Comprehensive Guide to Protein Glycosylation Analysis (LC‑MS/MS Workflow)
-
N-glycosylation: Occurs on asparagine (Asn) residues, typically within the consensus sequence N-X-S/T (X ≠ P).
-
O-glycosylation: Occurs on serine (Ser) or threonine (Thr) residues and is characterized by high structural heterogeneity without a strictly conserved consensus motif.
-
Less common glycosylation types: Including C-glycosylation, glycosaminoglycan (GAG) modifications, and sialylation.
-
High throughput: Enables simultaneous analysis of hundreds of glycopeptides.
-
High resolution and sensitivity: Allows discrimination of subtle glycan structural variants.
-
Quantitative capability: Supports both isobaric labeling (TMT/iTRAQ) and label-free quantification strategies.
-
Accurate site localization: MS/MS fragmentation data facilitate confident assignment of glycosylation sites and glycan structures.
-
Protein quantification (BCA assay)
-
Denaturation, reduction (DTT), and alkylation (IAA)
-
Enzymatic digestion using trypsin
-
HILIC: Enriches both N- and O-glycopeptides based on hydrophilicity.
-
Lectin affinity chromatography: Exploits lectin-glycan specificity for targeted enrichment.
-
TiO₂/IMAC: Primarily used for phosphopeptides but capable of enriching acidic glycopeptides such as sialylated species.
-
Hydrazide chemistry: Selectively captures N-glycopeptides following chemical oxidation.
-
HCD: Well suited for glycopeptide identification and quantitative analysis.
-
ETD/EThcD: Preserve labile glycan moieties and enhance confident site localization.
-
DDA: Appropriate for exploratory and discovery-driven studies.
-
DIA: Particularly effective for large-scale quantification and glycoproteome library construction.
-
Functional enrichment: GO and KEGG analyses to identify glycosylation-regulated biological pathways.
-
Disease association studies: For example, altered sialylation or branching patterns in cancer.
-
Structural modeling: Assessing the impact of glycosylation on protein three-dimensional conformation.
Protein glycosylation is a fundamental post-translational modification (PTM) that is widely distributed in eukaryotic cells. It plays critical roles in regulating protein folding, stability, subcellular localization, and molecular interactions. Glycosylation has become increasingly important in biopharmaceutical development, cancer biomarker discovery, and vaccine research. Compared with other common PTMs such as phosphorylation and acetylation, glycosylation exhibits pronounced structural diversity, extensive micro-heterogeneity, and substantial analytical complexity. Consequently, LC-MS/MS-based glycosylation analysis has emerged as a major focus in proteomics research, while simultaneously imposing higher requirements on data acquisition, analysis, and interpretation.
What Is Protein Glycosylation?
Protein glycosylation refers to the enzymatic attachment of oligosaccharide chains to specific amino acid residues within proteins. Major glycosylation types include:
Because glycosylation function is tightly linked to glycan structure, systematic characterization of glycosylation sites, glycan compositions, and glycoforms is essential for elucidating their biological roles.
Advantages of LC-MS/MS in Glycosylation Analysis
LC-MS/MS has become the method of choice for comprehensive glycoprotein characterization due to several key advantages:
At MtoZ Biolabs, high-resolution Orbitrap mass spectrometry platforms are combined with optimized sample preparation and database search strategies to deliver high-quality glycoproteomics services, enabling in-depth investigation of glycosylation-mediated regulation of protein function.
Complete LC-MS/MS Workflow for Protein Glycosylation Analysis
1. Sample Preparation and Protein Extraction
Samples may originate from cells, tissues, serum/plasma, or recombinant proteins. Preserving glycosylation integrity is essential, and buffer systems should avoid harsh deglycosylation reagents.
Following protein extraction, the workflow typically includes:
Note: Glycosylation can impede protease accessibility; therefore, dual-enzyme digestion strategies (e.g., trypsin combined with Glu-C) are often employed to improve sequence coverage.
2. Glycopeptide Enrichment
Because glycopeptides represent only a minor fraction of the total peptide mixture, enrichment is a critical determinant of analytical success. Common enrichment approaches include:
Integrating multiple enrichment strategies often substantially improves glycopeptide coverage.
