Exosome Gene Verification Service
Exosome Gene Verification Service utilizes qPCR technology to validate the expression levels of target genes in exosomes to confirm whether the gene expression in exosomes differs significantly from the control group, laying the foundation for subsequent functional research. Exosomes, as important nanoscale vesicles released by cells, carry various nucleic acids such as mRNA, miRNA, lncRNA, and circRNA, playing key roles in cellular communication, disease progression, immune regulation, and metabolic modulation. Analyzing the genetic content carried by exosomes under different physiological or pathological conditions provides valuable molecular information for mechanism studies, early disease diagnosis, treatment monitoring, and drug development.
Exosomal content analysis is typically conducted using high-throughput sequencing or omics technologies, which can effectively identify differentially expressed genes between experimental and control exosome groups. Once differential genes are identified, further verification is needed using other methods to confirm that their expression indeed differs across samples, thereby ensuring the accuracy of high-throughput data and laying the groundwork for subsequent functional studies. qPCR technology, which relies on highly specific primer design and advanced fluorescent labeling systems, can reliably measure even very small amounts of exosomal RNA.
Using qPCR technology, MtoZ Biolabs offers the Exosome Gene Verification Service to quantitatively analyze target genes, helping to determine gene expression in exosomes and providing solid and reliable data support for scientific discoveries and clinical translation.
Analysis Workflow
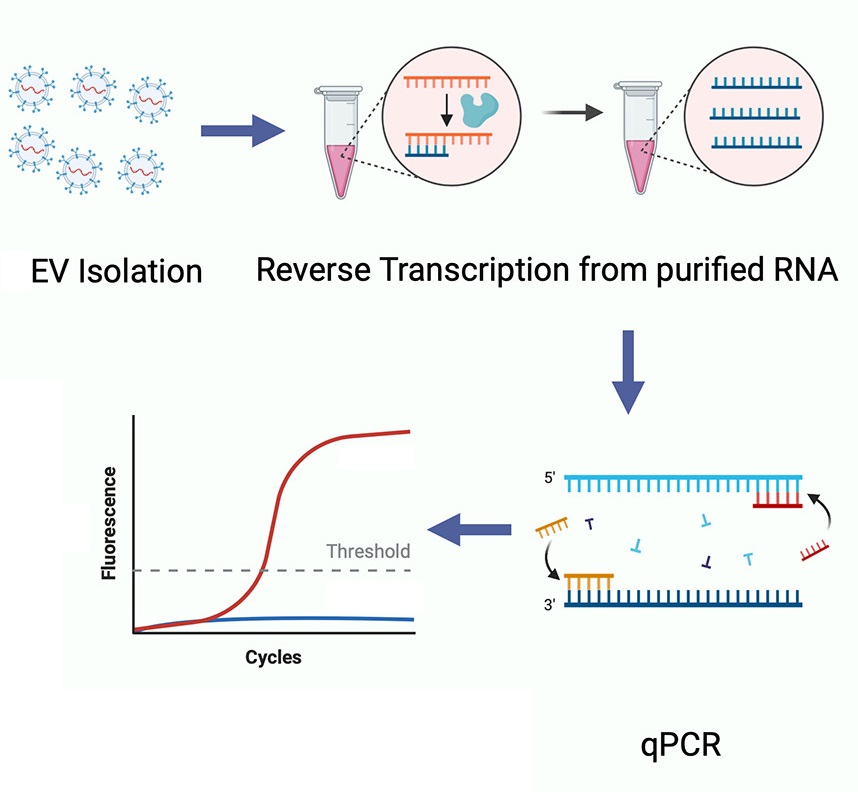
Singh A D. et al. Transplant Immunology. 2022.
1. Exosome Enrichment
Exosomes are separated and purified from the sample using methods such as ultracentrifugation, filtration concentration, reagent kit precipitation, or magnetic bead techniques.
2. Exosomal RNA Extraction
Total RNA is extracted from the exosomes.
3. cDNA Synthesis
The extracted exosomal RNA is reverse transcribed to synthesize cDNA.
4. qPCR Quantification Analysis
The expression levels of target genes are quantitatively analyzed using qPCR technology.
Service Advantages
1. Advanced Analysis Platform: MtoZ Biolabs established an advanced Exosome Gene Verification Service platform, guaranteeing reliable, fast, and highly accurate analysis service.
2. One-Time-Charge: Our pricing is transparent, no hidden fees or additional costs.
3. Experienced Team: MtoZ Biolabs has extensive experience in RNA extraction and qPCR analysis, ensuring highly accurate and reproducible results.
Applications
Exosomal Functional Mechanism Research
Verify the presence of specific miRNAs, lncRNAs, and mRNAs within exosomes to uncover their roles in tumor microenvironment regulation, immune modulation, and cell-to-cell communication.
