Malonylation Proteomics Analysis Service
- HCD (Higher-Energy Collision Dissociation): Effectively fragments peptides, generating rich b/y ions. However, malonylation is prone to neutral loss, potentially leading to the loss of modification site information.
- ETD (Electron Transfer Dissociation): Preserves malonylation modifications while promoting peptide backbone cleavage. Suitable for precise localization of modification sites.
- EThcD (ETD Combined with HCD): Combines the advantages of ETD and HCD, balancing modification protection with high peptide coverage. Currently, it is the most effective strategy for detecting malonylation modifications.
Malonylation Proteomics Analysis Service is designed for the identification and quantification of malonylated proteins across the proteome. Protein malonylation is a reversible post-translational modification (PTM) in which a malonyl group is covalently attached to the lysine residues of substrate proteins under enzymatic regulation. Since lysine residues are positively charged, malonylation converts this positive charge to a negative charge, which in turn affects protein conformation and protein-protein interactions. Malonylation plays a significant role in metabolic processes, particularly in energy metabolism and photosynthesis, impacting fatty acid synthesis, mitochondrial respiration, glycolysis, plant stress resistance, inflammatory responses, and type 2 diabetes. Beyond its critical regulatory functions in eukaryotic cells, malonylation also serves as an important metabolic regulation mechanism in prokaryotic organisms. Leveraging an advanced mass spectrometry platform, MtoZ Biolabs offers Malonylation Proteomics Analysis Service for the precise identification and quantification of malonylation-modified proteins, assisting researchers in exploring the role of malonylation in metabolic regulation, disease pathogenesis, and drug discovery.
Analysis Workflow
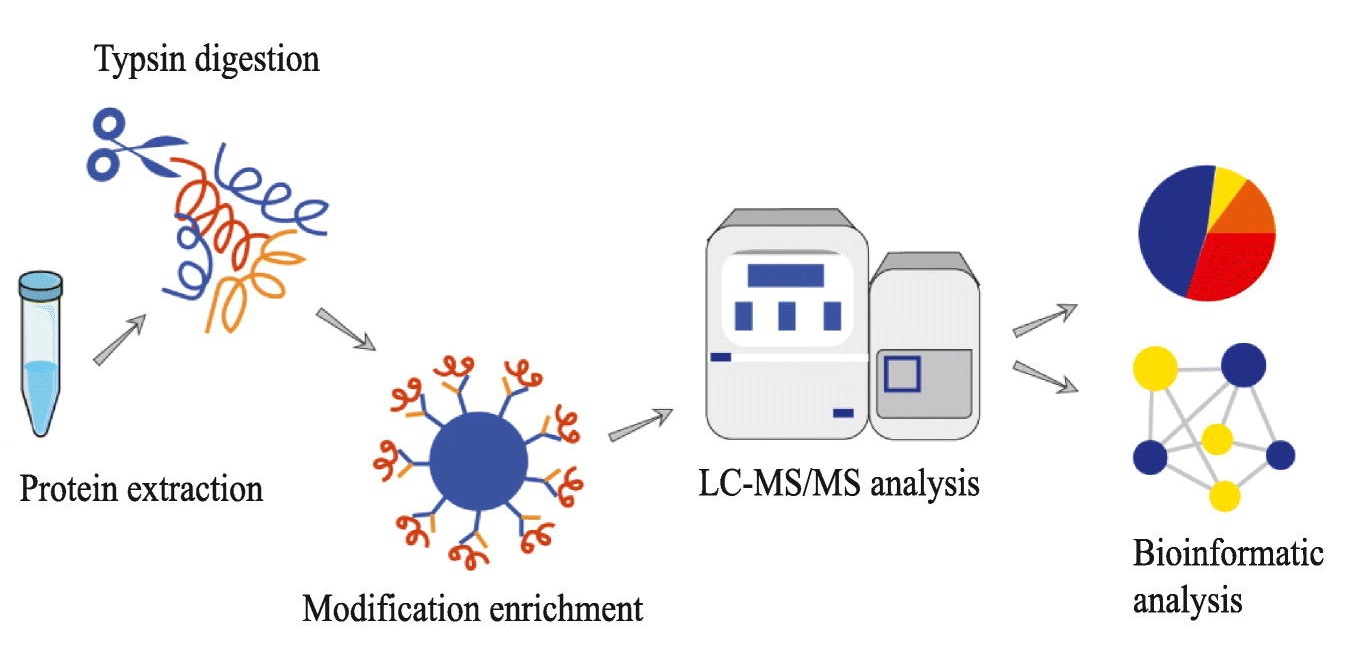
Liao Z. et al. Journal of proteomics. 2023.
1. Sample Preparation
Extract total protein and perform preprocessing.
Digest proteins using trypsin or Lys-C to generate peptides.
2. Malonylated Peptide Enrichment
Enrich malonylated peptides using specific antibodies or affinity chromatography methods.
3. Mass Spectrometry Analysis
Analyze peptides using nano-LC coupled with high-resolution mass spectrometry.
4. Data Analysis
Perform protein identification, malonylation site mapping, quantitative analysis, and bioinformatics analysis.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry (MS) Services Provider, provides advanced proteomics, metabolomics, and biopharmaceutical analysis services to researchers in biochemistry, biotechnology, and biopharmaceutical fields. Our ultimate aim is to provide more rapid, high-throughput, and cost-effective analysis, with exceptional data quality and minimal sample consumption. Leveraging advanced chromatography and mass spectrometry platforms, MtoZ Biolabs provides Malonylation Proteomics Analysis Service offering both qualitative and quantitative analysis of malonylated proteins. In addition, we offer a comprehensive range of post-translational modification (PTM) proteomics services, including phosphorylation, glycosylation, acetylation, ubiquitination, and more.
