N-Glycosylation Profiling Service
N-glycosylation profiling service is an analytical service that utilizes mass spectrometry and other high-throughput techniques to identify and quantify the structure, composition, sites, and relative abundance of oligosaccharide chains linked to asparagine (Asn) residues in proteins. This service can be applied to global glycan profiling, glycopeptide profiling, or site-specific glycosylation analysis.
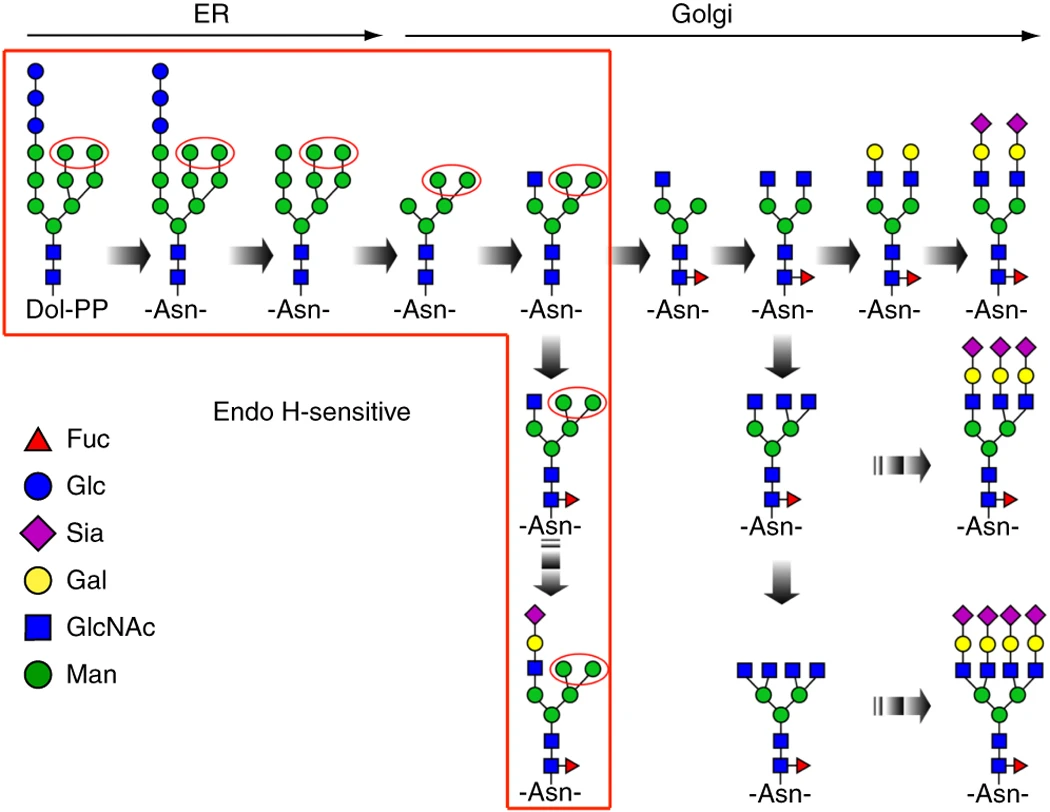
Cao L. et al. Nat Protoc. 2018.
Glycosylation is one of the most common and complex post-translational modifications (PTMs) of proteins. It is widely present in membrane proteins, secreted proteins, and plasma proteins, playing a critical role in regulating protein folding, stability, immune recognition, and intercellular communication. In particular, N-linked glycosylation plays a key role in antibody drug development, biomarker discovery, and disease mechanism research. N-linked glycosylation refers to the covalent attachment of oligosaccharide chains to the side-chain amide group of asparagine (Asn) residues in proteins, typically occurring at the consensus sequence “N-X-S/T” (where X ≠ P). The structures of N-glycans are diverse and mainly include high-mannose, complex, and hybrid types. Aberrant N-glycosylation is closely associated with a variety of diseases, including cancer, autoimmune disorders, and congenital disorders of glycosylation (CDG). In order to gain a deeper understanding of the regulatory mechanisms of protein function and its pathological associations, systematic mapping of N-glycosylation has become a research focus at the intersection of proteomics and glycomics.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
1. Target Protein N-Glycosylation Analysis
MtoZ Biolabs provides precise qualitative and quantitative analysis of N-glycosylation sites on target proteins using a high-resolution LC-MS/MS platform. By characterizing glycan structures, linkage types, and modification isomers, MtoZ Biolabs helps researchers gain deeper insights into how N-glycosylation affects protein conformation, activity, and stability.
