Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Analytical Service
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) is a technique that utilizes the selective absorption characteristics of molecules to infrared light for structural and compositional analysis. The basic principle is that different chemical bonds produce unique vibration absorption peaks within specific wavenumber ranges. By performing a fourier transform on the spectral data obtained from the interaction between the sample and infrared light, information about molecular functional groups, types of chemical bonds, and structural characteristics can be obtained. FTIR features simple operation, high sensitivity, and non-destructive detection, allowing for the rapid acquisition of molecular fingerprint spectra. It is widely applied in drug structure verification, excipient consistency analysis, polymer characterization, and formulation quality control, providing reliable support for research and production.
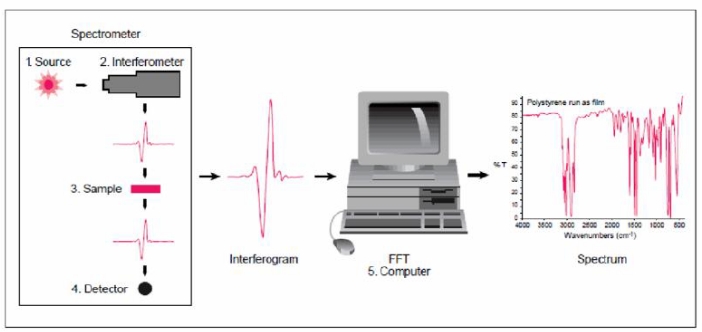
Ramaiah, G B. et al. International Journal of Engineering Technology Science and Research, 2017.
Figure 1. Working Principle of Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Based on the advanced fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) platform, MtoZ Biolabs has launched the fourier transform infrared spectroscopy analytical service, which enables precise detection of molecular structure and chemical composition in samples. By measuring the absorption spectra of molecules in the infrared region, this service can rapidly analyze functional group characteristics, intermolecular interactions, and structural changes within the sample. The final data output includes component identification, structural features, and purity information. This service is widely applied in the identification of drugs and excipients, impurity detection, and quality control, providing reliable support for pharmaceutical research, development, and production.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Type
Suitable for various forms of samples, including solids, liquids, gases, and films. Samples must be representative and meet the requirements of infrared spectroscopy detection.
2. Sample Purity
It is recommended to minimize impurities or moisture content to avoid interference with spectral absorption signals and to improve the accuracy and reproducibility of the analysis.
3. Sample Storage
Samples should be stored under dry and light-protected conditions to avoid moisture absorption or chemical degradation, ensuring stability before testing.
4. Sample Transportation
Samples should be transported in sealed containers. Solid samples should be kept dry, while liquid samples may require low-temperature or light-protected conditions to ensure sample integrity and data reliability.
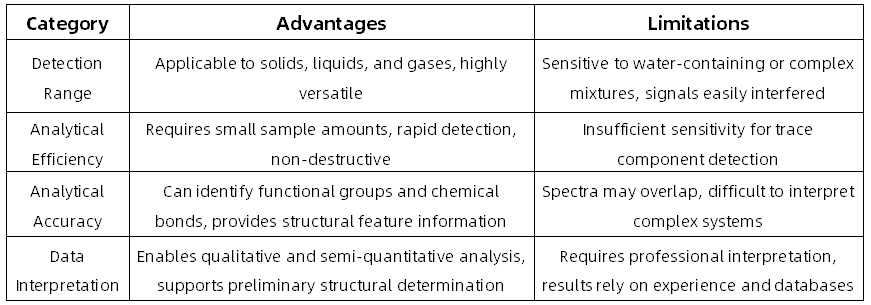
Advantages and Limitations
Applications
1. Drug Formulation Development
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy analytical service can be used to analyze the functional group structures of drugs and excipients, verify the rationality of formulation design, and ensure the stability and consistency of drugs in dosage forms.
2. Quality Control
By analyzing the structural characteristics of active pharmaceutical ingredients, intermediates, and finished products, FTIR can quickly identify impurities or batch-to-batch variations, enhancing quality monitoring during the production process.
3. Excipient Function Verification
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy analytical service can be used to evaluate the chemical stability and compatibility of excipients in formulations, providing data support for drug release mechanisms and formulation performance optimization.
4. Biomolecular Research
FTIR can be applied to the secondary structure characterization of biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids, helping to explore their conformational changes and interactions with drugs.
FAQ
Q1: Does the Sample Require Special Preparation?
A1: Usually, no complex preparation is needed, but powder samples should be finely ground, and liquids or solutions should be free of impurities to ensure accurate results.
Q2: Can FTIR Distinguish Different Crystal Forms?
A2: Under certain conditions, yes. Different crystal forms cause variations in molecular vibrations, which are reflected in the infrared spectra, making FTIR suitable for polymorphism studies and comparisons.
Q3: Does FTIR Damage the Sample?
A3: FTIR is generally a non-destructive technique, and samples can typically be reused for other analyses after measurement.
How to order?







