Neurological Diseases Diagnosis-Applied Exosomes
Exosomes are small extracellular vesicles, typically ranging from 40 to 200 nm in diameter, secreted by various cells, including neurons and glial cells. These vesicles carry proteins, lipids, RNA, and other biomolecules that reflect the physiological and pathological states of their source cells. In the nervous system, exosomes play a critical role in intercellular communication and can cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB). Importantly, exosomes can transport disease-specific molecules, such as tau proteins in Alzheimer's disease and alpha-synuclein in Parkinson's disease, thereby contributing to the pathogenesis and progression of neurological disorders. Given their ability to encapsulate disease markers and cross the BBB, exosomes offer a promising non-invasive approach for diagnosing, monitoring, and predicting outcomes of neurological diseases. MtoZ Biolabs provides comprehensive Neurological Diseases Diagnosis-Applied Exosomes services, including high-purity exosome isolation, biomarker discovery, and molecular profiling to support early diagnosis and monitoring of neurological disorders.
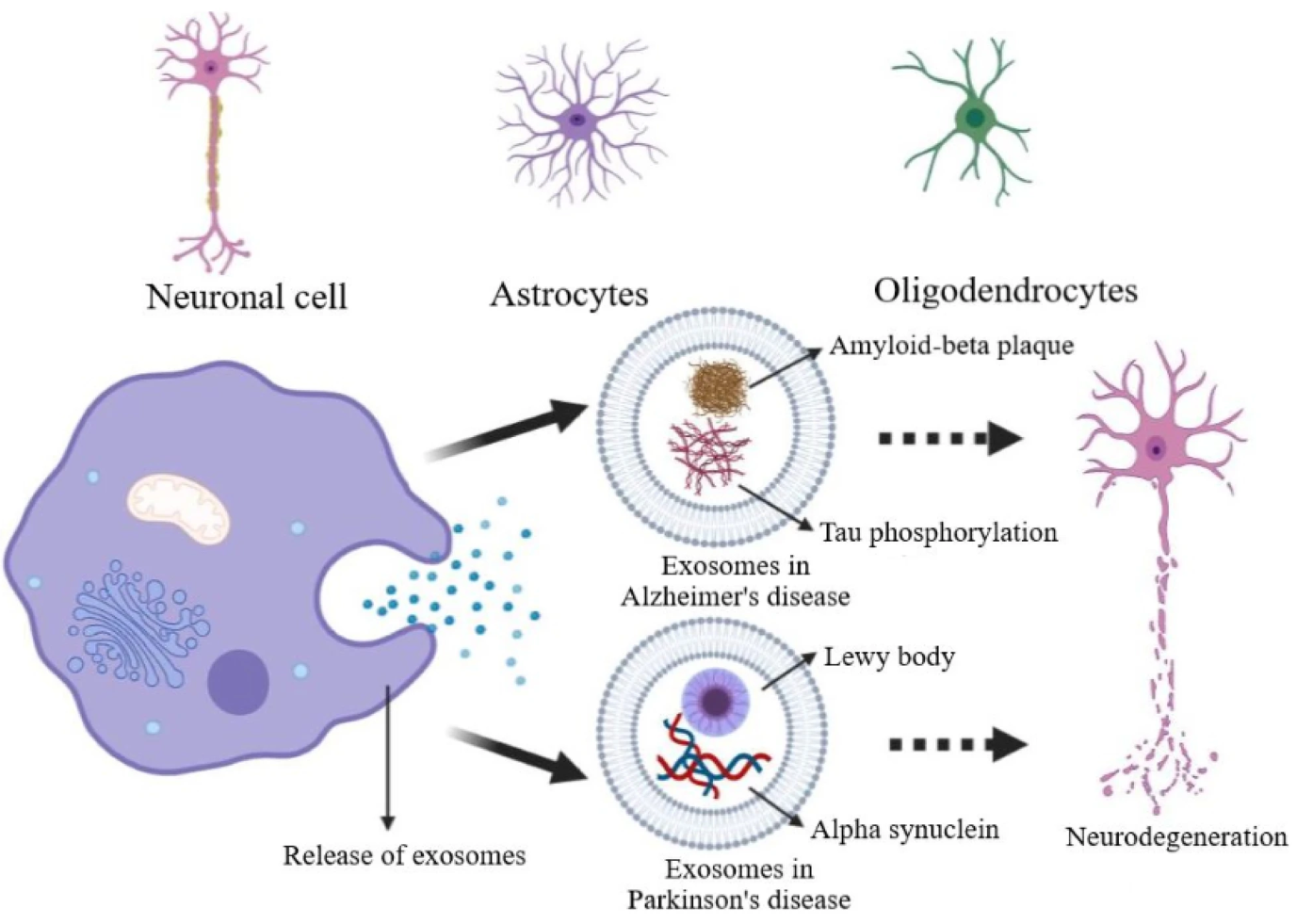
Figure 1. Release of Diseases-Carrying Exosomes from Various Neuronal Cells to Neighbouring Cells, Contributing to the Further Aggravation of Diseases
Service at MtoZ Biolabs
MtoZ Biolabs' Neurological Diseases Diagnosis-Applied Exosomes Service focuses on identifying exosome-based biomarkers to support the diagnosis and monitoring of neurological disorders, while also providing insights into underlying disease mechanisms. Leveraging advanced high-resolution mass spectrometry, next-generation sequencing (NGS), and cutting-edge exosome isolation technologies, MtoZ Biolabs offers end-to-end solutions covering exosome extraction, characterization, and multi-omics profiling.