2. N-Glycosylation Proteomics Analysis
MtoZ Biolabs employs advanced mass spectrometry techniques to systematically detect and compare N-glycosylated peptides within samples. This service enables efficient localization of N-glycosylation modification sites and reveals regulatory variations across different samples, providing reliable data support for comprehensive glycoproteomic analysis.
Analysis Workflow
N-glycosylation profiling service primarily follows the workflow below:
1. Sample Preparation
Client-provided samples undergo protein extraction and reduction/alkylation treatment to ensure compatibility with downstream analysis.
2. Digestion and Glycopeptide/Glycan Enrichment
Samples are digested using enzymes such as trypsin, and glycopeptides or glycans are enriched using methods such as lectin affinity enrichment or HILIC solid-phase extraction.
3. Mass Spectrometry Analysis
High-resolution LC-MS/MS is used to separate and detect glycopeptides or glycans, acquiring precursor and fragment ion information.
4. Data Processing and Structure Identification
Specialized software is used for glycan structure and site identification, including analysis of glycan composition, sequence, and linkage types.
5. Quantification and Bioinformatics Analysis
Quantitative analysis of glycan types and site-specific abundance is performed, followed by functional annotation and pathway analysis using bioinformatics tools.
Applications
N-glycosylation profiling has broad applications in the following areas:
Biopharmaceuticals
Assess glycosylation patterns of therapeutic proteins (e.g., monoclonal antibodies, fusion proteins) to ensure product quality and efficacy.
Disease Research
Investigate the role of N-glycosylation in diseases such as cancer and neurodegenerative disorders, and identify potential biomarkers.
Protein Function Studies
Examine how N-glycosylation affects protein structure and function, and elucidate its biological significance in cellular signaling and metabolic regulation.
Plant Science
Analyze glycosylation patterns in plant proteins to study their roles in plant development and stress responses.
Service Advantages
1. Advanced Analysis Platform: MtoZ Biolabs established an advanced N-glycosylation profiling service platform, guaranteeing reliable, fast, and highly accurate analysis service.
2. One-Time-Charge: Our pricing is transparent, no hidden fees or additional costs.
3. High-Data-Quality: Deep data coverage with strict data quality control. AI-powered bioinformatics platform integrates all N-glycosylation profiling service data, providing clients with a comprehensive data report.
4. Customized Service: Tailored analysis plans and report formats are provided based on the specific needs of each client to meet the requirements of diverse research projects.
Deliverables
1. Comprehensive Experimental Details
2. Materials, Instruments, and Methods
3. Total Ion Chromatogram & Quality Control Assessment (project-dependent)
4. Data Analysis, Preprocessing, and Estimation (project-dependent)
5. Bioinformatics Analysis
6. Raw Data Files
FAQ
Q. What Types of N-Glycans Can be Identified Through N-Glycosylation Profiling? Can Minor Structural Differences be Detected?
Our service can identify various types of N-glycans, including high-mannose, complex, and hybrid structures, along with features such as sialylation, fucosylation, and branching patterns. By utilizing high-resolution mass spectrometry and multiple fragmentation modes (e.g., HCD, ETD), we can analyze glycan composition, linkage order, and even certain isomeric differences. This is particularly suitable for detecting subtle glycan variations in highly complex samples.
Q. Can Both Glycan Structure and Glycosylation Site Information be Obtained Simultaneously?
Yes. MtoZ Biolabs provides site-specific N-glycosylation analysis at the glycopeptide level. This enables simultaneous identification of glycan structures and precise localization of the corresponding asparagine (Asn) attachment sites, helping to elucidate the spatial configuration and regulatory roles of protein glycosylation.
Q. Is Quantitative Comparison of Multiple Sample Groups Supported? Is Labeling Required?
We support both label-free quantification and chemical labeling strategies (e.g., TMT/iTRAQ). Label-free quantification is ideal for large sample sets or uneven experimental conditions, while TMT is suitable for high-throughput parallel comparisons. We will recommend the most appropriate strategy based on the objectives of your project.
