How to Perform High-Throughput Proteomics Analysis of Lactylation Modifications?
-
Comprehensive mapping of lactylation sites at the proteome-wide level
-
Characterization of dynamic changes in lactylation under diverse conditions
-
Elucidation of the interplay between lactylation and other post-translational modifications (PTMs)
-
Functional validation of key lactylated proteins within specific signaling pathways
-
Employ commercial anti-Kla polyclonal antibodies
-
Couple antibodies to Protein A/G magnetic beads for peptide-level immunoenrichment
-
Implement multi-round enrichment to improve recovery of lactylated peptides
-
Exploit the lactyl functional group for selective derivatization
-
Capture lactylated peptides using affinity materials
-
Particularly suited for profiling non-histone lactylation
-
DDA (Data-Dependent Acquisition): Suitable for novel site discovery
-
DIA (Data-Independent Acquisition): Suitable for large-scale quantitative comparisons
-
PRM (Parallel Reaction Monitoring): Suitable for targeted site verification
Protein lactylation represents a novel mechanistic link between lactate metabolism and epigenetic regulation. With growing interest in its roles in immunometabolism, stem cell differentiation, and the tumor microenvironment, there is an urgent need to establish a systematic, high-throughput platform for detecting lactylation modifications, enabling precise characterization of their modification landscapes and dynamic changes. However, inherent technical challenges, such as low abundance, weak specificity, and high background noise, often render conventional proteomic strategies inadequate for this task. This article provides a comprehensive overview of high-throughput lactylation proteomics, covering the entire workflow from experimental design and sample preparation through mass spectrometry analysis to bioinformatics interpretation, with emphasis on core considerations and optimization strategies.
Project Design
High-throughput proteomic studies of lactylation modifications generally address the following research objectives:
Recommended technical approach:

MtoZ Biolabs offers customized experimental design and grouping strategies tailored to research objectives, helping clients maximize data utilization and enhance scientific output.
Sample Preparation
Consistency among samples and stability of lactylation states are prerequisites for high-throughput lactylation proteomics.
1. Recommended Sample Types
(1) Cell lines and tissue specimens (e.g., tumor tissue, macrophage cell lines)
(2) Metabolically active models (e.g., LPS stimulation, hypoxic treatment, high-lactate exposure)
2. Protein Extraction and Inhibition
(1) Incorporate broad-spectrum deacetylase/delactylase inhibitors (e.g., TSA, NAM) into the lysis buffer
(2) Maintain cold-chain conditions to prevent enzymatic activation
(3) Add a protease inhibitor cocktail to prevent protein degradation
The optimized buffer system developed by MtoZ Biolabs maximizes the preservation of native lactylation states, ensuring data reliability.
Lactylated Peptide Enrichment
Method 1: Immunoenrichment Using Anti-Kla Antibodies
Method 2: Chemical Labeling-Based Enrichment
MtoZ Biolabs has developed a Sequential Kla Enrichment workflow for efficient capture of low-abundance lactylation modifications, enabling parallel processing of large sample sets.
LC–MS/MS High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry
1. Recommended platforms

2. Analytical Strategies
MtoZ Biolabs offers fully automated mass spectrometry operation integrated with QA/QC monitoring to ensure inter-batch consistency in high-throughput datasets.
Data Processing and Bioinformatics Analysis
1. Data Search and Lactylation Site Identification
(1) Use mainstream software such as MaxQuant, Spectronaut, and PD
(2) Specify lactylation mass shift (+72.0211 Da, K)
(3) Apply PTM Localization Score to retain high-confidence sites
2. Quantitative Analysis
(1) Label-based approaches (e.g., TMT/iTRAQ) are suitable for high-throughput quantification involving ≤10 groups
(2) Label-free approaches are suitable for time-course or dose–response experiments
(3) Perform statistical analysis using MSstats and Perseus
3. Bioinformatics Interpretation
(1) Conduct GO functional annotation and KEGG pathway enrichment of lactylated proteins
(2) Perform motif analysis to identify potential recognition sequences for modifying enzymes
(3) Integrate protein–protein interaction data (e.g., STRING) to construct regulatory networks
MtoZ Biolabs delivers integrated analysis reports encompassing lactylation modification profiles, differential sites, functional annotations, pathway enrichment, and interaction networks, enabling rapid biological interpretation.
Project Duration and Sample Requirements
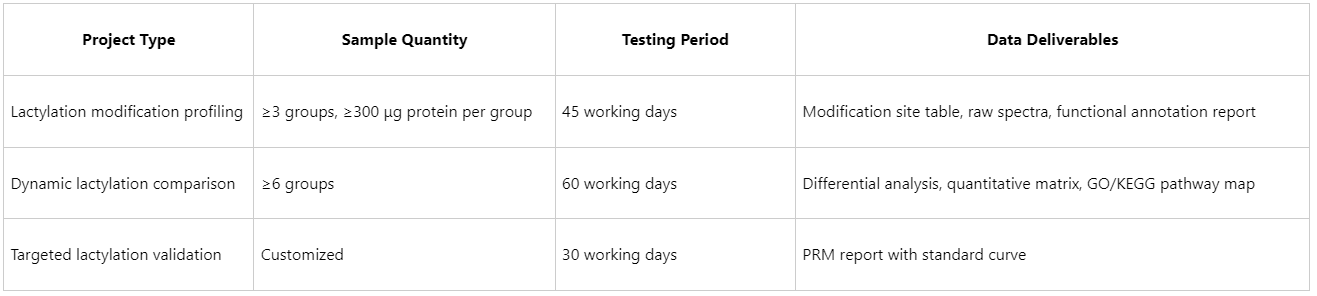
The success of high-throughput proteomics analysis of lactylation modifications hinges on standardized sample handling, specific enrichment strategies, high-throughput mass spectrometry, and automated data analysis. As technical platforms continue to advance, protein lactylation is poised to play a more prominent role in epigenetic regulatory networks, serving as a key technology for target discovery, disease mechanism elucidation, and drug screening. Leveraging nearly a decade of proteomics expertise, MtoZ Biolabs has developed a dedicated lactylation proteomics service platform, delivering an end-to-end solution from sample to biological insight. Researchers are welcome to consult with technical specialists for tailored project plans.
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
How to order?







