Mass Spectrometry Identification Service
Mass spectrometry identification measures the mass-to-charge ratio of molecules to analyze, quantify, and identify substances. Mass spectrometry is based on ionizing the sample and analyzing the ions according to their mass-to-charge ratio, providing information about the molecular weight, sequence, and structural features of the molecules. Mass spectrometry identification can solve the qualitative and quantitative challenges posed by complex samples that traditional methods struggle with, especially in proteomics, metabolomics, and drug development. It enables precise identification of proteins, metabolites and ADC, supporting research into disease mechanisms, target screening, and biomarker discovery.
Different samples require specific mass spectrometry techniques for identification in order to improve the accuracy and precision of identification. The more commonly used types of mass spectrometers in mass spectrometry identification are:
1. Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (TOF-MS)
TOF-MS conducts mass analysis based on the differences in flight times of ions in a vacuum, featuring high resolution and high mass accuracy. TOF-MS is commonly combined with electrospray ionization (ESI), suitable for analyzing biomacromolecules such as proteins, peptides, nucleic acids, and polysaccharides. Alternatively, when TOF-MS combines with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI), it can be used for high molecular weight and thermally unstable compounds.
2. Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry (Quadrupole MS)
Quadrupole MS employs an electric field generated by four parallel electrodes to filter ions by mass. It is commonly used for quantitative analysis and screening of target compounds.
3. Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry (Orbitrap MS)
Orbitrap MS utilizes the orbital motion characteristics of ions in an electrostatic field for mass analysis, combining high resolution with high mass accuracy. It is suitable for precise qualitative and quantitative analyses.
4. Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance Mass Spectrometry (FT-ICR MS)
FT-ICR MS utilizes a magnetic field to induce cyclotron motion of ions and employs Fourier transform to obtain mass spectrometry information. It offers extremely high resolution and is suitable for detailed analysis of complex samples.
The table below summarizes the mass analyzers commonly used in mass spectrometry identification and their corresponding characteristics.
Table 1. Commonly Used Mass Analyzers in Mass Spectrometry Identification
Jiang, Y. et al. ACS Meas Sci Au. 2024.
Service at MtoZ Biolabs
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider, provides advanced proteomics, metabolomics, and biopharmaceutical analysis services to researchers in biochemistry, biotechnology, and biopharmaceutical fields. MtoZ Biolabs offers professional mass spectrometry identification service characterized by advanced equipment and instruments, which includes Thermo Fisher Q Exactive HF and Orbitrap Fusion Lumos mass analyzer system, coupled with Nano-LC system. In the fields of proteomics, metabolomics, and small molecule compound identification, we have accumulated a wealth of successful cases. We offer high-quality and reliable mass spectrometry identification solutions to meet the diverse needs of both research and industry. If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us—we are dedicated to serving you.
1. Protein Mass Spectrometry Identification
The procedure of protein mass spectrometry identification involves digesting proteins into peptides, which are then separated, fragmented, ionised, and captured by mass spectrometers.
Kolker, E. et al. Trends Microbiol. 2006.
Figure 1. Workflow of Protein Mass Spectrometry Identification
2. Peptide Mass Spectrometry Identification
The peptide mass spectrometry identification process involves sample preparation, enzymatic digestion, ionization, and mass analysis. First, proteins are extracted from the sample and digested into peptides using enzymes like trypsin. The peptides are then ionized using techniques such as electrospray ionization (ESI) or MALDI, and introduced into the mass spectrometer for analysis. In the mass spectrometer, peptides are separated based on their mass-to-charge ratios (m/z) and fragmented. The resulting fragment ions are used to infer the peptide sequence, enabling the identification and quantification of proteins.
Smith, IR. et al. Anal Chem. 2022.
