How to Analyze Protein–Protein Interactions?
-
Elucidating protein functions and regulatory mechanisms
-
Mapping disease-associated signaling pathways
-
Identifying candidate therapeutic targets
-
Improving strategies for biomarker discovery
-
Expression of tagged bait proteins in cells
-
Immunoaffinity purification of protein complexes
-
Proteolytic digestion followed by LC-MS/MS analysis
-
Quantitative comparison of interaction abundances using label-free or TMT-based methods
-
High-sensitivity Orbitrap mass spectrometry platforms enabling detection of low-abundance interactors while minimizing background noise.
-
Customized experimental strategies supporting multiple affinity tags (FLAG, HA, Strep, GFP, etc.) and diverse host cell systems.
-
Integrated cross-linking MS and TMT-based multiplex quantification for investigating spatiotemporal interaction dynamics in complex biological samples.
-
Dedicated bioinformatics expertise to support PPI network construction and identification of key regulatory nodes.
Protein-protein interactions (PPIs) represent fundamental mechanisms underlying cellular function and biological processes. They play essential roles in signal transduction, metabolic regulation, and gene expression. Investigating PPIs facilitates the elucidation of disease mechanisms, the identification of therapeutic targets, and the construction of regulatory networks. With advances in mass spectrometry technologies, PPI detection has progressed from conventional validation approaches to high-throughput, quantitative, and structural analyses, providing a more comprehensive and system-level perspective for life science research.
Research Significance of Protein-Protein Interaction Analysis
Within physiological cellular environments, proteins rarely function independently. Instead, they typically exert biological effects through the formation of complexes or participation in signaling pathways with other proteins. Consequently, systematic characterization of protein interaction networks contributes to:
Major Approaches for Protein-Protein Interaction Analysis
1. Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP)
(1) Principle: Target proteins and their interacting partners are enriched using specific antibodies.
(2) Advantages: High specificity; well suited for validating known or predicted interactions.
(3) Limitations: Inefficient for detecting transient or low-affinity interactions; susceptible to non-specific associations.
2. Affinity Purification-Mass Spectrometry (AP-MS)
(1) Principle: A tagged bait protein is used to enrich interacting partners, which are subsequently identified by LC-MS/MS.
(2) Advantages: High-throughput capability; enables interaction capture under near-physiological conditions.
(3) Applications: Characterization of protein complex composition and analysis of interaction dynamics.
3. Yeast Two-Hybrid (Y2H) System
(1) Principle: Two proteins are fused to a DNA-binding domain and a transcriptional activation domain, respectively; their interaction activates reporter gene expression.
(2) Advantages: Suitable for large-scale interaction screening.
(3) Limitations: High false-positive rates; limited applicability to membrane proteins or proteins requiring post-translational modifications.
4. Protein Microarrays
(1) Principle: Thousands of proteins are immobilized on a solid surface to assess interactions with target proteins or small molecules.
(2) Advantages: Ultra-high throughput with minimal sample consumption.
(3) Limitations: Protein conformational integrity may affect binding performance.
5. Biophysical Approaches
Techniques such as surface plasmon resonance (SPR), isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC), and microscale thermophoresis (MST) enable precise quantification of binding affinities and kinetic parameters.
Mass Spectrometry-Based Strategies for PPI Analysis
To meet the increasing demand for high-throughput and quantitative analyses, mass spectrometry has become a central technology for systematic PPI network characterization.
1. AP-MS Combined with Label-Free or TMT Quantification
(1) Advantages: Allows parallel comparison of protein complex composition across multiple experimental conditions.
(2) Workflow:
2. Cross-Linking Mass Spectrometry (XL-MS)
(1) Principle: Chemical cross-linkers stabilize spatially proximal protein regions, enabling MS-based identification of cross-linked peptides.
(2) Advantages: Provides spatial and conformational insights into protein complexes.
(3) Applications: Structural analysis of macromolecular assemblies and detection of transient or weak interactions.
3. Interactomics
Integration of MS data with bioinformatics platforms and databases, such as Cytoscape, STRING, and BioGRID, enables the construction of large-scale PPI networks and facilitates pathway-level interpretation.
Selection of Appropriate PPI Analysis Methods
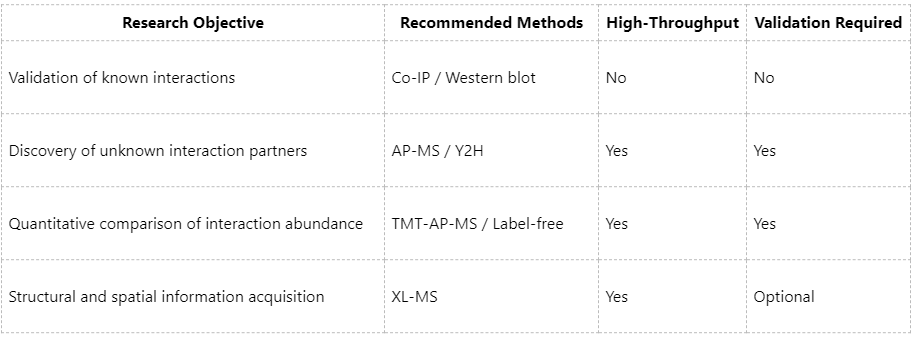
Technical Strengths of MtoZ Biolabs in PPI Research
Leveraging extensive experience in mass spectrometry platform development, MtoZ Biolabs has established a robust and scalable service framework for protein interaction studies:
With ongoing advances in single-cell omics, spatial multi-omics, and AI-driven protein structure prediction technologies (e.g., AlphaFold), PPI research is increasingly oriented toward higher resolution, dynamic profiling, and systems-level integration. The comprehensive integration of mass spectrometry data with bioinformatics analyses is expected to play a critical role in elucidating complex biological mechanisms. In this context, collaboration with experienced partners equipped with advanced analytical platforms and customized service capabilities can substantially enhance both research efficiency and discovery depth. If your research focuses on signaling pathways, therapeutic target identification, or protein complex characterization, MtoZ Biolabs provides professional technical support and customized analytical solutions upon request.
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
How to order?







