Circular Dichroism Based Carbohydrate Analysis Service
- Monosaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides
- Sulfated polysaccharides (e.g., heparin and related analogs)
- Glycoconjugates such as glycopeptides, glycoproteins, and glycolipids
- Carbohydrate-based drug candidates and excipients
- Sugar-functionalized nucleic acids and nanoparticle formulations
Carbohydrates are among the most abundant and structurally complex biomacromolecules in living systems. They are widely distributed on cell surfaces, within the extracellular matrix, and in secreted biomolecules, playing essential roles in structural support, molecular recognition, and signal transduction. Their complexity arises not only from the diversity of monosaccharide building blocks and glycosidic linkage types, but also from the variability and flexibility of their three-dimensional conformations. These conformational features directly influence carbohydrate interactions with proteins, nucleic acids, and other glycans, thereby modulating a wide range of physiological and pathological processes.
Circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy is a sensitive chiroptical technique that enables real-time, label-free detection of carbohydrate conformational properties in solution. CD analysis can provide insights into stereochemistry (D/L configuration), glycosidic linkage conformation (α/β anomers), and overall backbone folding patterns such as helices or coiled structures. In recent years, CD spectroscopy has seen growing applications in carbohydrate chemistry, glycomics, glycan-based vaccine development, and quality control of carbohydrate-based therapeutics. For example, CD can be used to monitor conformational transitions of heparin-like polysaccharides under varying pH or metal ion conditions, informing assessments of structural stability and formulation robustness.
(DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-16712-6_86)
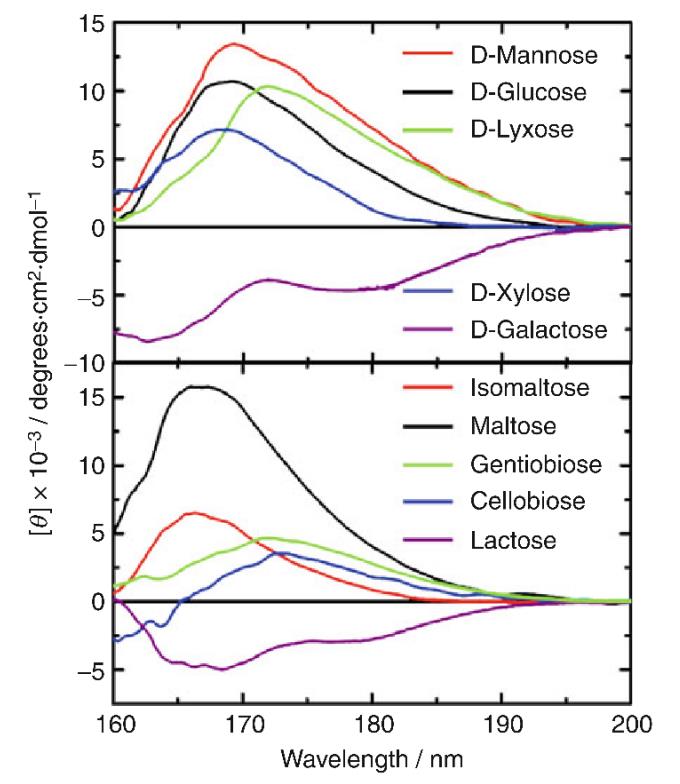
Figure1. Circular Dichroism Spectra of Different Monosaccharides and Disaccharides
Service at MtoZ Biolabs
MtoZ Biolabs offers comprehensive circular dichroism (CD) and synchrotron radiation circular dichroism (SRCD) spectroscopy services for carbohydrate analysis, powered by advanced instrumentation, curated glycan conformational databases, and integrated multi-omics data interpretation capabilities. Our platform supports researchers in investigating carbohydrate conformations, molecular recognition mechanisms, and structural consistency of polysaccharide-based therapeutics. Whether your focus is fundamental carbohydrate chemistry or preclinical development, we provide high-resolution, reliable analytical solutions tailored to your needs.
Our circular dichroism-based carbohydrate analysis services include, but are not limited to:
1. Determination of D/L configuration and glycosidic linkage type (α/β) in monosaccharides and oligosaccharides
2. Conformational analysis of polysaccharide backbones, including helical and folded structures
3. Monitoring of structural changes upon glycan-protein or glycan-nucleic acid interactions
4. Consistency evaluation of polysaccharide drugs and glycan-conjugated vaccines
Analysis Workflow

Why Choose MtoZ Biolabs?
✅Label-Free and Non-Destructive: CD analysis is performed directly in solution without labeling, preserving native glycan conformation for further use.
✅Sensitive to Fine Structural Differences: Effectively distinguishes subtle features such as α/β anomers and helical vs. non-helical arrangements.
✅Compatible with Complex Samples: Supports analysis in biological matrices; can be combined with SEC or HPLC for fraction-specific profiling.
✅Integrates with Other Techniques: Complements NMR, MS, XRD, and FTIR for comprehensive glycan structural characterization.
✅Real-Time Monitoring of Structural Changes: Ideal for tracking conformational shifts induced by pH, temperature, or ligand binding.
Sample Submission Suggestions
Sample Types:
Concentration: 0.1-1.0 mg/mL, adjusted based on molecular weight and absorbance characteristics
Buffer System: Use low-UV absorbance buffers such as ultrapure water, NaF, or 10 mM phosphate buffer; avoid components with strong UV absorbance
Volume: Minimum 300–500 μL per sample
Purity: High-purity, desalted samples are required to avoid interference from metal ions or other contaminants
Application
1. Conformational analysis of natural or synthetic polysaccharides
Including chitosan, dextran, heparin, and other biologically or pharmaceutically relevant glycans
2. Structural consistency assessment of glyco-conjugate vaccines
Characterization of glycan antigens and evaluation of conformational uniformity across batches
3. Investigation of glycan-protein recognition mechanisms
Including lectin-binding interactions and structure-function relationships in glycoprotein complexes
4. Quality control and stability studies of carbohydrate-based therapeutics
Monitoring conformational integrity under various formulation or storage conditions
5. Structural evaluation of glycosylated nucleic acids
Including aptamers, siRNAs, or sugar-functionalized oligonucleotides
Deliverables
• Raw CD spectral data (.txt or .csv format)
• Normalized CD curves (provided in image and PDF formats)
• Annotated spectra and conformational interpretation report
• Experimental Method and Parameter Sheet
• Comprehensive analysis Report
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Can CD spectroscopy distinguish between α- and β-glycosidic isomers?
A1: Yes. CD spectroscopy is highly sensitive to the stereochemistry at the C1 carbon of the sugar ring. Characteristic absorption bands in the far-UV region enable reliable differentiation between α- and β-configurations.
Q2: Is CD suitable for analyzing polysaccharide conformations?
A2: Absolutely. Polysaccharides with repeating 1,4- or 1,6-linkages often adopt helical structures, which exhibit distinctive CD signatures, making them well suited for conformational monitoring.
Q3: Can I submit a limited amount of sample for CD analysis?
A3: Yes. CD analysis typically requires only 100-500 μg of material, making it well suited for analyzing rare or precious carbohydrate samples.
If you would like to receive a service quote or discuss the compatibility of your project, please contact the scientific team at MtoZ Biolabs. We will provide a customized analytical strategy tailored to your research objectives, enabling deeper insight into glycan structure and function.
How to order?







