Common Pitfalls in Phosphoproteomics Experiments And How to Avoid Them
Phosphoproteomics is a critical research field dedicated to the systematic investigation of protein phosphorylation and its functional roles in cellular biology. Phosphorylation, dynamically regulated by protein kinases and phosphatases, modulates protein activity, subcellular localization, stability, and molecular interactions. This post-translational modification plays a central role in a wide range of biological processes, including signal transduction, cell cycle control, metabolic regulation, gene expression, and apoptosis. By leveraging mass spectrometry-based technologies, phosphoproteomics enables large-scale identification and quantification of phosphorylation sites, providing a powerful framework for dissecting signaling pathway regulation. With continuous advances in mass spectrometry instrumentation and bioinformatics methodologies, phosphoproteomics has found expanding applications in drug target discovery, investigation of drug resistance mechanisms, and biomarker identification, becoming an indispensable tool in modern life science research. Nevertheless, owing to the inherently low abundance, high dynamic turnover of phosphorylation events, and the complexity of downstream data interpretation, researchers frequently encounter practical challenges when conducting phosphoproteomics studies.
Are There Specific Requirements for Samples in Phosphoproteomics Analysis?
Sample preparation should be performed rapidly, at low temperatures, and in the presence of phosphatase inhibitors. Phosphorylation is highly labile during cell lysis; therefore, the following precautions are essential:
1. Samples should be immediately snap-frozen or rapidly lysed to minimize protein degradation.
2. Lysis buffers must contain multiple phosphatase inhibitors (e.g., Na₃VO₄, NaF, β-glycerophosphate).
3. A total protein input of at least 1-2 mg is recommended to ensure sufficient enrichment efficiency.
4. Animal tissue samples should be thoroughly homogenized, and lipid components should be removed to reduce nonspecific adsorption.
Why Is Phosphopeptide Enrichment Necessary?
1. Phosphopeptides Constitute Only a Small Fraction of Total Proteolytic Peptides (<2%)
Without enrichment:
(1) They are difficult to detect and identify by mass spectrometry.
(2) They are highly susceptible to interference from non-phosphorylated peptides, leading to inaccurate quantification.
(3) Critical low-abundance regulatory phosphorylation events may be missed.
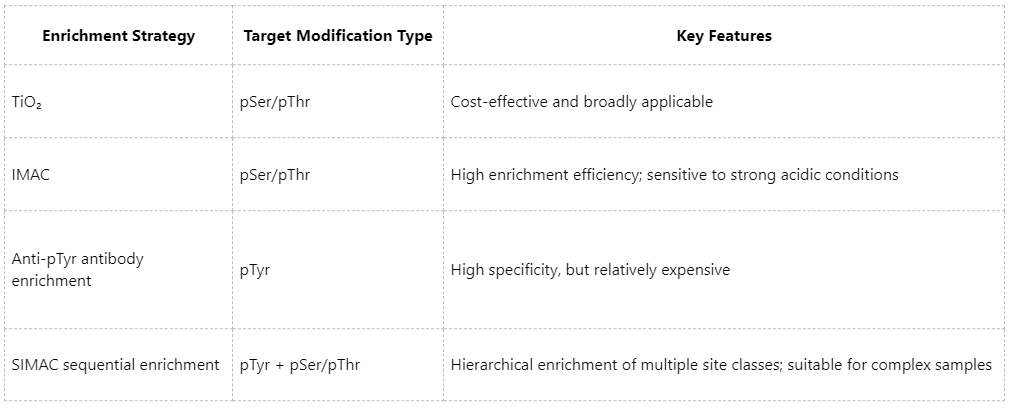
2. The Enrichment Strategy Directly Determines Analytical Depth
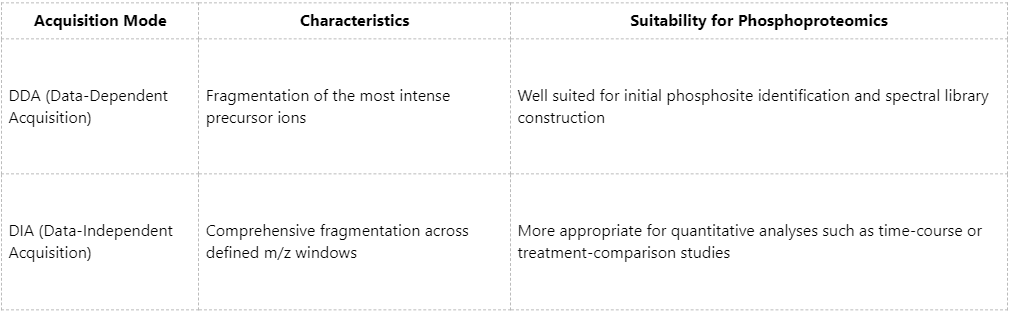
DDA or DIA: Which Acquisition Mode Is More Suitable for Phosphoproteomics?
How Can the Reliability of Phosphoproteomics Data Be Assessed?
High-quality phosphoproteomics datasets typically exhibit the following characteristics:
1. Identification of >5,000 peptides and >8,000 phosphorylation sites.
2. Phosphosite localization probability >0.75, indicating confident site assignment.
3. Pearson correlation coefficients >0.85 between biological replicates.
4. Clear enrichment of kinase signatures or signaling pathways.
5. Statistically significant quantitative changes consistent with known or expected biological phenomena.
How Can Biological Insights Be Extracted from Phosphoproteomics Data?
The primary value of phosphoproteomics lies in reconstructing signaling and regulatory networks. Common analytical strategies include:
1. Kinase-Substrate Network Analysis
Tools such as KSEA and KinMap enable inference of kinase activity changes, providing insights into potential drug targets or resistance mechanisms.
2. Pathway Enrichment Analysis
Databases such as KEGG and Reactome facilitate the identification of upregulated or downregulated regulatory modules.
3. Integrated Multi-Omics Analysis
Combining phosphoproteomics with proteomics, transcriptomics, and metabolomics can elucidate whether phosphorylation events drive functional phenotypes, such as altered metabolic flux or changes in cell proliferation rates.
4. Machine Learning-Based Clustering and Feature Extraction
These approaches support phosphoproteomic biomarker discovery and contribute to the development of personalized diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.
Phosphoproteomics is a technically demanding yet highly informative approach. Only through a comprehensive understanding of each experimental and analytical step can robust experimental designs be established and biologically meaningful regulatory mechanisms be uncovered. With professional expertise and extensive experience, MtoZ Biolabs provides technical support to facilitate high-quality phosphoproteomics research.
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
How to order?







