterns are suitable for rapid fingerprint comparison and for assessing conformational differences between sequences or mutants.
Thermal Stability Assessment: Temperature-gradient CD produces melting curves to estimate Tm values and cooperativity. For formulations such as mRNA/LNP, it can also compare higher-order structural stability before and after encapsulation.
Ligand/Protein Binding: Titration-induced spectral changes (intensity, peak position, or racemization) can qualitatively indicate binding events and ligand-induced conformational rearrangements. Combined with modeling, this approach can yield apparent affinity characteristics.
Thermal Denaturation and Refolding: By recording ellipticity changes in a temperature-controlled cell, CD can determine Tm values and folding thresholds, allowing comparison of stability under different buffer conditions, ionic strengths, or in the presence of ligands.
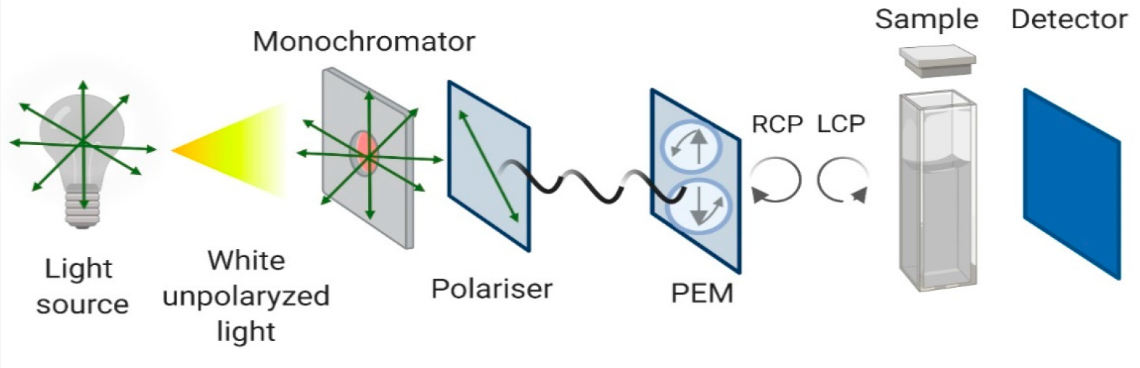
Pignataro, M.F. et al. Molecules. 2020.
Figure2. Schematic Representation of the Circular Dichroism Instrument Configuration
Service at MtoZ Biolabs
1. RNA Secondary Structure and Mutant Comparison
Standard far-UV nucleic acid CD (approximately 180–320 nm) with background correction; spectral features are compared with reference libraries or literature data to generate structural fingerprints and interpret conformational differences.
2. Thermal Melt and Annealing
Temperature-controlled heating and cooling scans fitted to two-state or multi-state models to report Tm and cooperativity parameters, assessing the effects of ions, pH, buffer composition, and additives on structural stability.
3. Folding Kinetics and Conformational Transition Monitoring
Continuous scans or fixed-wavelength time monitoring to analyze folding intermediates and rate constants; applicable to systems such as hairpins, riboswitches, and G-quadruplexes.
4. RNA–Ligand/Protein Interaction Characterization
Ligand titration combined with difference spectra to qualitatively assess binding-induced conformational changes; can be integrated with SPR, MST, or ITC to enhance quantitative resolution.
5. mRNA and Formulation Quality Assessment
Comparison of spectral profiles and thermal stability between free mRNA and LNP-encapsulated forms for formulation screening and quality monitoring during process scale-up.
