Micropore Measurement Analysis Service
Micropore Measurement is an important method used to characterize the micropore structural features of materials, capable of accurately obtaining parameters such as pore size, distribution, and specific surface area. Its basic principle is to measure the volume and morphological characteristics of micropores in the sample through techniques such as gas adsorption–desorption, mercury intrusion, or flow analysis, thereby revealing the physical properties and permeability of the pores. Micropore structures play a decisive role in the adsorption, catalysis, diffusion, and separation properties of materials, and are widely applied in various studies, including catalysts, controlled drug delivery, as well as energy conversion and storage.
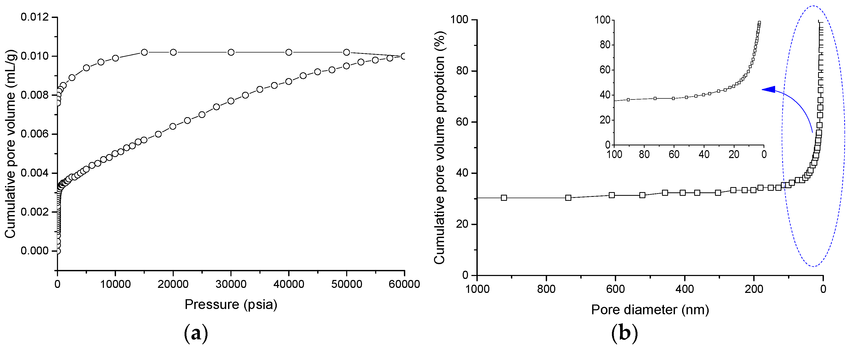
Pan, D J. et al. Applied Sciences, 2017.
Figure 1. Micropore Size Analysis.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Based on a high-performance micropore analysis platform, MtoZ Biolabs has launched the micropore measurement analysis service capable of accurately analyzing the pore structure and distribution characteristics of porous materials. The service primarily employs N₂ adsorption and CO₂ adsorption, suitable for micropore measurement with diameters less than 2 nm. By monitoring the adsorption and desorption processes of gases within the sample pores, key data such as pore size, distribution range, specific surface area, and pore volume can be obtained. The final output includes complete pressure–flow relationships and pore size distribution curves, providing reliable support for structural characterization and performance evaluation of films, filter media, biomembranes, and related porous matrices.
Analysis Workflow
1. Sample Preparation
Pretreat the sample to ensure surface uniformity and remove impurities, while performing wetting to facilitate smooth gas displacement.
2. Gas Adsorption
Use nitrogen or carbon dioxide adsorption methods, selecting the appropriate gas according to pore size range, for precise micropore structure measurement.
3. Pressurization and Displacement
Gradually increase the gas pressure to overcome the capillary action of the liquid, progressively opening the pores and displacing the liquid within.
4. Flow and Data Acquisition
Record changes in pressure and gas flow in real time to capture key signals during pore opening, generating pressure–flow curves and adsorption–desorption isotherms.
5. Result Analysis
Perform model fitting to output pore size distribution maps, specific surface area, and pore volume parameters, thereby revealing the micropore structural characteristics of the sample.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Types
Applicable to films, filter membranes, porous materials, and biologically related matrices. Samples must be uniform and representative to ensure accurate measurement results.
2. Sample Purity
It is recommended to remove impurities and moisture to avoid interference with gas adsorption and desorption signals, which may affect the analysis of pore size and specific surface area.
3. Sample Storage
Samples should be stored under dry, dark, and appropriate temperature conditions to prevent moisture absorption, oxidation, or light exposure that may alter structure and performance.
4. Sample Transportation
Samples must be transported in sealed containers, and if necessary, accompanied by desiccants or under cold chain conditions to ensure integrity and stability before reaching the testing platform.
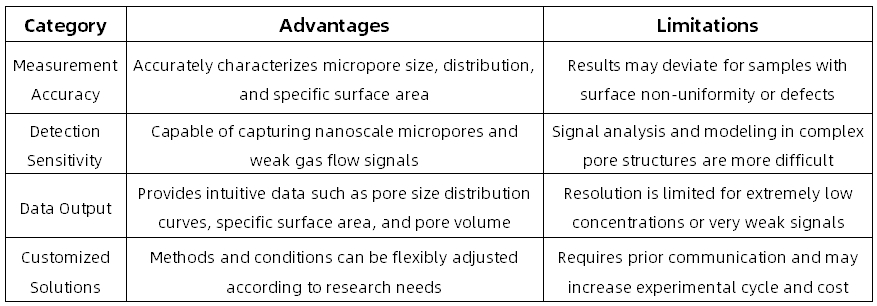
Advantages and Limitations
Applications
1. Cell Microenvironment Research
Through micropore characteristic analysis, the pore structure of cell culture matrices or scaffolds is revealed, supporting studies of cell adhesion, migration, and proliferation.
2. Biomembrane Permeability Detection
Micropore measurement analysis service can be used to characterize the pore size properties of natural or artificial biomembranes, evaluating their role in substance exchange and barrier function.
3. Nutrient and Molecular Transport Research
By analyzing the pore characteristics of porous materials in liquid or gas environments, their role in molecular diffusion, nutrient transport, and metabolic regulation can be evaluated.
4. Biological Sample Storage and Transport Research
Micropore measurement analysis service can be used to detect the pore performance of porous matrices, assessing their suitability in the preservation and transport of biological samples.
FAQ
Q1: Will the Test Damage the Sample?
A1: In general, this method is considered non-destructive and does not alter the overall structure of the sample, but some fragile materials may be slightly affected during testing.
Q2: Does It Support Customized Experimental Conditions?
A2: Yes. Depending on the research needs, the type of adsorption gas, temperature, and pressure range can be adjusted to meet different samples and research objectives.
Q3: Can It Be Used for Liquid Samples?
A3: This method is mainly applicable to solid samples or solid matrices. It is not suitable for liquids, which need to be prepared into an appropriate solid carrier first.
How to order?







