How Does Edman Sequencing Enable N-Terminal Protein Sequencing? Key Steps and Mechanisms
How Does Edman Sequencing Enable N-Terminal Protein Sequencing? The core principle of Edman degradation lies in the selective chemical degradation of N-terminal amino acids, where each amino acid residue at the protein’s N-terminus is sequentially removed through a cyclization–cleavage process and identified as a stable derivative. This method employs a chemical reaction in which phenyl isothiocyanate (PITC) specifically reacts with the N-terminal amino acid, allowing for stepwise cleavage and identification of the N-terminal residues in a polypeptide chain, thereby enabling N-terminal protein sequencing. The key steps of Edman degradation include coupling, cleavage, conversion, and detection, which are repeated in cycles until the target sequence is fully elucidated. A detailed analysis of these steps and their underlying mechanisms is provided below:
Detailed Experimental Procedure of Edman Sequencing
1. Sample Preparation
(1) Protein purification: The protein sample must be highly purified to minimize background interference during sequencing.
(2) Immobilization: The sample is typically immobilized on glass fiber or PVDF membranes to enhance chemical stability during degradation.
(3) Verification of N-terminal accessibility: The N-terminus must be free of modifications such as acetylation or methylation; otherwise, Edman sequencing cannot proceed.
2. Reaction Workflow
(1) PITC derivatization: In an alkaline buffer (e.g., triethylamine), PITC reacts with the free N-terminal amino group to form a phenylthiocarbamoyl derivative.
(2) Acid-induced cleavage: Treatment with trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) induces intramolecular cyclization, cleaving the terminal amino acid as a PTH derivative.
(3) Extraction: The resulting PTH-amino acid is extracted using an organic solvent to facilitate subsequent analysis.
3. Identification of PTH-Amino Acids
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is used to separate and identify the PTH-amino acid by comparison with reference standards.
4. Iterative Sequencing
Residual compounds are removed by washing, and the process is repeated to sequentially identify each N-terminal amino acid until the full sequence is elucidated.
Mechanistic Elucidation of Edman Sequencing
1. Selective Chemical Reaction
Phenyl isothiocyanate (PITC) selectively reacts with the N-terminal amino acid, leaving internal peptide bonds intact and thus preserving the structural integrity of the polypeptide.
2. Mild Degradation Conditions
Compared with other chemical degradation techniques, such as acid hydrolysis, Edman sequencing operates under relatively mild conditions, minimizing non-specific cleavage and preventing extensive degradation of the protein or polypeptide.
3. Efficient Cyclization and Cleavage
Under acidic conditions, the derivatized N-terminal residue undergoes cyclization, which facilitates its efficient cleavage and release. This process occurs without disrupting the remaining portion of the peptide chain.
4. Stable PTH-Amino Acid Detection
The resulting phenylthiohydantoin (PTH)-amino acids exhibit stable chromatographic and spectroscopic properties, allowing for accurate identification using techniques such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).
Advantages and Limitations of Edman Sequencing
1. Advantages
(1) Highly specific in determining N-terminal amino acid sequences, without requiring database alignment
(2) Enables precise verification of protein translation initiation sites or affinity tags
(3) Provides accurate N-terminal structure characterization for small peptides, synthetic peptides, and chemically modified proteins
2. Limitations
(1) Requires highly purified and homogeneous protein samples, as even minor contaminants can significantly interfere with sequencing accuracy
(2) Ineffective for proteins with chemically blocked N-termini, such as N-terminal acetylation or other modifications
(3) Limited throughput when analyzing long sequences or samples with high molecular complexity
(4) Has reduced sensitivity in detecting post-translational modifications at the N-terminus
Edman sequencing achieves stepwise identification of N-terminal amino acids through a series of precise and sequential chemical reactions. Despite inherent challenges such as low throughput and limited read length, it remains indispensable in applications such as short peptide sequencing, N-terminal modification analysis, and regulatory quality control. Looking forward, integration with technologies like mass spectrometry, microfluidics, and artificial intelligence may revitalize this classical method and expand its relevance in modern proteomics. MtoZ Biolabs offers comprehensive N-terminal protein sequencing services based on Edman degradation, committed to delivering high-quality mass spectrometry solutions for your research needs.
Edman Degradation vs Mass Spectrometry: Which Is Better Suited for N-Terminal Protein Sequencing?
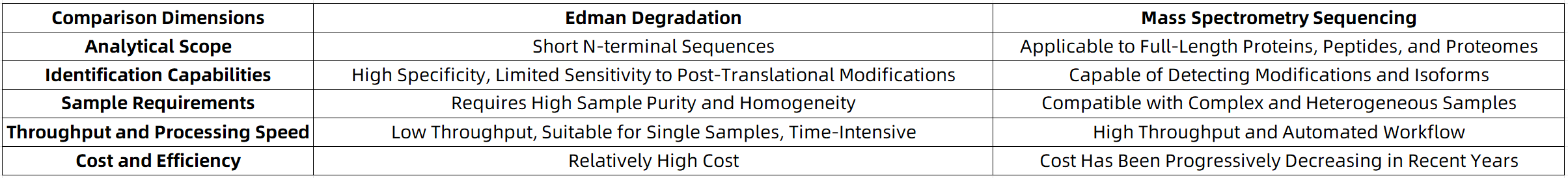
MtoZ Biolabs integrates automated Edman degradation instrumentation with a high-sensitivity HPLC system and complementary mass spectrometry (MS) sequencing data to offer a comprehensive solution for N-terminal protein structure validation and full-length protein sequencing. This integrated platform is tailored to meet the analytical demands of both basic research and pharmaceutical development. For researchers encountering challenges in N-terminal sequence verification or tag expression analysis, MtoZ Biolabs provides professional, rapid, and customizable sequencing services.
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
How to order?







