Neoantigen Identification Service
- Leverages advanced algorithms for precise and reliable neoantigen prediction.
- Offers a comprehensive workflow from sample processing to accurate neoantigen identification.
- Ensures high sensitivity and specificity through cutting-edge multi-omics technologies.
- Provides tailored analysis to meet personalized immunotherapy research needs.
- Delivers clinically actionable insights with robust bioinformatics pipelines and validation.
The Neoantigen Identification Service is a cutting-edge approach designed to discover tumor-specific antigens, known as neoantigens, that arise from somatic mutations unique to cancer cells. These neoantigens are absent in normal tissues and exhibit high immunogenicity, making them ideal targets for personalized immunotherapies. By leveraging advanced genomic and proteomic technologies, the Neoantigen Identification Service enables precise identification and characterization of neoantigens, paving the way for breakthroughs in cancer treatment.
Neoantigens play a pivotal role in cancer immunotherapy by activating tumor-specific T cells without triggering autoimmunity. Unlike self-antigens, which may lead to off-target effects, neoantigens are uniquely derived from tumor mutations and are processed and presented on the cell surface by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules, making them recognizable to the immune system. Accurate neoantigen identification is essential for the development of personalized cancer vaccines, adoptive T cell therapies, and immune checkpoint inhibitors, which have revolutionized cancer treatment in recent years.
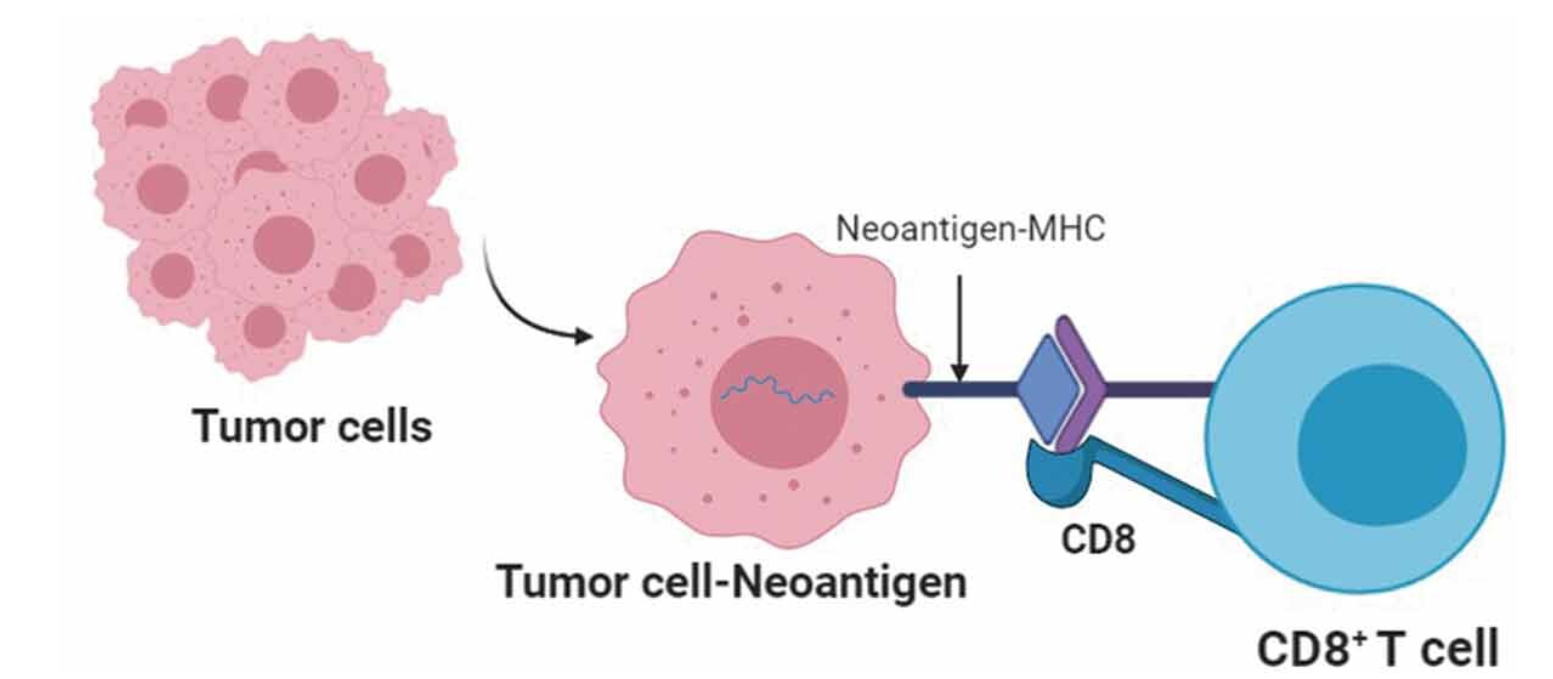
Ebrahimi, N. et al. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2022.
