Glycation Quantitative Analysis Service
Glycation quantitative analysis is a highly sensitive analytical technique dedicated to detecting and quantifying protein glycation levels. Glycation is a non-enzymatic reaction that typically occurs at lysine residues or N-terminal amino groups of proteins, where they covalently bind to reducing sugars (such as glucose) to form early glycation products, which may ultimately develop into advanced glycation end-products (AGEs). This modification can significantly affect the structure, stability, and function of proteins, thereby influencing their biological performance and therapeutic properties. This service integrates high-resolution mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) with various quantification strategies to systematically identify glycation sites and accurately assess changes in their abundance.
The glycation quantitative analysis service is widely applied in the development and quality control of monoclonal antibodies and recombinant proteins, mechanism studies of AGE-related diseases (such as diabetes, neurodegenerative diseases, and chronic inflammation), protein stability and aging process research, as well as monitoring of glycation products during food processing and storage. It provides essential data support for evaluating protein quality, safety, and functional risk.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Based on a high-resolution mass spectrometry platform, MtoZ Biolabs offers a glycation quantitative analysis service focused on detecting and quantifying non-enzymatic glycation modifications in proteins. This service enables the analysis of glycation sites, modification types, and relative abundances in antibodies, recombinant proteins, or complex biological samples. It provides high-quality data, including site-specific glycation information, peptide sequences, mass spectra, and relative or absolute quantification results. The service supports structural quality assessment, process consistency verification, and functional relevance studies.
Analysis Workflow
1. Protein Extraction and Digestion
Target proteins are extracted from antibodies, recombinant proteins, or complex biological samples, followed by reduction and alkylation. Proteins are then digested with trypsin to preserve glycation modification information.
2. Glycated Peptide Enrichment
Glycated peptides are enriched using solid-phase extraction or affinity-based strategies to remove background interference and enhance the detection of low-abundance modifications.
3. LC-MS/MS Detection
High-resolution liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), such as Orbitrap, is employed for precise qualitative and quantitative analysis of glycated peptides.
4. Data Analysis and Report Delivery
Using specialized databases and algorithmic tools, glycation sites, peptide sequences, and abundance changes are interpreted. A comprehensive graphical and tabular report is delivered to support structural analysis, functional research, and quality control.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Types
Compatible with various sample types, including purified monoclonal antibodies, recombinant proteins, cell lysates, and plasma. High-purity protein samples are recommended to ensure optimal analysis quality.
2. Buffer Requirements
Avoid buffer systems containing SDS, glycerol, high salt, reducing agents, or sugars, as they may interfere with mass spectrometry analysis. Use MS-compatible buffers whenever possible.
3. Sample Transport
Samples should be stored at –80°C and shipped on dry ice to maintain the stability of glycation modifications. For liquid samples, lyophilized or concentrated forms are preferred to ensure sample integrity.
Service Advantages
1. High-Sensitivity Detection
Leveraging high-resolution mass spectrometry platforms such as Orbitrap, combined with optimized digestion and enrichment workflows, enables precise identification of low-abundance glycation modifications, enhancing detection coverage and data reliability.
2. One-Time-Charge
Our pricing is transparent, no hidden fees or additional costs.
3. Flexible Quantification Strategies
Supports various quantification approaches including label-free and TMT-based methods, accommodating diverse experimental designs for comparative or dynamic glycation level analysis.
4. End-to-End Service
From sample preparation and MS detection to data analysis and result interpretation, we provide standardized or customized full-process solutions to accelerate scientific research and biopharmaceutical development.
Applications
1. Antibody and Recombinant Protein Drug Development
The glycation quantitative analysis service can be used to evaluate the impact of different expression systems or process conditions on glycation modifications, optimize protein structural stability and pharmacological performance, and support drug consistency studies.
2. Disease Mechanism and Biomarker Discovery
By investigating the role of glycation modifications in diseases such as diabetes and Alzheimer’s, this service aids in identifying early diagnostic biomarkers or potential therapeutic targets.