Biomarker Validation
Confirm potential exosome-based biomarkers at the gene level to support the development of liquid biopsy diagnostics.
Novel Nucleic Acid Drug Development
Evaluate the capacity of exosomes as delivery vehicles for siRNA and miRNA, and confirm the efficient loading and expression of nucleic acids within exosomal carriers.
FAQ
Q. What Types of Samples can be Processed for Exosome Gene Verification Service?
MtoZ Biolabs can handle a wide range of sample types, including but not limited to plasma, serum, urine, saliva, cerebrospinal fluid, amniotic fluid, cell culture supernatants, and isolated exosomes from these sources.
Q. Are Different Primer Design Strategies Used for miRNA, lncRNA, circRNA, and mRNA?
Yes, MtoZ Biolabs employs customized qPCR primer design strategies tailored to each specific type of exosomal nucleic acid, including miRNA, lncRNA, circRNA, and mRNA, to ensure high specificity and accuracy of detection.
Case Study
This study utilized qPCR to quantitatively detect and validate candidate miRNAs extracted from plasma-derived exosomes of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) patients and healthy controls. Through qPCR analysis, the authors confirmed multiple miRNAs that were significantly differentially expressed in exosomes from AIS patients, with some miRNAs showing marked upregulation or downregulation. These miRNAs demonstrated strong diagnostic discrimination capabilities. The findings not only validated the differential expression of exosomal miRNAs but also further supported their potential value as non-invasive diagnostic biomarkers for AIS.
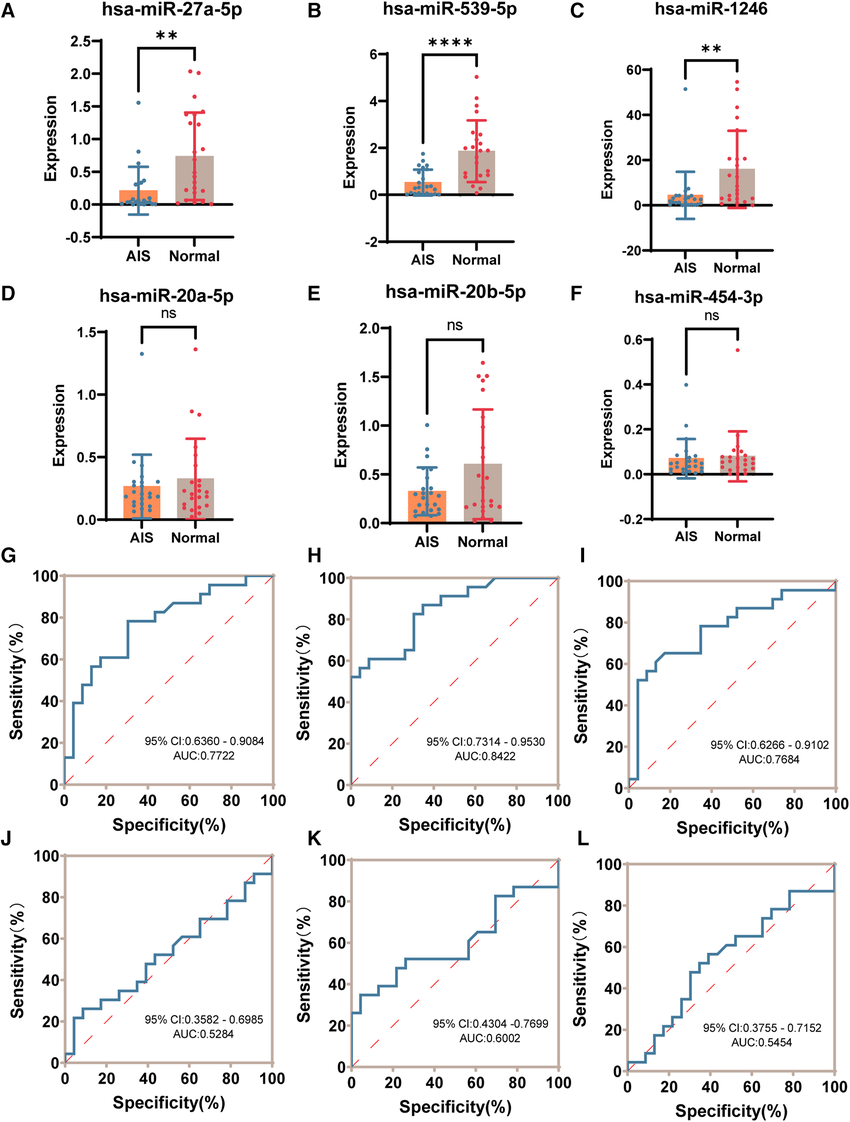
Yuan P. et al. Frontiers in Pediatrics. 2024.
How to order?