Case Study
This study conducted a systematic analysis of glycan structures in the plasma of COVID-19 patients. It was found that, compared to healthy controls, the N-glycosylation profile of COVID-19 patients—especially those with severe illness—underwent significant changes. Specifically, there was a marked increase in sialylated and low-branched oligomannose-type glycans, along with a significant decrease in non-sialylated complex-type structures such as A2G2. These glycan alterations were strongly associated with inflammatory states, suggesting that N-glycosylation patterns could serve as potential biomarkers for assessing the severity of COVID-19.
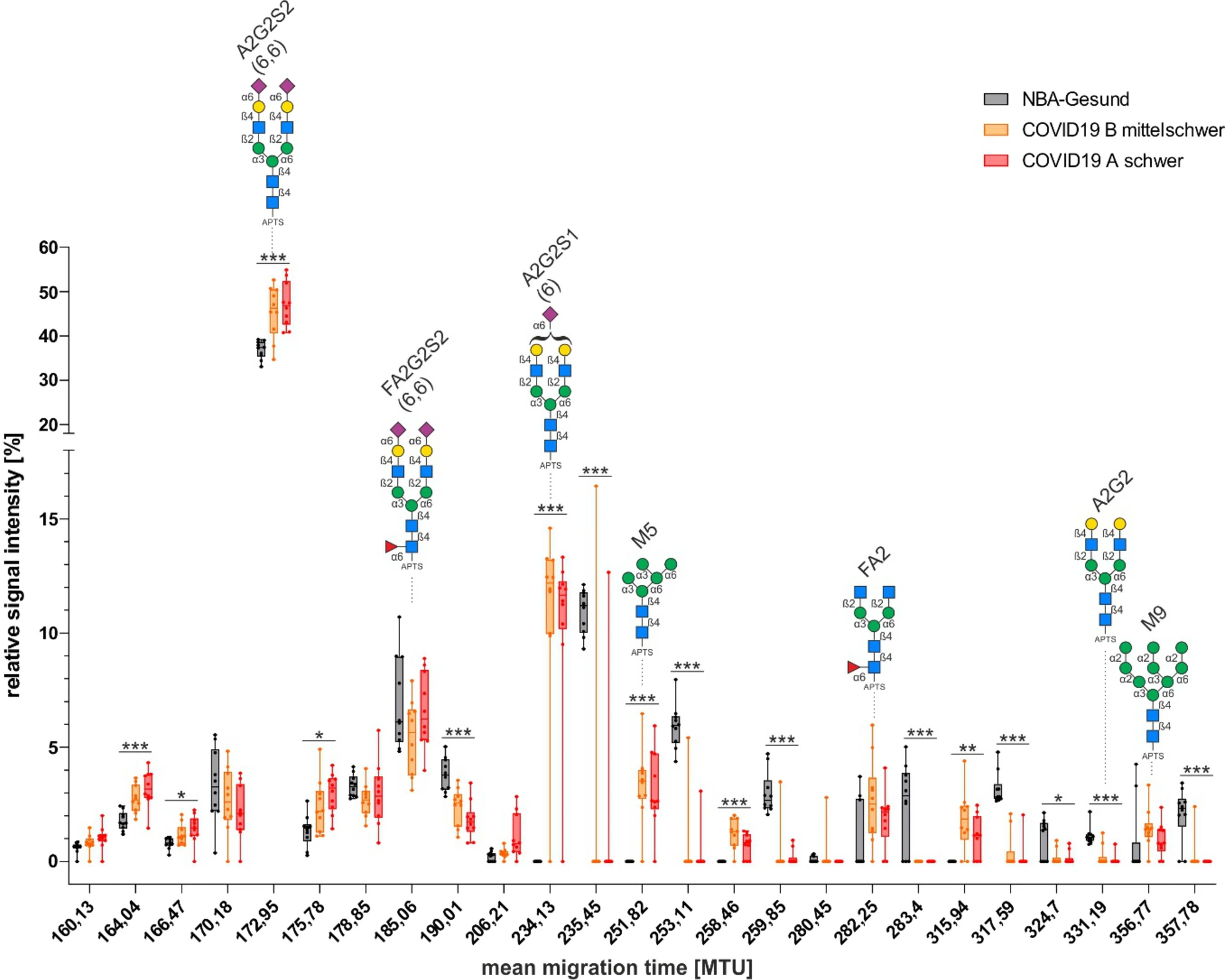
Beimdiek J. et al. Respir Res. 2022.
How to order?