Our service portfolio includes exosomal proteomics (LC-MS/MS-based protein profiling), whole transcriptome sequencing (RNA-seq), exosomal miRNA sequencing, lncRNA sequencing, and circRNA sequencing, enabling a deep understanding of exosome-derived biomolecules associated with neurological diseases. These services help identify novel biomarkers for early diagnosis, monitor disease progression, and reveal exosome-mediated intercellular communication pathways involved in neurodegeneration, neuroinflammation, and neuronal repair. Our customizable solutions support academic research, clinical biomarker development, and therapeutic strategy design, empowering clients to translate exosome insights into impactful diagnostic and therapeutic innovations. Contact us to explore tailored solutions for your research.
Service Advantages
1. Advanced Multi-Omics Platforms
Comprehensive exosomal proteomics, transcriptomics (mRNA, lncRNA, circRNA), and small RNA (miRNA) sequencing enable in-depth molecular profiling for neurological disease biomarker discovery.
2. End-to-End Customized Solutions
One-stop service from exosome isolation, characterization, multi-omics analysis to data interpretation, fully tailored to specific neurological research or clinical needs.
3. High Sensitivity and Accuracy
State-of-the-art techniques ensuring sensitive detection of low-abundance biomarkers and rigorous quality control for reproducible and clinically relevant results.
4. Transparent Pricing and Professional Support
Clear cost structures with expert consultation throughout the project to ensure successful outcomes aligned with research or clinical goals.
Applications