Applications
Metabolic Regulation Research
Helps elucidate how malonylation regulates glycolysis, the TCA cycle, and lipid metabolism.
Epigenetics
Malonylation Proteomics Analysis Service can be used to investigate the role of malonylation in histone modifications and gene expression regulation.
Disease Mechanism and Drug Target Research
Identifies the role of malonylated proteins in disease progression.
Detects disease-associated malonylated proteins, facilitating the discovery of potential biomarkers and drug targets.
FAQ
Q. How to Optimize Mass Spectrometry Fragmentation Modes to Improve the Accuracy of Malonylation Modification Identification?
The identification of malonylation modifications primarily relies on LC-MS/MS (liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry). However, due to the high polarity and dicarboxyl functional group of malonylation, it is prone to modification loss during fragmentation, affecting the precise localization of modification sites. Therefore, optimizing fragmentation modes is crucial:
Case Study
This study utilized Malonylation Proteomics Analysis to map the lysine malonylation landscape in Toxoplasma gondii. The results demonstrated that malonylation is widely present in glycolysis, the TCA cycle, energy metabolism, and ribosomal proteins, suggesting its potential role in parasite metabolic regulation and host adaptation. This study represents the first comprehensive characterization of Kmal modifications in the proteome of a parasite, providing critical data for further exploration of parasite metabolic regulation mechanisms and the identification of potential anti-infective targets.
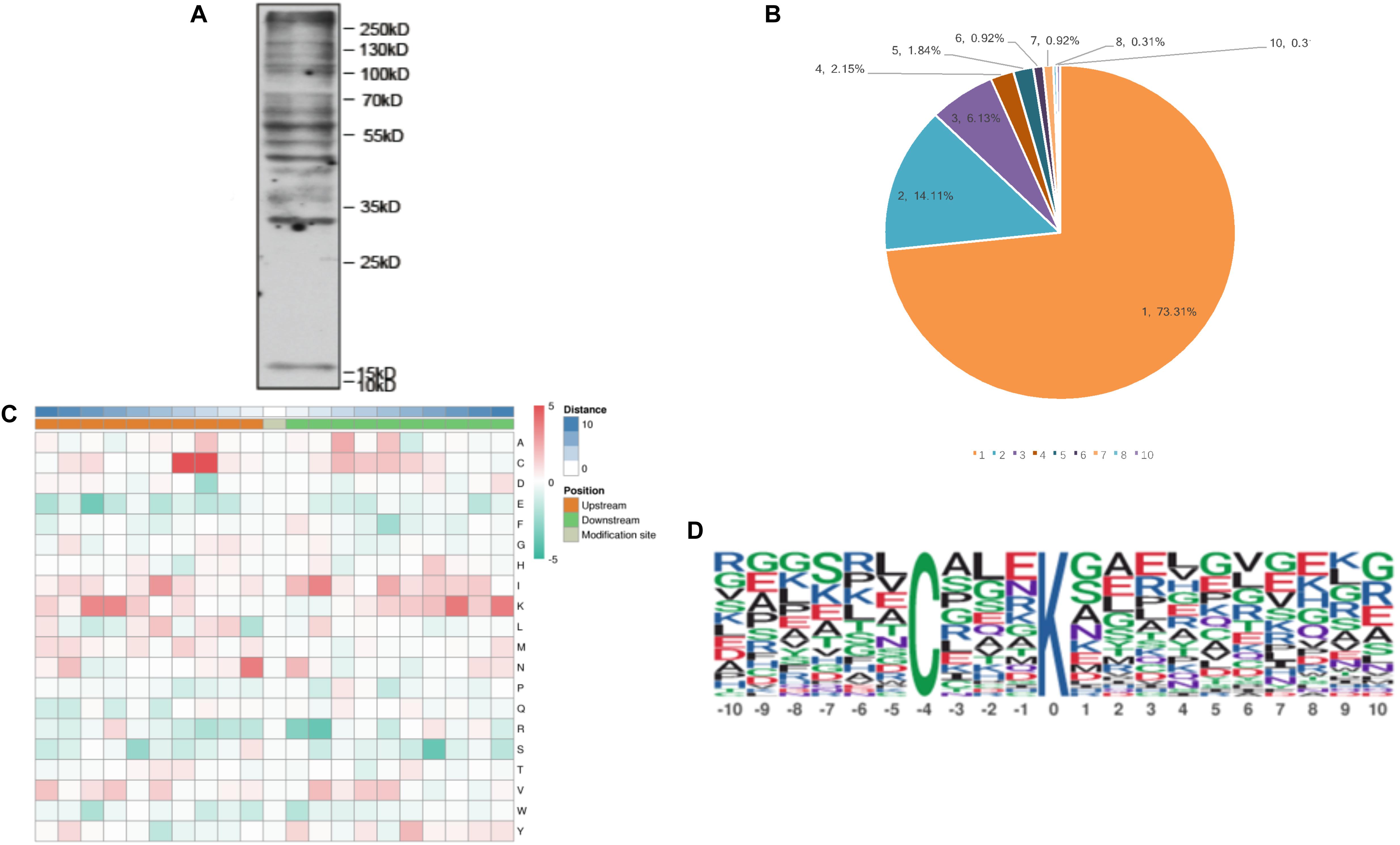
Nie L B. et al. Frontiers in Microbiology. 2020.
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
How to order?







