Insect Cell Glycosylation Patterns Analysis Service
Insect Cell Glycosylation Patterns Analysis Service is a specialized service based on high-resolution mass spectrometry and glycan enrichment techniques, designed to systematically identify and characterize N-linked and O-linked glycosylation types, glycan structures, linkage patterns, and glycosylation distribution features in proteins expressed by insect cells.
Glycosylation is one of the most critical post-translational modifications affecting the quality, functionality, and immunogenicity of recombinant proteins. Insect cell expression systems are widely used in the production of vaccines, virus-like particles (VLPs), gene therapy vectors, and therapeutic proteins due to their advantages in high expression yield, low cost, and suitability for complex protein production. However, compared to mammalian cells, insect cells exhibit distinct glycosylation mechanisms, including: simplified glycan structures, predominantly high-mannose or short-branched complex types; lack of sialylation capability; and potential presence of immunogenic non-human glycans such as α1,3-fucose. These differences may affect the stability and biological activity of the target protein and potentially trigger undesired immune responses. Therefore, systematic evaluation and monitoring of glycosylation patterns in insect cell-derived proteins are essential for ensuring vaccine safety, formulation consistency, and biosimilarity assessment.
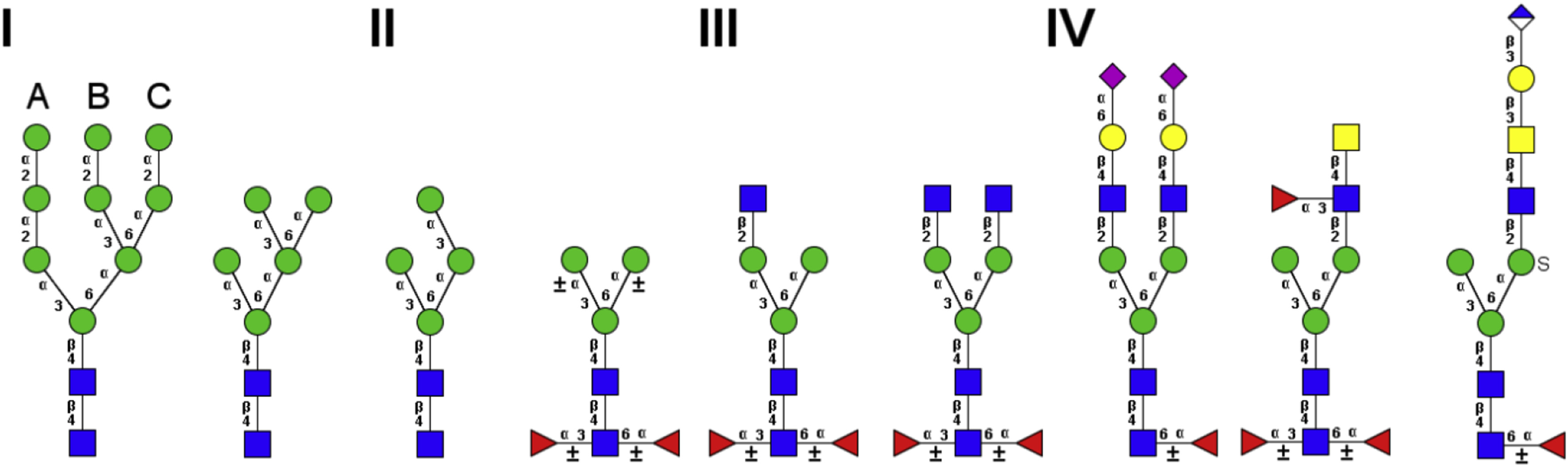
Walski T. et al. Insect Biochem Molec. 2017.
Figure 1. N-glycan types present in insects.