Analysis Workflow
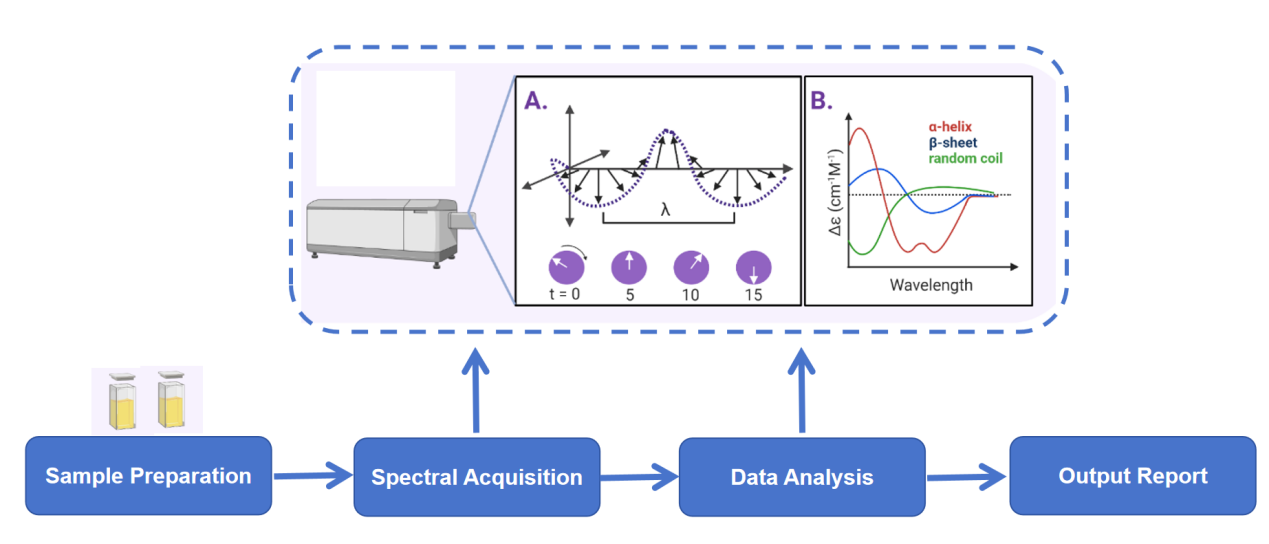
Why Choose MtoZ Biolabs?
✅ In-solution, in situ measurement: Eliminates conformational bias caused by crystallization or immobilization.
✅ Multi-mode integration: Enables structural fingerprinting, thermal stability, kinetics, and interaction analyses on a single platform.
✅ Low sample consumption: Generates high signal-to-noise data from minimal RNA quantities, making it ideal for precious samples.
✅ Quantitative parameter delivery: Provides Tm, cooperativity, conformational ratio changes, kinetic rate constants, and other key metrics.
Applications
Analysis of RNA secondary structure types and conformational differences in mutants.
Structural studies of RNA G-quadruplexes and riboswitches, including evaluation of ion effects.
Detection of conformational changes induced by RNA–small molecule, metal ion, or protein binding.
Thermal stability assessment and formulation optimization for mRNA/LNP preparations.
Sample Submission Suggestions
· Sample Type: In vitro transcribed RNA, chemically synthesized RNA, mRNA, aptamers, G-quadruplexes, ribozymes, and related RNA species ect..
· Purity: ≥ 90%, free of contaminants such as proteins, surfactants, and fluorescent dyes.
· Buffer System: Low UV-absorbance buffers (e.g., Na-phosphate, NaCl, KCl) with specified ionic conditions.
· Storage and Transport: Store at low temperature and protect from light (−20 °C or below); ship on dry ice.
Deliverables
Raw CD spectra data
Secondary structure composition analysis
Thermal stability curves
Conformational change analysis
Comprehensive experimental report
FAQ
Q1: Can the RNA Circular Dichroism Assay Service detect RNA–protein interactions?
A1: Yes. Binding and conformational rearrangements can be qualitatively assessed through titration-induced CD difference spectra, and quantitative analysis can be performed when combined with ITC or MST.
Q2: Is the CD assay suitable for mRNA/LNP formulations?
A2: Yes. It can compare spectral profiles and thermal stability before and after encapsulation, supporting process optimization.
How to order?







