Phosphorylated Exosomal Proteomic Detection Service
Phosphorylated Exosomal Proteomic Detection Service utilizes high-resolution mass spectrometry to identify and quantify phosphorylated proteins within exosomes, helping to reveal the role of phosphorylated proteins in disease development, signal transduction, and cellular function regulation. Exosomes are nanoscale extracellular vesicles secreted by cells that carry various functional molecules, including proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. They are widely involved in intercellular communication, signal transduction, and immune regulation, among other biological processes. Protein phosphorylation, an important post-translational modification (PTM), plays a crucial role in regulating signaling pathways, modulating exosomal biological functions, and mediating the onset and progression of diseases. Using advanced high-resolution mass spectrometry combined with efficient phosphorylated peptide enrichment techniques, MtoZ Biolabs offers the Phosphorylated Exosomal Proteomic Detection Service to analyze phosphorylation modifications in exosomal proteins, helping researchers explore disease-related molecular mechanisms and potential drug targets from the perspective of exosomes.
Analysis Workflow
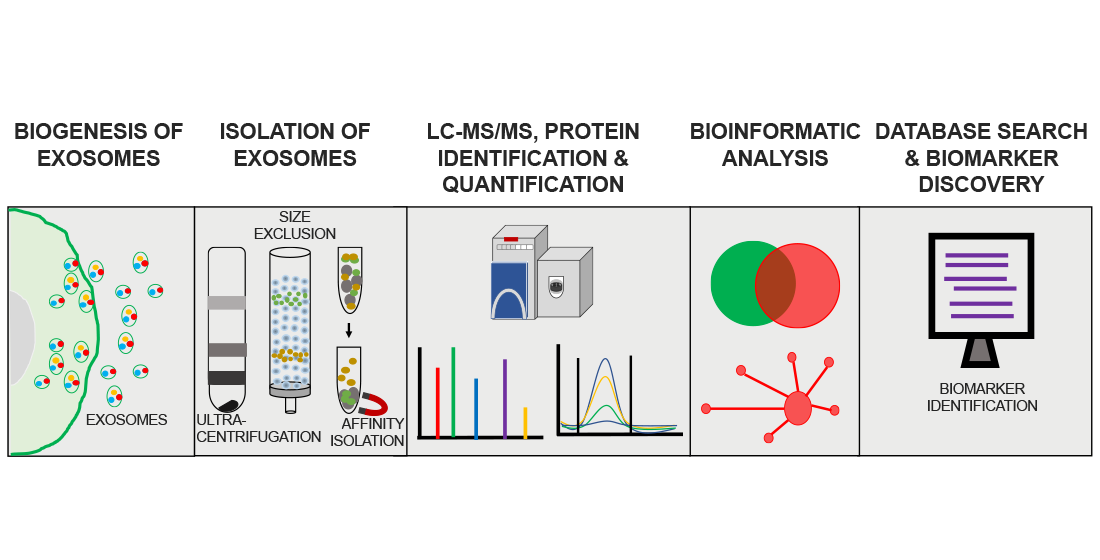
Mathew B. et al. Brain Sciences. 2021.
Figure 1. Exosome Proteomics Analysis Workflow.
1. Sample Preparation and Exosome Isolation
Select appropriate methods based on project requirements to extract high-purity exosomes. Perform quality verification of the exosomes.
2. Exosomal Protein Extraction and Digestion
Extract exosomal proteins and digest them to obtain peptide segments.
3. Phosphorylated Peptide Enrichment
Enrich phosphorylated peptides using methods such as IMAC or TiO₂.
4. Mass Spectrometry Detection
Use a high-resolution mass spectrometry system to separate, identify, and quantify phosphorylated peptides.
5. Data Analysis and Reporting
Use specialized software to analyze mass spectrometry data, identify and quantify phosphorylated proteins, and perform bioinformatics analysis. Provide a detailed report.
Applications
Disease Biomarker Discovery
Systematically detect exosomal phosphorylated proteins to identify dynamic biomarkers of diseases.
Signal Pathway Mechanism Analysis
Uncover how phosphorylated proteins carried by exosomes influence target cell signaling, metastasis, and immune regulation, among other biological processes.
Tumor Microenvironment Research
Analyze the role of phosphorylated proteins in exosomes in communication between tumor cells, immune cells, and stromal cells, revealing dynamic changes in the tumor microenvironment.
Drug Target Exploration
Identify disease-related exosomal phosphorylated proteins as potential drug development targets, advancing new drug screening and treatment strategy optimization.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Using high-resolution mass spectrometry, MtoZ Biolabs offers Phosphorylated Exosomal Proteomic Detection Service providing accurate and comprehensive analysis of phosphorylated proteins in exosomes, delivering high-quality data support for clients' research. MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry (MS) Services Provider, provides advanced proteomics, metabolomics, and biopharmaceutical analysis services to researchers in biochemistry, biotechnology, and biopharmaceutical fields. Our ultimate aim is to provide more rapid, high-throughput, and cost-effective analysis, with exceptional data quality and minimal sample consumption.
FAQ
Q. The Content of Phosphorylated Exosomal Proteins is Low, How can We Improve the Detection Sensitivity?
Phosphorylated exosomal proteins indeed present challenges such as low abundance and complex modification sites. To enhance detection sensitivity, we utilize efficient phosphorylated peptide enrichment technologies (such as IMAC metal ion affinity chromatography and TiO₂ nanoparticle enrichment), which significantly improve the capture efficiency of low-abundance phosphorylated peptides. Additionally, combining high-resolution nano-LC-MS/MS enables highly sensitive separation and multistage mass spectrometry analysis of low-abundance phosphorylated peptides, achieving site-level precise identification. Moreover, by using internal standard calibration and efficient sample preparation workflows, we minimize sample loss, improve phosphorylated protein coverage, and enhance quantitative accuracy, ensuring the depth and reliability of the final data.
Deliverables
1. Comprehensive Experimental Details
2. Materials, Instruments, and Methods
3. Total Ion Chromatogram & Quality Control Assessment (project-dependent)
4. Data Analysis, Preprocessing, and Estimation (project-dependent)
5. Bioinformatics Analysis
6. Raw Data Files
Case Study
The study used Phosphorylated Exosomal Proteomic Detection technology to analyze phosphorylated proteins in plasma-derived exosomes from breast cancer patients. The results revealed that several signal transduction-related phosphorylated proteins (such as EGFR, AKT, STAT3) were significantly upregulated in the exosomes of breast cancer patients. Additionally, some phosphorylated sites exhibited subtype-specificity, suggesting that these phosphorylated proteins are not only involved in tumor initiation and progression but also have the potential to serve as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for breast cancer.
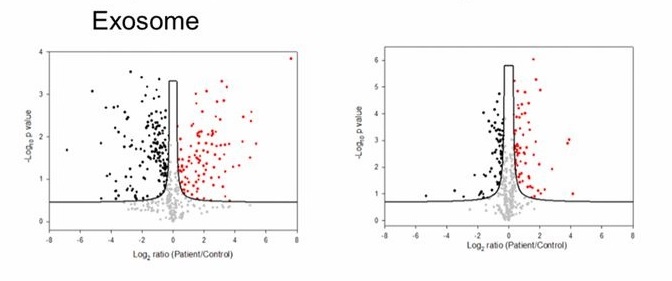
Chen I. et al. P Natl Acad Sci Usa. 2017.
Figure 2. Comparison of Phosphorylated Proteome in Exosomes from Healthy Individuals and Cancer Patients.
How to order?