Leveraging advanced mass spectrometry and chromatography platforms, MtoZ Biolabs offers the Insect Cell Glycosylation Patterns Analysis Service enabling systematic characterization of N-linked and O-linked glycosylation types, glycan structures, and distribution features in proteins expressed by insect cells. This service identifies non-human glycan residues, evaluates glycan differences across expression systems, and supports vaccine development, vector assessment, and process consistency control.
Analysis Workflow
The main workflow of the Insect Cell Glycosylation Patterns Analysis Service is as follows:
1. Sample Preparation
Extract the target protein and perform pretreatment steps such as concentration and buffer optimization.
2. Digestion and Glycan Release
Digest the target protein using enzymes such as trypsin, followed by glycan release for structural analysis.
3. Enrichment and Derivatization of Glycopeptides or Glycans
Select appropriate enrichment methods, such as lectin affinity or HILIC, to isolate glycosylated components of interest.
4. Mass Spectrometry Detection and Data Acquisition
Perform LC-MS/MS analysis using a high-resolution mass spectrometry platform to obtain high-quality spectra.
5. Structural Annotation and Data Analysis
Use specialized software to identify glycan structures, classify glycan types, quantify abundance, and compare results across samples.
Applications
Biotherapeutic Development
Analyze glycosylation patterns in insect cell-expressed proteins to optimize therapeutic efficacy, pharmacokinetics, and immunogenicity.
Vaccine Production
Ensure consistency and reproducibility of antigen glycosylation profiles to maintain vaccine effectiveness and safety.
Functional Protein Research
Elucidate the functional consequences of specific glycan structures and clarify the roles of glycosylation in protein–protein interactions, signaling pathways, and cellular processes.
Service Advantages
1. Advanced Analysis Platform: MtoZ Biolabs established an advanced Insect Cell Glycosylation Patterns Analysis Service platform, guaranteeing reliable, fast, and highly accurate analysis service.
2. One-Time-Charge: Our pricing is transparent, no hidden fees or additional costs.
3. High-Data-Quality: Deep data coverage with strict data quality control. AI-powered bioinformatics platform integrates all Insect Cell Glycosylation Patterns Analysis Service data, providing clients with a comprehensive data report.
4. Customized Service: Provide personalized analysis solutions and reports according to customer needs.
FAQ
Q. Can Insect Cell-Specific Non-Human Glycan Residues such as α1,3-Fucose and β1,2-Xylose be Accurately Identified?
Yes. MtoZ Biolabs utilizes high-resolution LC-MS/MS platforms combined with glycan derivatization techniques (e.g., permethylation) and structural database matching to accurately detect insect-specific glycan residues such as α1,3-fucose and β1,2-xylose. In addition, enrichment strategies (e.g., lectin-based selection) and specific fragmentation modes (e.g., CID/HCD) can enhance the sensitivity for identifying these immunogenic structures.
Q. Can You Provide Comparative Glycan Profiling with CHO or HEK293 Expression Systems?
Yes. We can perform glycan profile comparisons between proteins expressed in insect systems and those expressed in mammalian systems using the same mass spectrometry platform and analysis workflow. This includes glycan composition mapping, quantitative distribution analysis, and major glycoform consistency assessment. We can also annotate the absence of mammalian-specific modifications (such as sialylation or extended complex-type glycans) in insect-derived products.
Case Study
In this study, the authors expressed Orysata in Drosophila S2 cells to obtain glycosylated recombinant protein, and compared it with the non-glycosylated native form of Orysata. The results showed that glycosylated Orysata exhibited significantly reduced activity in regulating the expression of immune-related genes, suggesting that glycosylation may impair its interaction with immune cell surface receptors by altering the protein’s conformation or masking key functional sites. This study highlights the substantial impact of glycosylation patterns introduced by the expression system on recombinant protein function, and underscores the need to carefully assess the potential effects of glycosylation on the biological activity of immune-relevant proteins produced in insect cell expression systems.
