How to Perform Untargeted Metabolomics?
- VIP (Variable Importance in Projection) score > 1
- P-value < 0.05
- Fold change (FC) > 1.5 or < 0.67
- Accurate mass-to-charge ratios (m/z)
- Isotopic patterns
- MS/MS fragmentation spectra
- Database matching against HMDB, METLIN, MassBank, KEGG, etc.
- Pathway enrichment analysis using resources such as KEGG or Reactome
- Metabolic network reconstruction by integrating transcriptomic and proteomic data to build multi-omics interaction maps
- Advanced mass spectrometry instrumentation, including the Thermo Orbitrap Exploris 240, which enables broader metabolite coverage
- A standardized workflow with stringent quality control from sample preparation through data analysis
- Customized services that integrate metabolomics with proteomics and transcriptomics for comprehensive multi-omics studies
- Extensive research collaboration experience, having served more than 300 academic institutions and biopharmaceutical companies
Untargeted metabolomics refers to the comprehensive analysis of thousands of metabolites in biological samples using high-resolution mass spectrometry techniques (e.g., LC-MS/MS or GC-MS), without predefining target compounds. This approach aims to capture metabolic perturbations arising from disease, environmental changes, or pharmacological interventions. Untargeted metabolomics is a small-molecule profiling strategy designed to systematically detect as many metabolites as possible in a given sample. Its overarching objective is to characterize broad metabolic alterations in an unbiased manner, thereby facilitating the discovery of potential biomarkers, physiological states, and perturbed pathways. Compared with targeted approaches, untargeted metabolomics offers broader coverage, making it particularly suitable for exploring novel mechanisms and generating new hypotheses.
How to Perform Untargeted Metabolomics?
Untargeted metabolomics is typically carried out in five essential steps:
1. Sample Collection and Preprocessing
Biological matrices such as plasma, urine, tissue, cells, and feces can be used. At this stage, the critical requirement is to preserve the native composition of metabolites while minimizing degradation and artificial bias.
(1) Preprocessing Techniques: protein precipitation (e.g., methanol, acetonitrile), liquid–liquid extraction, and solid-phase extraction.
(2) Key Considerations: avoid repeated freeze–thaw cycles, ensure consistent sampling time points, and standardize handling procedures.
2. Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Analysis
Several analytical platforms are commonly employed in untargeted metabolomics:
(1) LC-MS (liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry): suitable for neutral and polar metabolites, such as organic acids and amino acids
(2) GC-MS (gas chromatography–mass spectrometry): applicable to volatile or derivatized small molecules, including fatty acids and carbohydrates
(3) CE-MS (capillary electrophoresis–mass spectrometry): primarily for charged metabolites
(4) HRMS (high-resolution mass spectrometry): instruments such as Orbitrap or TOF enable accurate structural elucidation and metabolite identification
3. Data Preprocessing
Raw spectral data must undergo rigorous preprocessing to ensure analytical reliability. Major steps include:
(1) Peak detection
(2) Peak alignment
(3) Noise reduction and imputation of missing values
(4) Signal normalization
These processes critically determine the robustness of subsequent statistical analyses.
4. Multivariate Statistical Analysis and Identification of Differential Metabolites
The focus of untargeted metabolomics lies in pattern recognition and discrimination between groups. Commonly applied methods include:
(1) Principal Component Analysis (PCA): an unsupervised approach for visualizing global sample distributions
(2) Partial Least Squares–Discriminant Analysis (PLS-DA): a supervised method for uncovering intergroup variations
(3) Criteria for differential metabolite selection:
5. Metabolite Identification and Pathway Enrichment Analysis
(1) Metabolite identification remains one of the most challenging aspects of untargeted metabolomics and is typically based on:
(2) Subsequent analyses include:
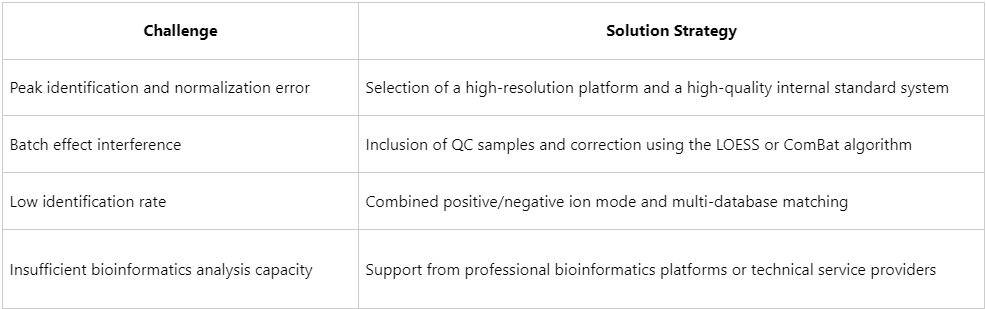
Common Challenges and Optimization Strategies in Untargeted Metabolomics
MtoZ Biolabs: A High-Standard Service Platform for Untargeted Metabolomics
As a leading provider of multi-omics solutions in life sciences, MtoZ Biolabs offers significant advantages in untargeted metabolomics:
Untargeted metabolomics provides a systems-level perspective for elucidating metabolic alterations in biological processes. Successful application of this approach depends not only on advanced instrumentation but also on standardized workflows and expert data analysis. If you plan to conduct untargeted metabolomics research, we welcome you to consult MtoZ Biolabs, where we provide full-process, one-stop technical support for your scientific projects.
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
How to order?