Figure 1. Recognition of Tumor Neoantigens by CD8 T Cells
Service at MtoZ Biolabs
MtoZ Biolabs offers a comprehensive Neoantigen Identification Service that utilizes advanced multi-omics technologies, including whole-exome sequencing (WES), RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq), and mass spectrometry-based immunopeptidomics, to identify tumor-specific neoantigenic peptides with exceptional accuracy. Our Neoantigen Identification Service employs state-of-the-art sequencing platforms and robust bioinformatics pipelines to ensure precise mutation calling, epitope prediction, and binding affinity analysis. The Neoantigen Identification Service empowers researchers with actionable insights to advance personalized cancer immunotherapy and develop novel immunotherapeutic strategies tailored to individual tumor profiles.
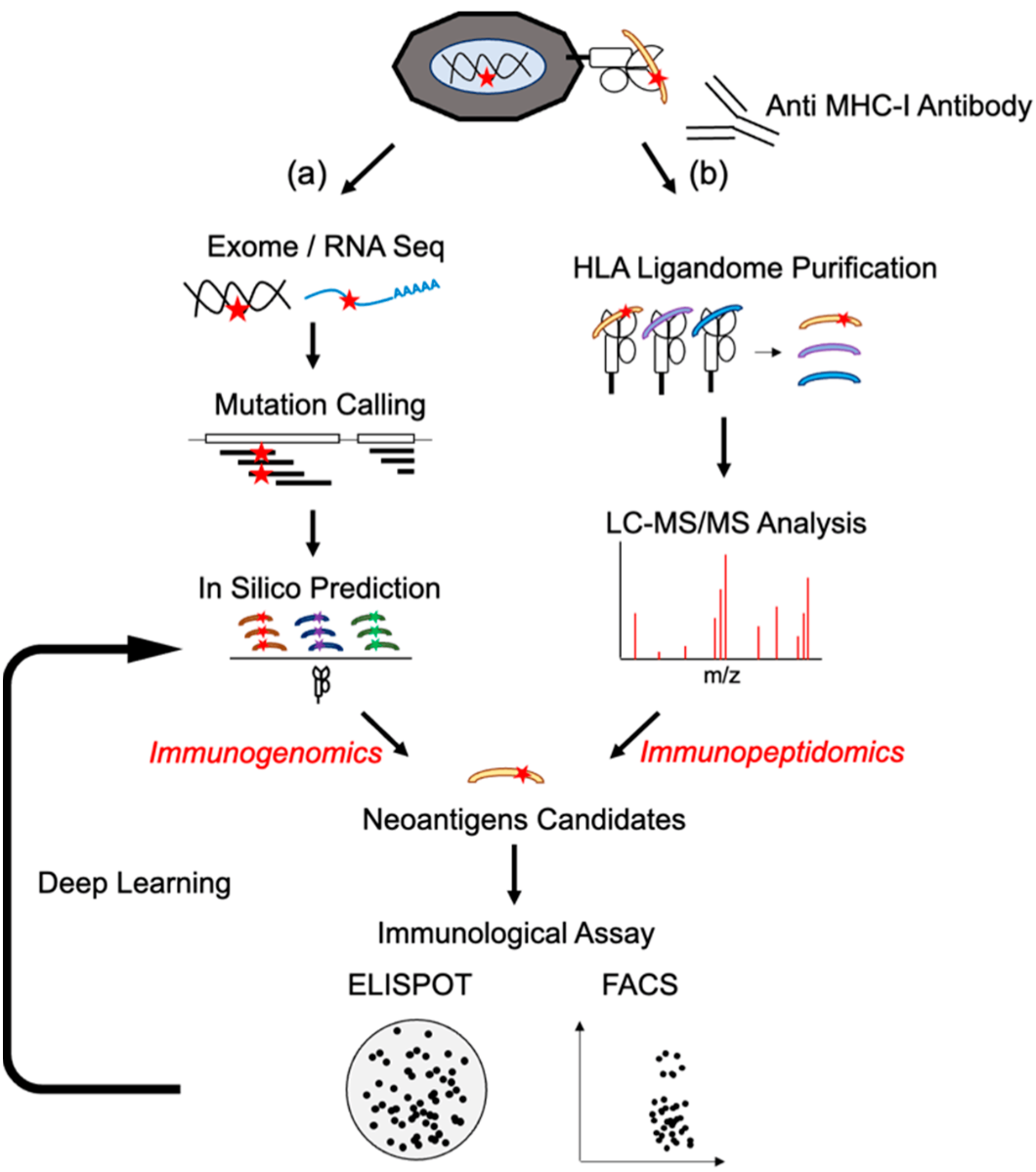
Figure 2. Neoantigen Identification by Immunogenomic or Immunopeptidomic Method
Service Advantages
Applications
1. Personalized Cancer Vaccines
The Neoantigen Identification Service enables the development of patient-specific cancer vaccines by identifying neoantigens that activate tumor-specific T cells, enhancing therapeutic precision and efficacy.
2. Tumor Microenvironment Studies
Provides critical insights into how neoantigens interact with immune cells in the tumor microenvironment, aiding research into immune evasion and resistance mechanisms.
3. Biomarker Discovery
Identifies neoantigens as potential biomarkers to monitor tumor progression, treatment response, and immune activity in cancer patients, advancing translational research.
4. Adoptive T Cell Therapy
Supports the design of adoptive T cell therapies by identifying neoantigens as specific targets for engineering T cells, boosting their ability to selectively attack tumor cells.
Case Study
Neoantigen Identification for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC)
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is a highly aggressive subtype with limited treatment options. Neoantigen-based immunotherapy offers a promising solution by targeting tumor-specific antigens derived from somatic mutations. Using a Neoantigen Identification Service pipeline, researchers analyzed tumor samples from four TNBC patients and the MDA-MB-231 cell line through whole-exome sequencing, transcriptomics, and proteomics. Bioinformatic predictions identified 95 neoantigen candidates across the patients and 27 from MDA-MB-231. Validation using HLA-binding assays confirmed 66% of patient-derived and 21 of 27 MDA-MB-231 neoantigens as capable of binding to HLA molecules. This highlights the necessity of experimental validation to ensure immunogenicity. This study demonstrates the effectiveness of Neoantigen Identification Service in identifying and validating neoantigens, paving the way for personalized immunotherapies and advancing vaccine development for TNBC.