Exosome-based diagnostics offer promising applications across a wide spectrum of neurological diseases (Figure 2), providing non-invasive biomarker discovery and disease monitoring solutions. These diseases include, but are not limited to:
A. Glioma
B. Parkinson’s Disease (PD)
C. Brain Stroke
D. Alzheimer’s Disease (AD)
E. Brain Ischemia
F. Brain Haemorrhage
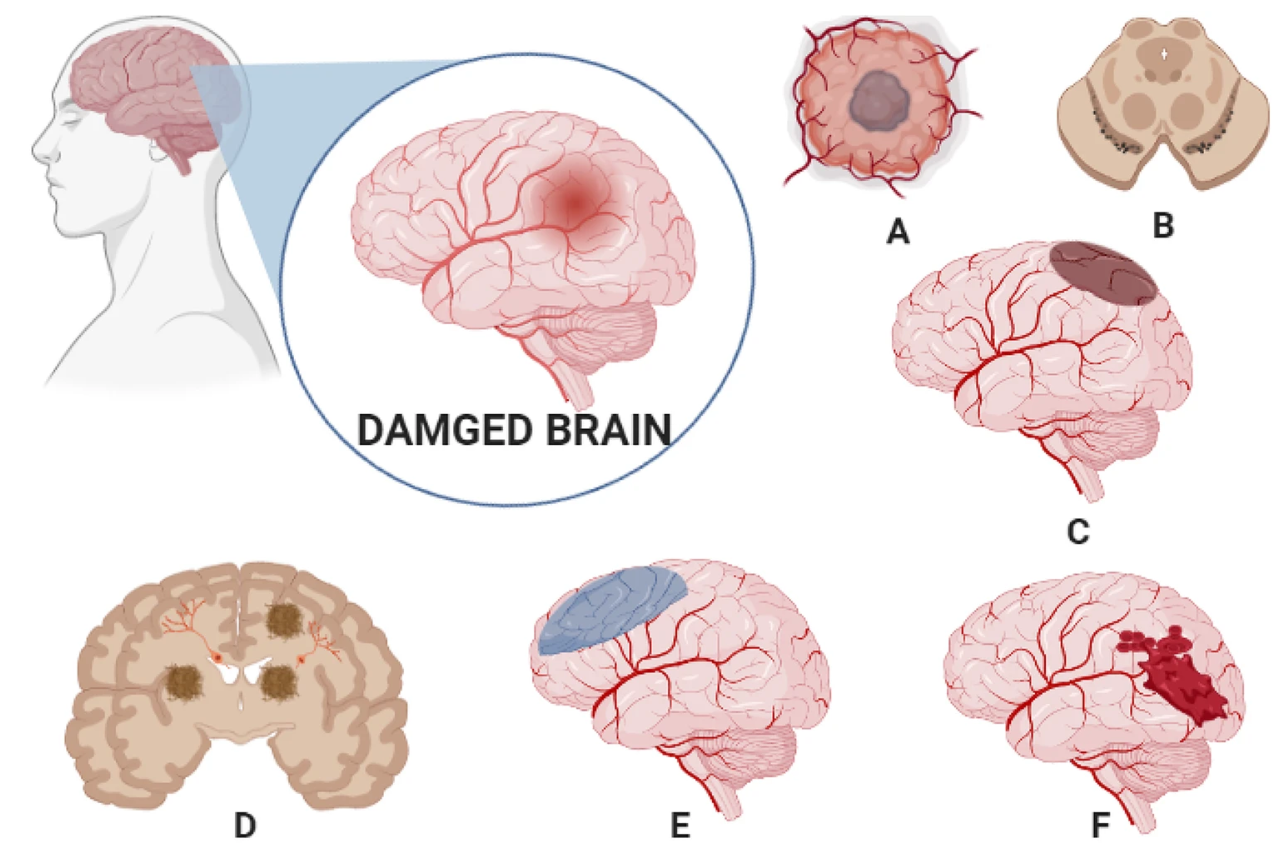
Figure 2. Various Brain Diseases Treated using Exosomes
Case Study
Exosome-Based Detection of circSV2b in Parkinson’s Disease Diagnosis
Parkinson’s disease (PD) lacks reliable non-invasive biomarkers for early diagnosis. Covalently closed circular RNAs (circRNAs) in serum exosomes, protected from degradation, offer promising biomarker potential due to their stability and blood-brain barrier penetration. This study identified circSV2b as a PD-associated circRNA through RNA-seq in MPTP-induced PD mice. circSV2b was significantly downregulated in the striatum (STR), substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc), and serum exosomes of PD mice. Functional validation revealed that circSV2b overexpression restored dopamine levels, improved motor deficits, and mitigated oxidative stress via the miR-5107-5p-Foxk1-Akt1 axis. Mechanistically, circSV2b acted as a competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA), sponging miR-5107-5p to derepress Foxk1, which transcriptionally activated Akt1 to enhance mitochondrial autophagy. The significant reduction of circSV2b in serum exosomes highlights its potential as a non-invasive PD biomarker. This aligns with the utility of exosomal circRNAs for neurological disease diagnostics, enabling early detection and monitoring of PD progression. This case underscores the value of exosome-derived circRNAs, exemplified by circSV2b, in advancing PD diagnosis and therapeutic targeting.