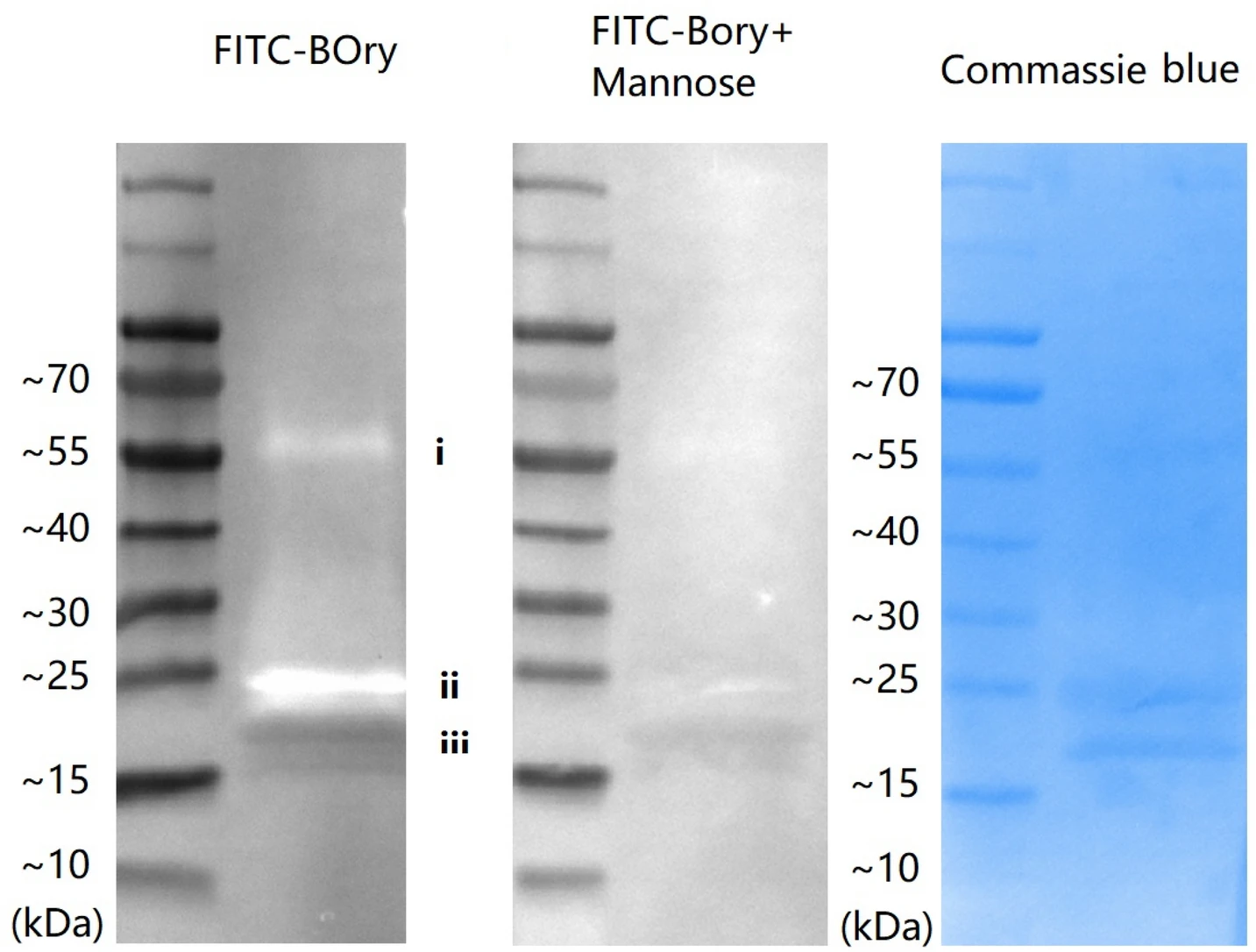
Chen P. et al. Sci Rep. 2021.
Figure 2. Glycan of YOry binding by BOry.
How to order?