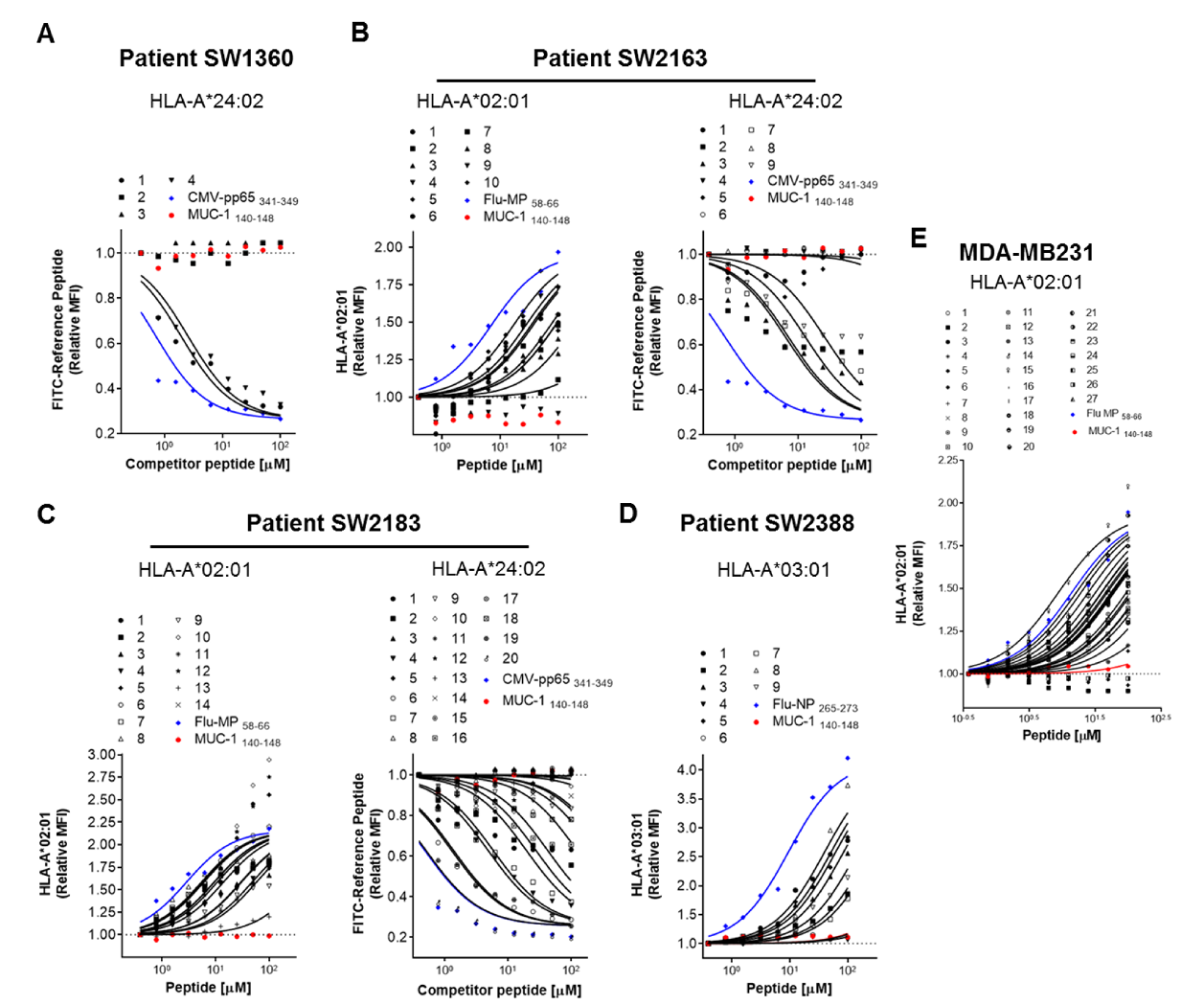
Figure 3. Screening of Neoantigen Candidates for a Personalized Vaccine for TNBC
FAQ
Q: What strategies are used to distinguish subclone neoantigens in highly heterogeneous tumors?
To distinguish subclone neoantigens in highly heterogeneous tumors, strategies like deep sequencing of tumor genomes and transcriptomes are employed to identify mutation-specific peptides. Single-cell RNA sequencing aids in understanding clonal dynamics. Computational algorithms predict neoantigens based on mutational landscape, while mass spectrometry (MS)-based proteomics, integrated with Neoantigen Identification Services, facilitates the validation of subclone-specific neoantigens, ensuring precision in targeting and immunotherapy.
How to order?







