De Novo Sequencing of Protein Drugs: Challenges and Breakthroughs
-
Enrichment of modified peptides using techniques such as HILIC for glycopeptide capture
-
Optimization of instrument settings to enhance detection of low-abundance modified ions
-
A combined analytical workflow integrating a PTM-targeting module with manual validation to enable synchronous analysis of both sequence and modification maps
-
Rational back-translation and gene cloning
-
Transient transfection and expression validation
-
Functional characterization via ELISA, Western blot, and bioactivity assays
-
Structural modeling and stability analysis in comparison with the reference biologic
-
Sequence determination and comparative analysis of fully human antibody drugs
-
Comprehensive glycoform profiling of Fc fusion proteins
-
Identification and optimization of active regions in recombinant enzymes
-
Characterization and correction of expression system-induced post-translational modifications
Introduction: The “Sequence Blind Spot” of Protein Drugs
With the rapid advancement of biopharmaceutical technologies, protein-based therapeutics—including monoclonal antibodies, fusion proteins, and recombinant enzymes—have emerged as a leading class in drug development. However, obtaining the complete sequence information of these protein drugs is a fundamental and critical task in various stages such as biosimilar development, quality consistency assessment, patent circumvention design, and retrospective analysis of legacy therapeutics. Conventional sequencing approaches largely depend on access to reference gene sequences or production cell lines, making them ineffective when expression vectors or source cells are unavailable. In such cases, mass spectrometry–based De Novo sequencing has opened a new avenue for elucidating the structure of protein drugs.
What Is De Novo Sequencing of Protein Drugs?
De Novo sequencing refers to a technique that infers the primary structure of a protein directly from mass spectrometry data, without relying on any existing sequence database. The workflow typically includes:
1. Multi-enzyme digestion of the protein sample: Generates peptide fragments with high sequence coverage
2. Acquisition of high-resolution MS/MS data: Captures fragment ions from the peptides
3. Sequence inference using De Novo algorithms: Reconstructs the amino acid sequence of each peptide
4. Peptide assembly and integration into full-length sequence: Yields the complete protein sequence
5. Verification of functional sites and post-translational modifications: Ensures functional equivalence and confirm expression viability
This approach is particularly valuable for marketed or developmental protein drugs in cases where the original sequence is inaccessible. It provides an effective strategy for sequence reconstruction and structural elucidation.
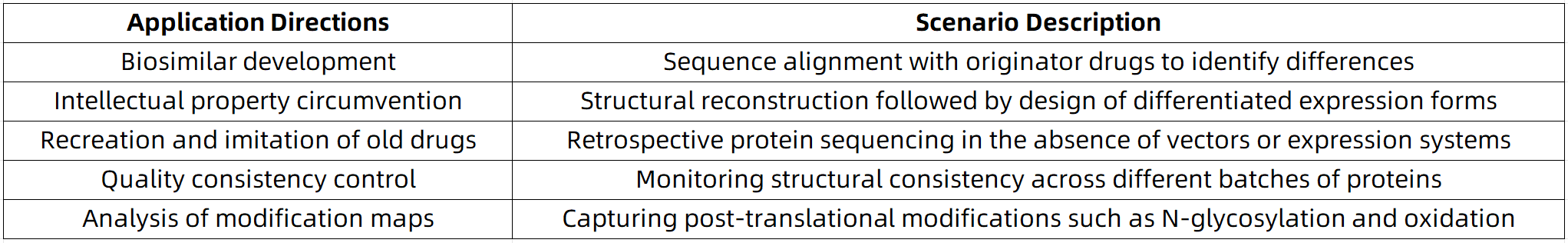
Core Application Scenarios of De Novo Sequencing in Protein Drugs
Technical Challenges: Where Are the Difficulties in De Novo Sequencing of Protein Drugs?
Although De Novo sequencing technology offers promising capabilities for the characterization of protein drugs, several substantial technical challenges persist in real-world applications:
1. Extended Sequence Length and Structural Complexity
Protein drugs often exceed 50 kDa in molecular weight and contain multiple structural domains and functional modules, making it difficult to achieve comprehensive sequence coverage with a single protease. The challenge is even greater for proteins that are highly compact or span multiple transmembrane regions, where proteolytic efficiency and uniformity are difficult to ensure.
MtoZ Biolabs' Solution:
A multi-protease digestion strategy combined with staggered coverage design—employing enzymes such as trypsin, GluC, and chymotrypsin in parallel—enhances the proportion of overlapping peptide regions and improves overall sequence completeness.
2. Interference from Homologous Regions and Coexisting Isomers
Many protein drugs, such as monoclonal antibodies and fusion proteins, contain highly homologous domains. Peptides derived from these regions often exhibit nearly identical sequences, leading to potential misassignments by sequencing algorithms. Additionally, isomeric variants introduced by the expression system—such as partial deamidation or glycosylation heterogeneity—further complicate accurate sequence reconstruction.
MtoZ Biolabs' Solution:
An in-house developed algorithm for intelligent mismatch detection, coupled with a template-guided alignment framework, enables weighted analysis of homologous regions. Manual verification is also incorporated to ensure the reliability of sequence assembly.
3. Impact of Post-Translational Modifications on Interpretation Accuracy
Protein drugs frequently undergo post-translational modifications (PTMs) such as N-glycosylation, O-glycosylation, phosphorylation, and oxidation. These modifications may cause shifts in fragment ion masses or irregular signal intensities in mass spectrometry data, thereby complicating De Novo sequence interpretation.
MtoZ Biolabs' Solution:
Key Breakthrough: From Accurate Sequencing to Functional Expression
The ultimate objective of De Novo sequencing is not merely to decode the amino acid sequence, but more critically, to generate a recombinant protein that retains its biological function. In the context of biosimilar and generic drug development, recovering the sequence alone is insufficient; it is essential to confirm both expression feasibility and functional equivalence.
Building upon De Novo sequencing results, MtoZ Biolabs offers a comprehensive suite of services including:
By integrating “sequence elucidation → expression validation → structural evaluation” into a closed-loop workflow, MtoZ Biolabs delivers practical, application-oriented technical solutions for pharmaceutical clients.
MtoZ Biolabs: A Specialized Team for Protein Drug Structural Characterization
As a specialized mass spectrometry platform serving the life sciences sector, MtoZ Biolabs has completed numerous De Novo sequencing projects for both marketed and investigational protein therapeutics, including:
Leveraging the advanced Orbitrap Fusion Lumos mass spectrometer, a robust multi-enzyme digestion strategy, and a proprietary toolchain integrating structural templates with intelligent algorithms, MtoZ Biolabs is capable of delivering full-length sequences of complex protein drugs within 3–4 weeks, along with optional downstream recombinant verification services.
In the era of globalized, personalized, and cost-effective biologics, De Novo sequencing has evolved from a research technique to a strategic enabler of core technology deployment for biopharmaceutical companies. It not only resolves challenges posed by undefined sequences, but also lays a solid data foundation for quality assurance, intellectual property protection, and innovative protein engineering. With its precision analytical platform, experienced bioinformatics team, and agile delivery system, MtoZ Biolabs is committed to empowering more enterprises and academic institutions to confidently acquire the complete structural identity of protein therapeutics, accelerating the advancement of biopharmaceutical innovation landscape.
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
How to order?