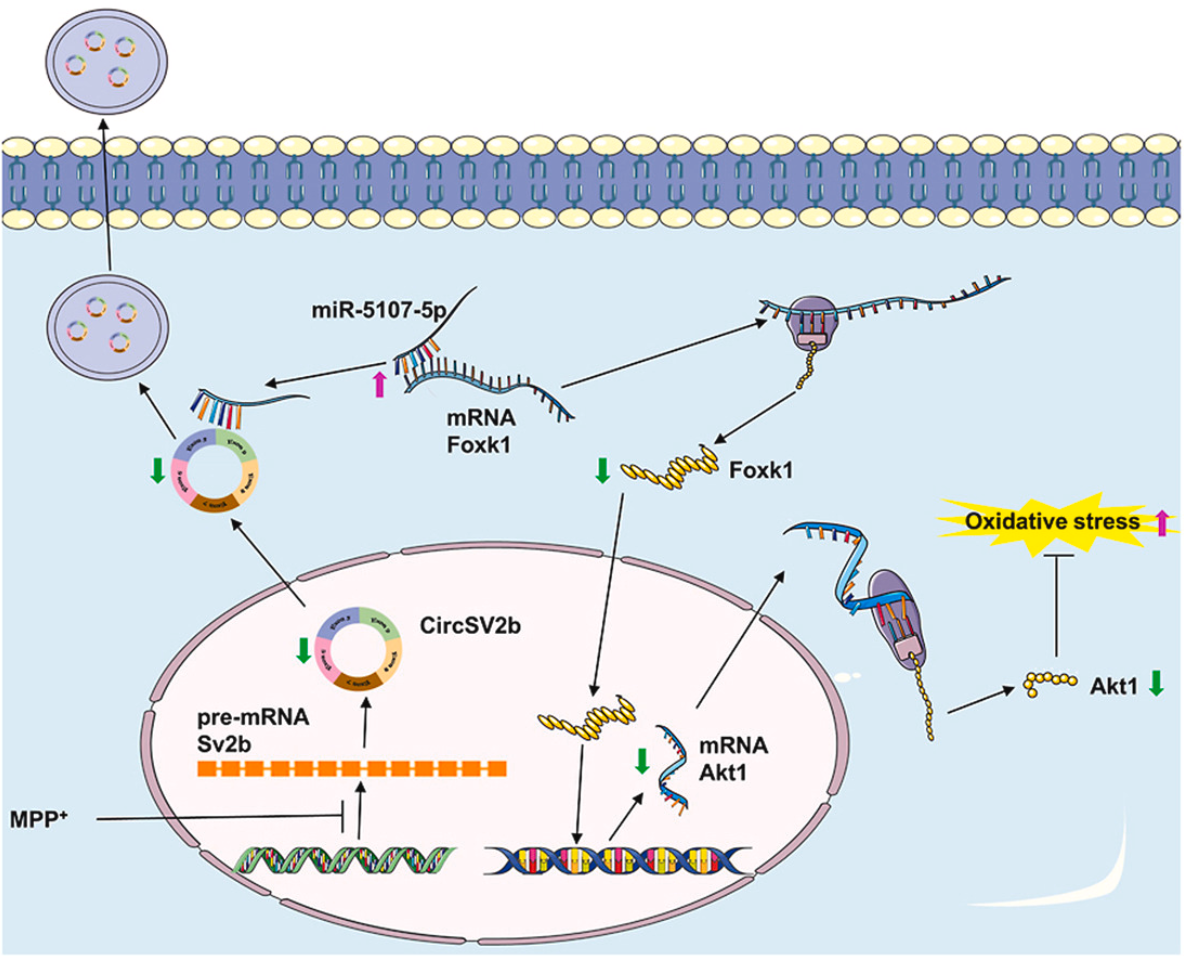
Figure 3. Schematic Summary of the Mechanism of CircSV2b in MPTP-Induced PD
FAQ
Q: What are the advantages of using exosomes over traditional biomarkers in neurological diagnostics?
Exosomes offer several advantages over traditional biomarkers in neurological diagnostics. Unlike conventional biomarkers that may degrade rapidly or poorly reflect disease-specific changes, exosomes are stable nanovesicles that protect their cargo of proteins, RNAs, and lipids, preserving critical disease-related information. They cross the blood-brain barrier, enabling non-invasive access to central nervous system-derived molecules through peripheral fluids like blood and cerebrospinal fluid. Additionally, exosomes carry cell-type-specific and disease-specific signatures, allowing for highly sensitive and specific detection of neurological disorders, including early-stage and heterogeneous diseases such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and gliomas. Their dynamic cargo also enables real-time monitoring of disease progression and therapeutic response, offering a powerful platform for precision diagnostics in neurology.
How to order?







