Label-free Exosomal Proteomic Detection Service
- Disease diagnosis and monitoring (e.g., tumor biomarker discovery)
- Disease mechanism research (e.g., cancer, autoimmune diseases, neurodegenerative diseases)
- Cellular biology research (e.g., cell communication mechanisms)
Label-free Exosomal Proteomic Detection Service employs label-free quantitative proteomics technology to perform qualitative and relative quantitative analysis of the exosomal proteome. Exosomes are nanoscale extracellular vesicles secreted by cells that carry various functional molecules, including proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, and are widely involved in intercellular communication, signal transduction, immune regulation, and other essential biological processes. Studying exosomal proteins helps reveal cellular physiological states, pathological changes, and intercellular interactions. Label-free quantification is a widely used technique in mass spectrometry-based analysis that allows for the identification and relative quantification of proteins in biological samples without the need for isotope or chemical labeling. Compared with labeled methods, label-free quantitative technology is more flexible and suitable for analysis of various sample types and the presence or absence of differential proteins. Leveraging a high-resolution mass spectrometry platform, MtoZ Biolabs offers Label-free Exosomal Proteomic Detection Service to qualitatively and quantitatively analyze exosomal protein composition, enabling the identification of exosome-specific proteins, differentially expressed proteins, and their potential biological functions.
Technical Principles
Label-free quantitative proteomics primarily utilizes two strategies for quantification:
1. Spectral Counting: This method infers the relative abundance of a protein in a sample by counting the number of spectra produced by that protein in mass spectrometry analysis.
2. Chromatographic Peak Area Measurement: By measuring the chromatographic peak area of all peptide segments of a protein in the MS1 (first stage mass spectrometry), the average intensity is calculated, which in turn is used to infer the abundance of the corresponding protein.
Analysis Workflow
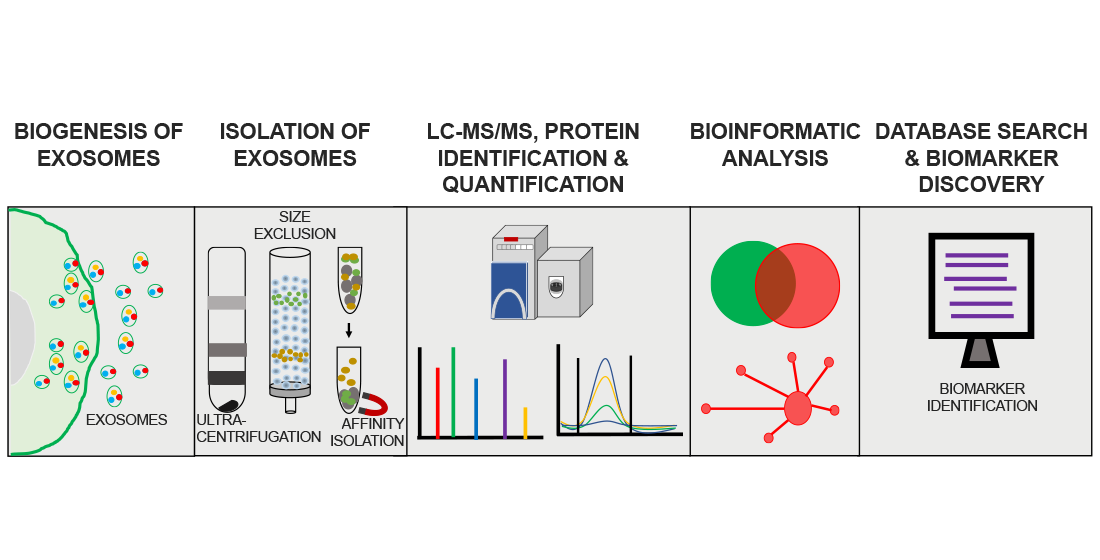
Mathew B. et al. Brain Sciences. 2021.
1. Sample Preparation and Exosome Isolation
Select appropriate methods based on project requirements to extract high-purity exosomes. Perform quality verification of the exosomes.
2. Exosomal Protein Extraction and Digestion
Extract exosomal proteins and digest them to obtain peptide segments.
3. Mass Spectrometry Detection
Use high-performance liquid chromatography and high-resolution mass spectrometry to analyze the peptides.
4. Data Analysis and Report
Use specialized software to analyze the mass spectrometry data, perform protein identification, quantification, and bioinformatics analysis. Provide a detailed report.
Service Advantages
1. Short Experimental Cycle: No need for expensive isotope labeling reagents.
2. High Flexibility: No sample quantity limitations and suitable for various sample types.
3. Advanced Analysis Platform: MtoZ Biolabs established an advanced Label-free Exosomal Proteomic Detection Service platform, guaranteeing reliable, fast, and highly accurate analysis service.
4. One-Time-Charge: Our pricing is transparent, no hidden fees or additional costs.
5. High-Data-Quality: Deep data coverage with strict data quality control. AI-powered bioinformatics platform integrates all Label-free Exosomal Proteomic Detection Service data, providing clients with a comprehensive data report.
