Powder X-ray Diffraction Analytical Service
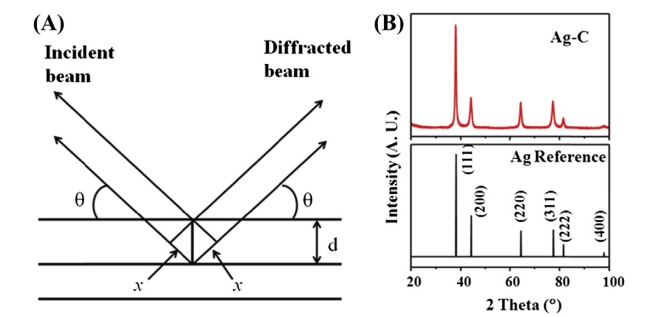
Powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) is a widely used technique in crystal material analysis, primarily for the identification and characterization of unknown crystalline materials. By directing X-rays onto a sample, the X-rays interact with the crystals to produce a diffraction pattern. PXRD generates a series of diffraction peaks rather than discrete spots as seen in single-crystal diffraction, with each peak corresponding to a specific crystal plane. The intensity of the peaks reflects the atomic density and orientation probability of that plane. Analyzing the diffraction pattern can reveal information such as the crystal structure, lattice constants, and interplanar distances of the sample. PXRD technology offers high precision and non-destructive advantages, providing detailed structural features and physical properties of the sample.
Bashir, S. et al Advanced Nanomaterials and their Applications in Renewable Energy, 2015.
Figure 1. Power X-ray Diffraction Experiment.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Using advanced X-ray diffraction instruments, MtoZ Biolabs' powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) analytical service enables precise analysis of the crystal structure and physical properties of powder samples. This service involves exposing the sample to X-rays, which interact with the material to produce a diffraction pattern. By accurately analyzing the diffraction peaks, we can determine the sample's crystal structure, phase composition, grain size, interplanar spacing, purity, and more. This service provides reliable support for physical and chemical properties research, quality control, and assessing the material's potential applications.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Type
Applicable to powder-form samples, which can be inorganic or organic substances. The sample should have a uniform particle size and be free from significant impurities to ensure the accuracy of the analysis.
2. Sample Purity
It is recommended that the sample purity be no less than 90%, with removal of non-target components to reduce interference and improve the reliability of the analysis.
3. Sample Storage and Transport
Samples should be stored in dry, sealed containers to prevent moisture or contamination. During transport, ensure the sample remains stable. Powder samples should be packaged securely and, if necessary, transported at low temperatures to maintain stability.
Advantages and Limitations
Applications
1. Drug Development
The powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) analytical service can be used to assess the stability, solubility, and bioavailability of drugs, ensuring the stability of their physicochemical properties.
2. Chemical Analysis
In the production process of chemicals, PXRD can be used to detect the crystal form and phase composition of raw materials and products, ensuring product quality consistency.
3. Biopharmaceuticals
The powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) analytical service can be used to analyze the crystallization characteristics of drug formulations and excipients, supporting the functional research and development of biomaterials.
4. Food and Nutrition
PXRD can be applied to food and nutritional products to evaluate the crystallization state of components, ensuring the quality and stability of the products.
FAQ
Q1: Can PXRD detect amorphous samples?
A1: PXRD is primarily used for analyzing crystalline samples. Amorphous substances like glass usually do not produce clear diffraction signals through PXRD unless complemented by special techniques such as small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS).
Q2: Does sample preparation affect the accuracy of results?
A2: Yes, the uniformity, particle size, and purity of the sample directly affect the quality of the diffraction pattern. It is recommended that the sample particles be of an appropriate size and free from impurities to ensure high-quality analytical results.
Q3: Can PXRD detect polymorphism in samples?
A3: Yes, PXRD can identify and differentiate multiple polymorphs within a sample through distinct diffraction patterns. It is very effective in determining crystal structure diversity and distinguishing different crystallization forms.
How to order?