Figure 2. Workflow of Peptide Mass Spectrometry Identification
3. Antibody-Drug-Conjugate Mass Spectrometry Identification
The ADC mass spectrometry identification process begins with sample preparation to extract the ADC complex, followed by enzymatic digestion or chemical cleavage to break it into smaller peptides and drug molecules. The sample is then ionized using techniques such as electrospray Ionization (ESI) or matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI). The ions are separated based on their mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) in the mass spectrometer, and fragmentation techniques are used to obtain structural information on both the peptides and the drug molecules. Finally, data analysis and database comparison enable the identification of the ADC's molecular composition, drug loading, and linker structure.
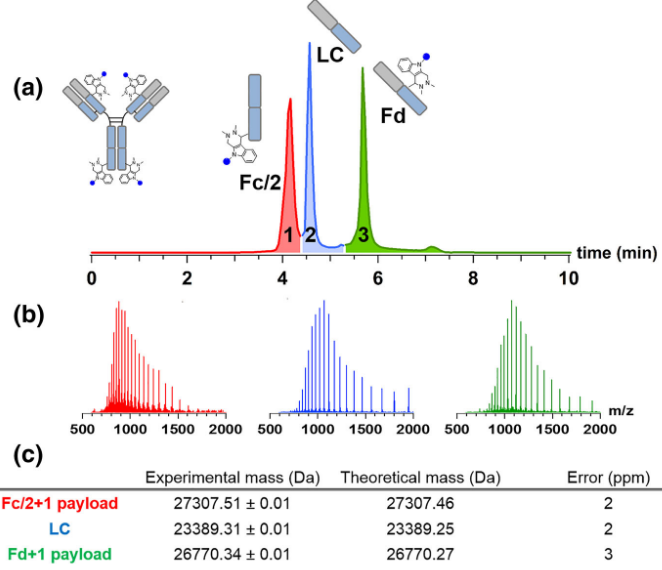
Hernandez-Alba, O. et al. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2019.
Figure 3. Workflow of Antibody-Drug-Conjugate Mass Spectrometry Identification
Service Advantages
1. Advanced Instrumentation: MtoZ Biolabs is equipped with high-end mass spectrometers that provide high sensitivity and high-resolution detection capabilities. This effectively addresses the challenge of detecting low-abundance target substances and improves identification accuracy.
2. Professional Technical Team: The company boasts an experienced team of scientists and technicians who are proficient in handling complex samples and data analysis techniques. They can solve challenges related to data complexity and spectrum interpretation, providing reliable identification results.
3. Optimized Sample Preparation Processes: MtoZ Biolabs utilizes advanced sample preparation and pretreatment methods to reduce matrix effects and ionization efficiency differences. This ensures effective identification of target compounds and enhances the accuracy of qualitative and quantitative results.
4. Extensive Databases and Standard Libraries: MtoZ Biolabs has comprehensive mass spectrometry databases and standard libraries, supporting accurate identification of isomers and novel compounds. This overcomes the limitations caused by the lack of standards and databases.
FAQ
1. During the sample preparation process, what factors can lead to experimental failure and affect the reproducibility of mass spectrometry identification?
Incomplete protein lysis and solubilization can result in insufficient extraction of target substances, affecting detection results. Contamination during sample handling, especially from compounds in detergents and low-quality plastics, can interfere with mass spectrometry analysis, causing signal suppression or instrument contamination. Common environmental contaminants like keratins (from skin and dust) can also consume detection time in mass spectrometry, reducing the acquisition of useful data. Additionally, the numerous and time-consuming sample preparation steps can easily introduce biases and losses, impacting the reproducibility of the experiment. Therefore, strictly controlling the sample preparation process, preventing contamination, and optimizing handling methods are crucial for ensuring the success and reproducibility of mass spectrometry identification.
Deliverables
1. Comprehensive Experimental Details
2. Materials, Instruments, and Methods
3. Relevant Liquid Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry Parameters
4. The Detailed Information of Mass Spectrometry Identification
5. Mass Spectrometry Image
6. Raw Data
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
Mass Spectrometry-Based Protein Identification Service
How to order?