3. Protein Aging and Functional Inactivation Studies
The glycation quantitative analysis service supports the analysis of glycation changes in proteins under conditions of long-term storage, stress, or aging, helping to assess the impact on protein activity and structural stability.
4. Food and Nutritional Science Research
Applied to the quantitative analysis of Maillard reaction products during food processing, it helps examine the influence of glycation on nutritional value, flavor development, and food safety.
Case Study
1. Quantitative Analysis of Glycation and its Impact on Antigen Binding
This study aimed to quantitatively analyze the impact of antibody glycation on antigen-binding capacity, using a human IgG1 monoclonal antibody as the research subject. Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) combined with glycated peptide enrichment strategies was employed to identify and quantify glycation modifications at multiple lysine residues, with particular focus on modifications within the variable and Fc regions. Results showed that glycation accumulated progressively during antibody storage, and certain sites near the antigen-binding region significantly reduced binding affinity, with glycation in the variable region having the most pronounced effect. The study concludes that glycation not only alters antibody structure but may also compromise its functional activity, underscoring the importance of quantitative glycation monitoring in antibody drug development and quality control.
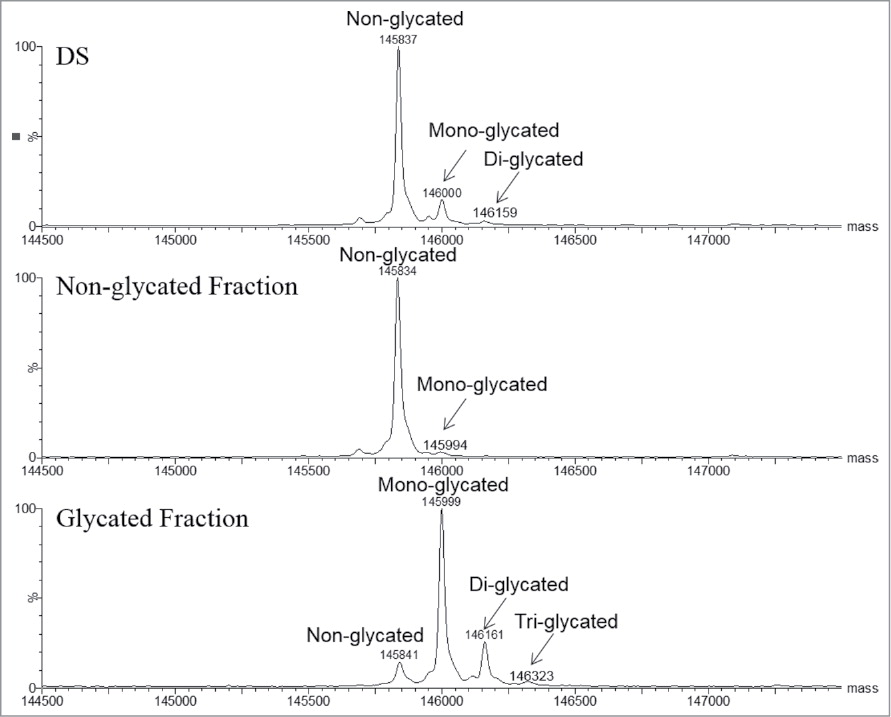
Mo, J J. et al. mAbs, 2018.
Figure 1. Intact LC-MS Analysis of EndoS Treated mAb1.
FAQ
Q1: What Types of Glycation Modifications Can this Service Detect?
A1: The service primarily detects non-enzymatic glycation modifications in proteins, including early glycation products (such as Amadori compounds) and advanced glycation end-products (AGEs), with a focus on modifications at lysine residues and N-terminal amino groups.
Q2: Can Site-Specific Quantitative Data Be Provided?
A2: Yes. We utilize high-resolution mass spectrometry combined with label-free or TMT-based quantification strategies to deliver qualitative and relative abundance information for specific glycation sites, supporting comparative analysis across multiple sample groups.
How to order?







