Microscopic Infrared Spectroscopy Analytical Service
Microscopic infrared spectroscopy is an analytical method that combines infrared spectroscopy with microscopic imaging, enabling the study of the chemical composition and molecular structure of samples at the micron or even smaller scale. Its basic principle is that molecules produce characteristic absorptions under infrared irradiation, and by recording absorption spectra at different wavelengths, information on functional groups and intermolecular interactions can be revealed. Microscopic infrared technology allows qualitative and semi-quantitative analysis while maintaining the microstructure of the sample. This method, due to its high sensitivity, non-destructive nature, and high spatial resolution, is widely applied in micro-area composition analysis and is suitable for foreign substance identification and particle component analysis.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Based on an advanced microscopic infrared spectroscopy platform, MtoZ Biolabs has launched the microscopic infrared spectroscopy analytical service, which enables spectral acquisition and compositional analysis of samples at the micron scale. By analyzing the characteristic absorption signals of samples in the infrared region, their molecular composition, chemical functional group characteristics, and distribution differences can be revealed. The service ultimately provides clear infrared spectral curves and visual imaging data, helping researchers achieve micro-area composition tracing, particle component identification, and complex sample structural analysis in biomedical research.
Analysis Workflow
1. Sample Preparation
Prepare and pretreat samples such as cells, tissue sections, films, or particles according to research requirements to ensure uniformity and representativeness.
2. Microscopic Positioning
Accurately locate the target area under the microscope to achieve observation and detection at the micron scale.
3. Spectral Acquisition
Use a microscopic infrared spectrometer to collect infrared absorption signals across different wavelength ranges and obtain characteristic spectra of the sample.
4. Data Processing
Process the acquired spectral data with background subtraction, baseline correction, and signal optimization to ensure accurate and reliable results.
5. Result Output
Generate complete infrared spectral curves and composition analysis reports, directly displaying molecular composition, functional group characteristics, and spatial distribution information.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Type
Suitable for tissue sections, cells, films, and particle samples, which should be uniform and representative. For powders or particle samples, it is recommended to press them into pellets or fix them on an appropriate substrate to facilitate spectral analysis.
2. Sample Purity
It is recommended to minimize impurities and contaminants to avoid interference with infrared signals, which could affect the accuracy of composition determination.
3. Sample Storage
Samples should be stored in dry, dark, and low-temperature conditions to prevent moisture absorption, oxidation, or light exposure that may alter their chemical properties and structure.
4. Sample Transport
During transportation, sealed containers should be used. If necessary, cold-chain transport should be applied to ensure the stability and integrity of the samples before reaching the analytical platform.
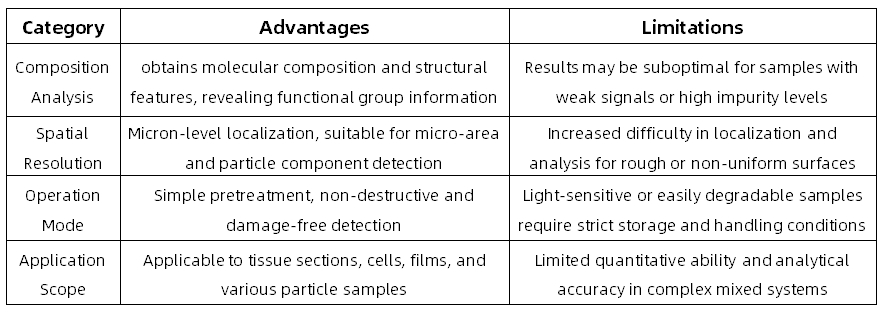
Advantages and Limitations
Applications
1. Tissue and Cell Analysis
The microscopic infrared spectroscopy analytical service can be used for micro-area composition detection of tissue sections and cell samples, helping to study molecular composition and local structural differences.
2. Foreign Substance Identification
By rapidly identifying unknown particles or impurities in biological samples or pharmaceutical preparations, their chemical properties can be determined.
3. Particle Component Detection
Through the analysis of tiny particles in drug, blood, or tissue samples, potential sources and compositions can be revealed.
4. Drug and Formulation Research
The microscopic infrared spectroscopy analytical service can be applied to functional group analysis and stability studies of pharmaceutical raw materials, excipients, and formulations, supporting quality control.
FAQs
Q1: What Is the Difference Between Microscopic Infrared Spectroscopy and Conventional Infrared Spectroscopy?
A1: Conventional infrared spectroscopy is mainly used for overall composition and structural analysis of samples, while microscopic infrared spectroscopy, combined with microscopy, can perform compositional analysis in the micron-scale range of specific areas, making it suitable for micro-area detection of heterogeneous samples.
Q2: Will the Detection Damage the Sample?
A2: Microscopic infrared spectroscopy is a non-destructive detection method and generally does not cause substantial damage to samples. However, for light-sensitive or easily degradable samples, storage and operating conditions should still be carefully managed.
Q3: What Factors May Affect the Detection Results?
A3: Uneven sample thickness, high levels of impurities, rough surfaces, or background interference may all affect the results. Therefore, it is recommended to strictly control quality during sample preparation and storage.
How to order?