3. LC-MS/MS Method Optimization
Due to their high molecular weights, extensive isomerism, and complex fragmentation behavior, glycopeptides require carefully optimized MS methods:
(1) Instrument Selection: High-resolution platforms such as Orbitrap Exploris or Fusion Lumos are recommended.
(2) Fragmentation Strategies
(3) Acquisition Modes
MtoZ Biolabs offers customized HCD-ETD hybrid acquisition strategies based on extensive experience in glycopeptide method optimization, enabling more accurate structural characterization.
4. Data Interpretation and Glycan Annotation
Comprehensive glycopeptide analysis requires integrated computational workflows:
(1) Database Searching
Byonic, pGlyco, and MSFragger-Glyco enable identification of glycan compositions, with support for customized glycan databases to enhance specificity.
(2) Glycan Annotation
Structural interpretation relies on diagnostic MS/MS fragment ions (B and Y ions), supported by manual validation using tools such as GlycoWorkbench and GlycoMod.
(3) Quantitative Analysis
Both isobaric labeling and label-free approaches are applicable, with emphasis on relative abundance changes among glycoforms derived from the same peptide backbone.
5. Bioinformatics and Functional Interpretation
Following glycosylation site and glycan annotation, downstream analyses include:
MtoZ Biolabs provides comprehensive bioinformatics support, enabling researchers to translate complex glycosylation datasets into biologically meaningful insights.
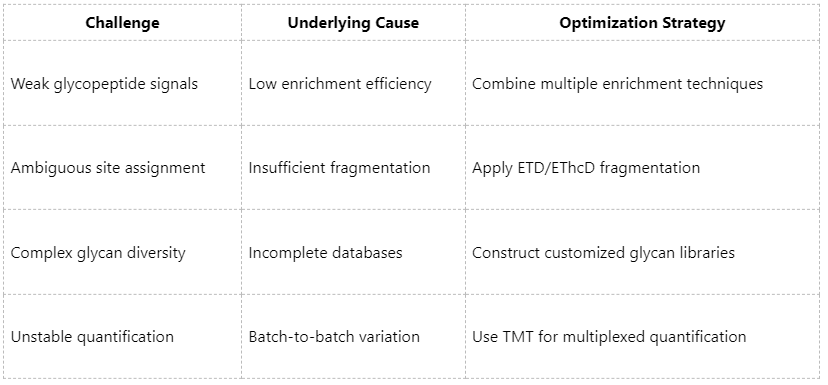
Common Challenges and Optimization Strategies
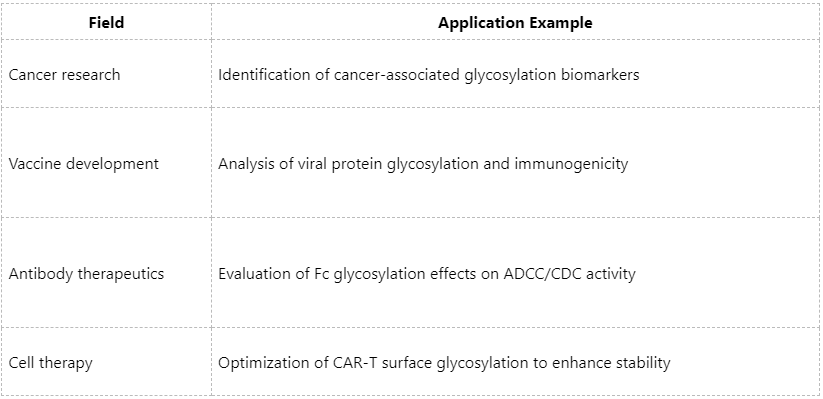
Application Scenarios: From Basic Research to Biopharmaceuticals
With continued advances in high-resolution mass spectrometry and bioinformatics methodologies, protein glycosylation analysis is evolving toward greater analytical rigor and precision. Across both fundamental research and biopharmaceutical development, a comprehensive understanding of glycosylation modifications is expected to open new directions in life science research. MtoZ Biolabs is dedicated to delivering high-coverage and high-sensitivity glycoproteomics services, encompassing the entire analytical pipeline from sample preparation and glycopeptide enrichment to LC-MS/MS acquisition and downstream bioinformatics analysis, thereby facilitating the translation of complex datasets into biologically meaningful discoveries.
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
How to order?







