Kynurenine Pathway-Mediated Tryptophan Metabolism analysis service
- For enzyme activity assays, fresh tissue or freshly prepared cell lysates are preferred.
- For cell culture supernatants, the media should not contain phenol red to avoid interference with mass spectrometry.
Tryptophan metabolism plays a central role in immune regulation, neurobiology, and cancer biology, with over 90% of dietary tryptophan being catabolized via the kynurenine pathway (KP). This pathway produces a variety of bioactive metabolites, including kynurenine (KYN), kynurenic acid (KYNA), 3-hydroxykynurenine (3-HK), quinolinic acid (QA), and picolinic acid (PA), which are implicated in immune escape, neuroinflammation, and redox imbalance. Dysregulation of KP-mediated tryptophan metabolism has been associated with numerous pathological conditions, such as cancer, major depressive disorder, Alzheimer’s disease, and autoimmune diseases.
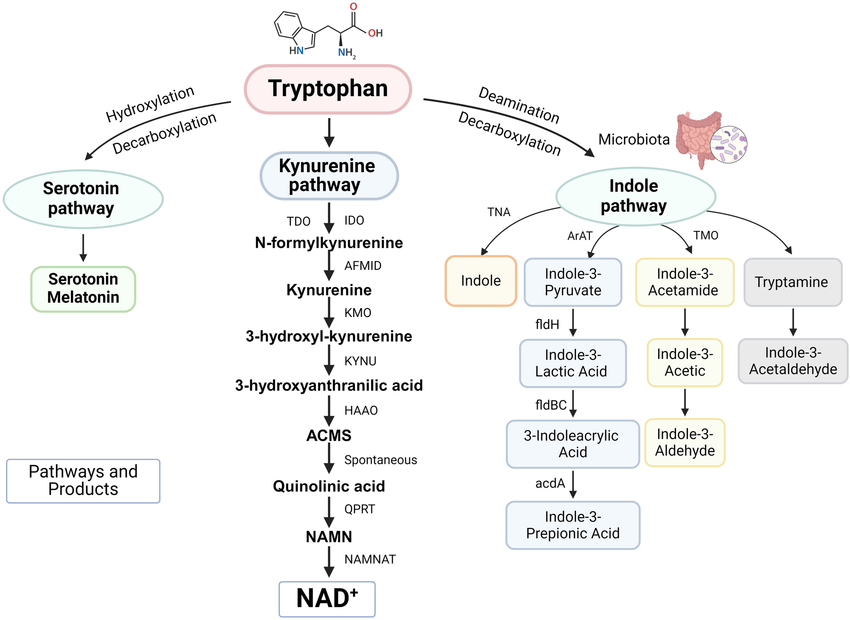
Ren C, et al. FASEB J. 2024.
Figure1. Primary Metabolic Pathways of Tryptophan
Service at MtoZ Biolabs
MtoZ Biolabs offers a comprehensive kynurenine pathway-mediated tryptophan metabolism analysis service based on high-sensitivity LC-MS/MS platforms. Our service enables precise quantification of tryptophan catabolites and profiling of key enzymes such as indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO1/2), tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (TDO), and kynurenine aminotransferases (KATs). This service supports studies in immunometabolism, disease biomarker discovery, drug mechanism validation, and therapeutic response monitoring.
Kynurenine pathway-mediated tryptophan metabolism analysis service at MtoZ Biolabs
1)Kynurenine Pathway Metabolite Profiling
Quantification of key metabolites including tryptophan, kynurenine, 3-hydroxykynurenine, kynurenic acid, and quinolinic acid.
2)Enzyme Activity and Expression Analysis
Assessment of the activity and expression levels of critical enzymes such as IDO1, IDO2, TDO, and KATs using LC-MS/MS-based proteomics or enzyme-linked assays.
3)Metabolic Pathway Mapping
Integration of data into comprehensive pathway analyses, identifying key metabolic disruptions in disease conditions.
4)Disease-Specific Metabolic Profiling
Profiling of kynurenine pathway metabolites in various disease models (e.g., cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, autoimmune disorders).
Why Choose MtoZ Biolabs?
Precise Quantification: High-sensitivity LC-MS/MS ensures accurate measurement of kynurenine metabolites at low concentrations, even in complex samples.
Pathway-Level Analysis: In-depth profiling of kynurenine metabolites and enzymes provides comprehensive insights into metabolic shifts and dysregulation in disease.
Tailored Multi-Omics Solutions: Integration with proteomics and transcriptomics enhances understanding of the kynurenine pathway's role in disease mechanisms and treatment responses.
Versatile Sample Compatibility: Supports analysis of diverse biological samples (e.g., serum, tissue, urine) for flexible experimental designs.
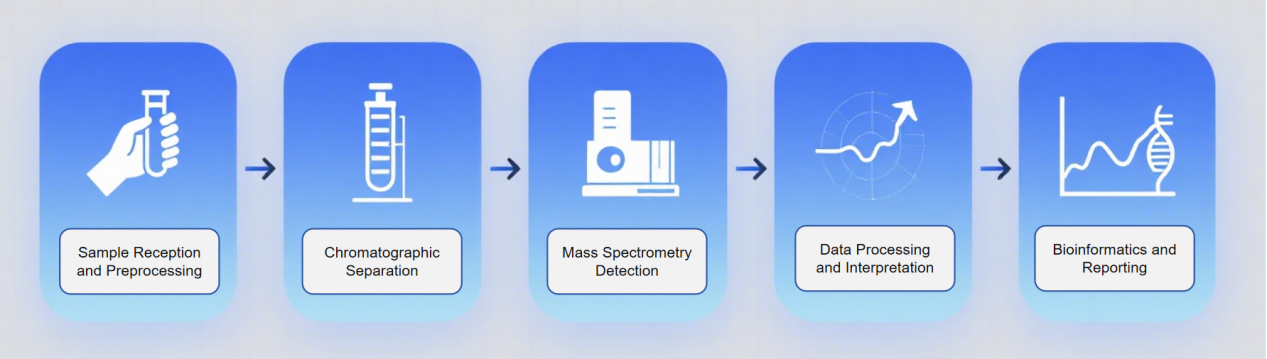
Analysis Workflow
Sample Submission Suggestions
Serum/Plasma: ≥200 µL
Tissue (solid): ≥200 mg
Urine: 500 µL
Cell Culture Supernatants: ≥2 mL
CSF: ≥200 µL
Saliva: ≥2 mL
Fecal Samples: ≥200 mg
Additional Notes:
Applications
✅ Cancer Research: Profiling kynurenine metabolites in tumor microenvironments to study immune escape and therapeutic response.
✅ Neurodegenerative Diseases: Investigating kynurenine metabolites' role in neuroinflammation and neuroprotection in diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
✅ Immunology: Understanding how tryptophan metabolism affects immune modulation in autoimmune diseases or chronic inflammation.
✅ Drug Development: Identifying metabolic biomarkers and assessing drug efficacy in modulating the kynurenine pathway.
✅ Clinical Diagnostics: Exploring kynurenine pathway biomarkers for monitoring disease progression or treatment responses.
Deliverables
Detailed Report: Comprehensive metabolite quantification, pathway analysis, and enzyme activity data.
Raw Data Files: Mass spectrometry data files (e.g., mzML, mzXML) for further analysis.
Bioinformatics Analysis: Pathway maps, metabolic flux analysis, and correlation with disease markers or therapeutic outcomes.
How to order?