Applications
Examples of applications for the Label-free Exosomal Proteomic Detection Service include:
FAQ
Q. What is the Sensitivity, Accuracy, and Reproducibility of the Label-free Method in Exosomal Proteomics Analysis? How does it Compare to Label-based Methods (e.g., TMT, iTRAQ)?
The label-free method offers relatively high sensitivity in exosomal proteomics analysis and can detect a large number of proteins, but its quantification accuracy for low-abundance proteins is slightly lower than that of label-based methods. With proper experimental standardization and quality control, the reproducibility of the Label-free method is generally good. Compared to label-based methods (such as TMT and iTRAQ), the label-free method offers several advantages: no need for expensive labeling reagents, fewer sample requirements, simpler protocols, and higher throughput. However, its drawbacks include slightly lower quantification accuracy and slightly lower data stability and quantitative consistency between batches.
Deliverables
1. Comprehensive Experimental Details
2. Materials, Instruments, and Methods
3. Total Ion Chromatogram & Quality Control Assessment (project-dependent)
4. Data Analysis, Preprocessing, and Estimation (project-dependent)
5. Bioinformatics Analysis
6. Raw Data Files
Case Study
This study employed label-free exosomal proteomics to analyze exosomal proteins in the urine of bladder cancer patients, aiming to identify potential biomarkers associated with bladder cancer. Through quantitative analysis of the exosomal proteins, the study identified several key protein markers that can distinguish bladder cancer patients from healthy individuals. The results demonstrated that these biomarkers exhibit high diagnostic sensitivity and specificity, offering valuable potential for early diagnosis and monitoring of bladder cancer.
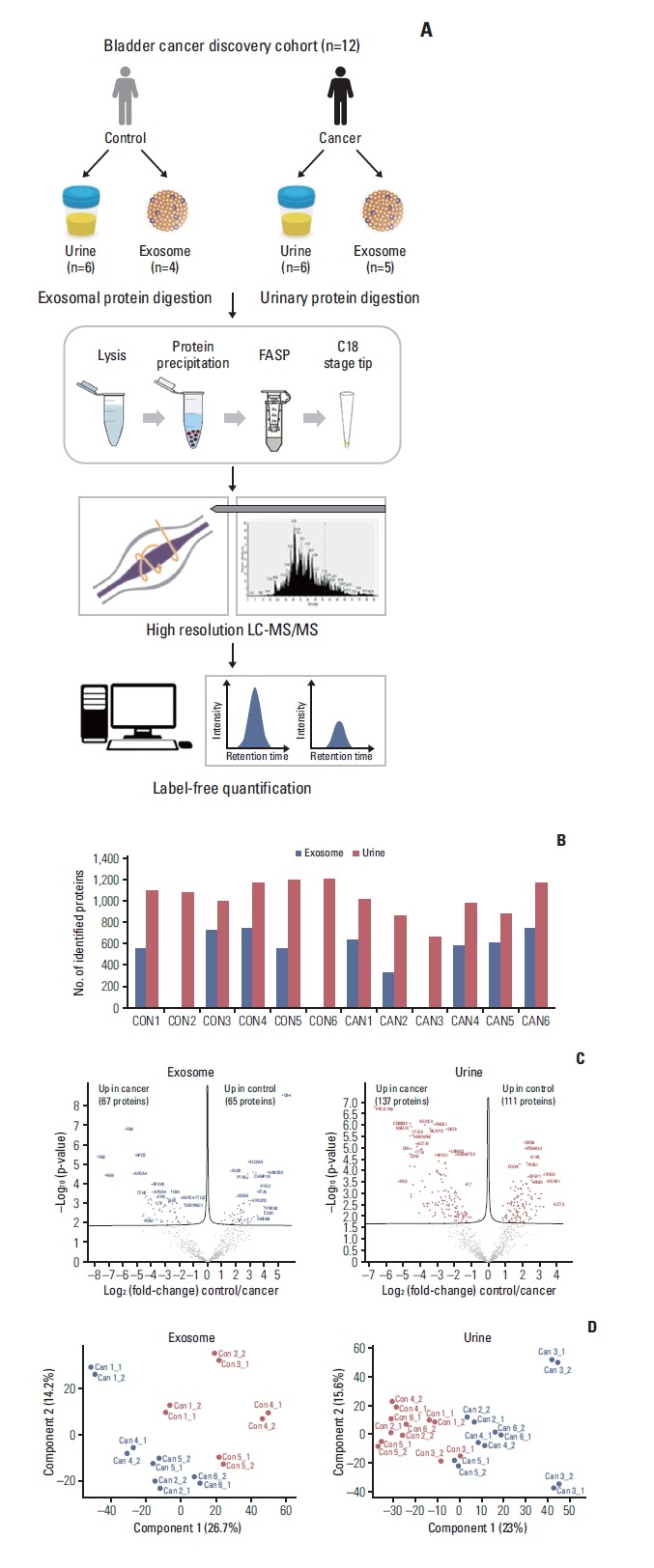
Suh J. et al. Cancer Res Treat. 2022.
How to order?







