How HLA Immunopeptidomics Advances Cancer Antigen Recognition?
The Core Question in Cancer Immunotherapy: How Do T Cells Recognize Tumors?
T cells do not directly recognize cancer cells themselves; instead, they assess whether a cell is abnormal through peptides presented by major histocompatibility complex (MHC, also known as HLA) molecules. Consequently, identifying and characterizing HLA-presented peptides, particularly those derived from oncogenic mutations, aberrantly expressed proteins, or viral integrations, collectively known as cancer antigen peptides, is fundamental to the development of tumor vaccines, TCR-T cell therapies, and other immunotherapeutic approaches. One of the key technologies enabling this process is HLA immunopeptidomics.
What Is HLA Immunopeptidomics?
HLA immunopeptidomics is a mass spectrometry–based analytical discipline that systematically identifies endogenous peptides (typically 8–12 amino acids in length) presented by HLA molecules in vivo. These peptides reflect the cell’s metabolic state, mutational landscape, and antigenic burden, acting as the molecular identifiers recognized by T cells. Rather than answering the question of which proteins are expressed, HLA immunopeptidomics seeks to determine how these proteins are processed, cleaved, and ultimately presented for T-cell surveillance.
How Does HLA Immunopeptidomics Reveal Authentic Antigen Presentation?
1. Immunoaffinity Purification Coupled with Mass Spectrometry
HLA immunopeptidomics typically involves using specific antibodies to isolate HLA-I/II complexes from the cell surface, releasing their bound peptides, and identifying peptide sequences using high-resolution mass spectrometry (e.g., Orbitrap Exploris 480).
Compared with computational prediction, this experimental approach offers several distinct advantages:
(1) Direct identification of endogenously presented antigenic peptides
(2) Detection of mutation-derived peptides (neoantigens)
(3) Characterization of peptides originating from atypical sources, such as viral or transposon-derived proteins
MtoZ Biolabs has established a robust and high-throughput workflow for HLA peptide purification and detection. The platform is compatible with diverse sample types, including cell lines, tumor tissues, and PBMCs, and supports low-input analyses requiring as few as one million cells.
2. Focusing on Neoantigens
Neoantigens are novel peptides arising from tumor-specific mutations or gene fusions. Because they are expressed exclusively in tumor tissues and absent from normal cells, they represent ideal targets for T-cell–mediated immune recognition. By integrating mass spectrometry data with patient-specific genomic information (e.g., WES or RNA-seq), HLA immunopeptidomics enables:
(1) Personalized identification of neoantigens
(2) Parallel validation of peptides derived from multiple mutation sites
(3) Immunogenicity assessment of preferentially presented peptides
These capabilities provide essential support for the design of personalized cancer vaccines and the engineering of TCR-T cell therapies.
3. Overcoming the Limitations of Prediction-Based Screening
Current antigen discovery pipelines largely depend on HLA-binding prediction algorithms such as NetMHCpan; however, only 10–20% of predicted peptides are actually presented in vivo. HLA immunopeptidomics offers direct experimental validation, thereby preventing the selection of predicted targets that fail to elicit immune responses in practice.
4. Exploring Modified and Non-Canonical Antigens
Certain cancer-associated antigens originate from unconventional sources, including:
(1) Translation products from non-coding genomic regions (e.g., uORFs, lncRNAs)
(2) Peptides modulated by post-translational modifications such as phosphorylation or methylation
(3) Spliced or hybrid peptides generated through proteolytic processing
Application Value: HLA Immunopeptidomics as a Driver of Precision Cancer Immunotherapy
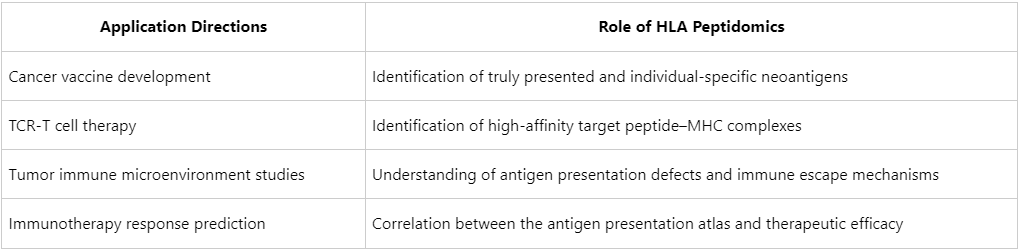
MtoZ Biolabs: Comprehensive HLA Immunopeptidomics Solutions
MtoZ Biolabs provides an end-to-end HLA immunopeptidomics research workflow that spans from experimental design to advanced data interpretation:
(1) High-affinity enrichment of HLA complexes to improve detection of low-abundance peptides
(2) State-of-the-art mass spectrometry platform (Orbitrap Exploris coupled with nanoLC) supporting large-scale parallel analyses
(3) Integrated bioinformatics pipeline combining HLA typing, mutant peptide mapping, and immunogenicity scoring
(4) Multi-omics integration incorporating transcriptomic, proteomic, and single-cell datasets to pinpoint key antigen sources
(5) Collaborative development options supporting TCR-T target discovery, vaccine design, and translational applications
As cancer immunotherapy becomes increasingly personalized and precise, prediction-based approaches alone are insufficient for translational research and clinical development. By combining experimental validation, high sensitivity, and broad antigen coverage, HLA immunopeptidomics provides an authentic molecular view of tumor antigen presentation. MtoZ Biolabs is dedicated to advancing research and practical applications in this field, offering professional support for neoantigen discovery, immune target development, and T-cell engineering, empowering research teams to remain at the forefront of cancer immunotechnology.
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
How to order?







