CD47-Expressed Exosome Modification Service
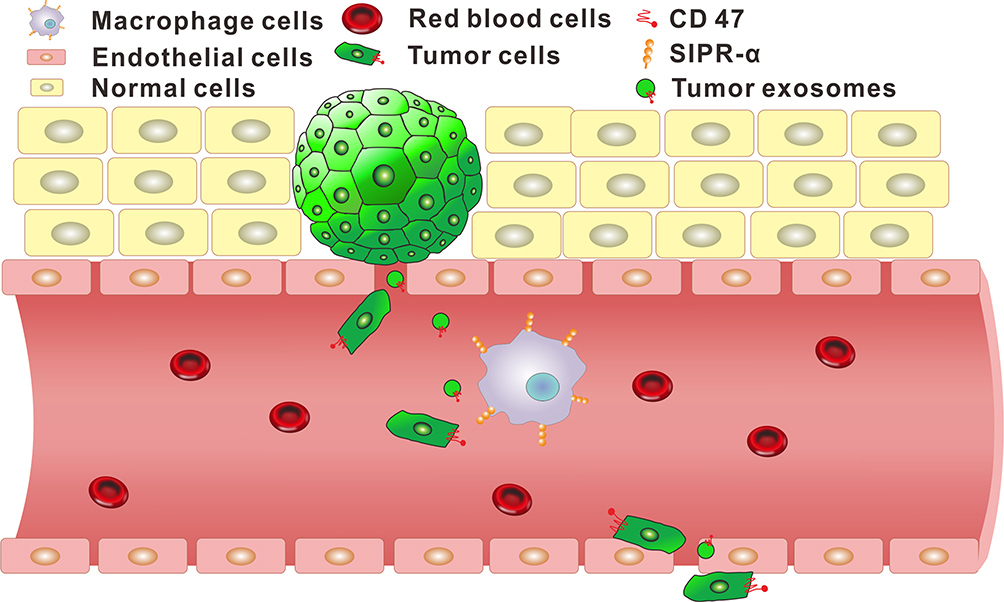
CD47 is a transmembrane glycoprotein that is widely expressed in various cell types. It primarily interacts with signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα) to inhibit macrophage phagocytosis, thereby enabling immune evasion. CD47-modified exosomes are generated through genetic engineering or chemical modification, ensuring the stable expression of CD47 on the exosomal membrane to enhance biocompatibility and circulation stability. The genetic engineering approach involves the overexpression of CD47 in exosome-producing cells, allowing its natural integration into the exosomal membrane during secretion. In contrast, the chemical modification approach employs conjugation techniques or bio-orthogonal chemistry to anchor CD47 onto the surface of isolated and purified exosomes.
The CD47-expressed exosome modification service has broad applications in various biomedical fields. It can be utilized for drug delivery, reducing the rapid clearance of exosomes by the reticuloendothelial system (RES) and improving delivery efficiency. In tumor immunotherapy, CD47-modified exosomes enhance targeting capabilities and improve therapeutic outcomes. Additionally, this technology plays a significant role in stem cell therapy, tissue repair, and autoimmune disease regulation. The development of CD47-modified exosomes provides an innovative solution for the application of exosomes in precision medicine and biotherapeutics.
Lian, S. et al. Oncotargets and Therapy, 2019.
Figure 1. The Function of CD47 in Tumors and Exosome.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Using genetic engineering or chemical modification techniques, MtoZ Biolabs provides the CD47-expressed exosome modification service to enable the stable expression of CD47 on the exosomal membrane, enhancing its immune evasion capability and in vivo stability. The service includes exosome purification, particle size analysis, protein expression validation, and functional assessment, guaranteeing that CD47-modified exosomes meet high-quality standards in terms of structural integrity, modification stability, and biological functionality. Ultimately, we deliver high-purity, high-quality CD47-modified exosomes along with a detailed experimental report, providing reliable data support for immunotherapy, drug delivery, stem cell research, and cancer treatment.
Service Advantages
1. High-Quality Exosome Preparation and Validation
Utilizing high-precision ultracentrifugation, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA), and high-resolution mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) platforms, we ensure exosome purity, uniform particle size distribution, and the stability of CD47 modification.
2. One-Time-Charge
Our pricing is transparent, no hidden fees or additional costs.
3. Efficient and Precise Modification
Utilizing advanced genetic engineering techniques, we ensure the stable expression of CD47, or alternatively, employ chemical conjugation methods to directly modify the exosome surface. This guarantees CD47 activity and functional integrity, optimizing the biological effects of exosomes.
4. Customized Services
MtoZ Biolabs offers flexible CD47-expressed exosome modification strategies tailored to client needs. We provide a comprehensive, one-stop solution covering exosome source selection, modification optimization, functional validation, and data analysis, catering to diverse research directions and personalized requirements.
Applications
1. Tumor Immunotherapy
CD47-modified exosomes can inhibit phagocytosis by the reticuloendothelial system (RES), enhancing their stability in vivo. This makes them effective tumor-targeting drug delivery vehicles, improving therapeutic efficiency while reducing side effects.
2. Stem Cell Therapy and Tissue Regeneration
The CD47-expressed exosome modification service enhances stem cell survival, minimizes clearance by the immune system, and increases the success rate of stem cell therapies. It is widely applied in tissue repair and regenerative medicine.
3. Precision Drug Delivery
Leveraging CD47’s immune evasion properties, modified exosomes serve as highly efficient carriers for RNA, proteins, or small-molecule drugs, playing a crucial role in the treatment of cancer, inflammatory diseases, and neurodegenerative disorders.
4. Autoimmune Disease Modulation
The CD47-expressed exosome modification service can regulate the immune system and reduce abnormal immune responses, demonstrating potential applications in the research and treatment of autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Case Study
1. Camouflage Strategies for Therapeutic Exosomes Evasion from Phagocytosis
This study aims to explore the enhancement of immune evasion in exosomes through CD47 modification, thereby reducing phagocytosis and improving in vivo stability. The study subjects include natural exosomes and CD47-modified exosomes, with a focus on analyzing CD47 expression on the exosomal surface and its impact on phagocytosis. The research employs two modification strategies: genetic engineering and chemical conjugation. CD47 is either overexpressed in exosome-producing cells or conjugated onto the surface of purified exosomes using coupling techniques. Various analytical methods, including flow cytometry (FACS), nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and in vivo pharmacokinetic studies, are used to evaluate CD47 expression levels, particle size distribution, stability, and circulation time. The results indicate that CD47-modified exosomes significantly reduce macrophage phagocytosis, prolong their half-life in circulation, and improve drug delivery efficiency. The study concludes that CD47 modification effectively enhances the immune evasion capability of exosomes, making them promising drug delivery vehicles and immune regulatory tools, offering new strategies for cancer therapy, inflammation modulation, and stem cell therapy.
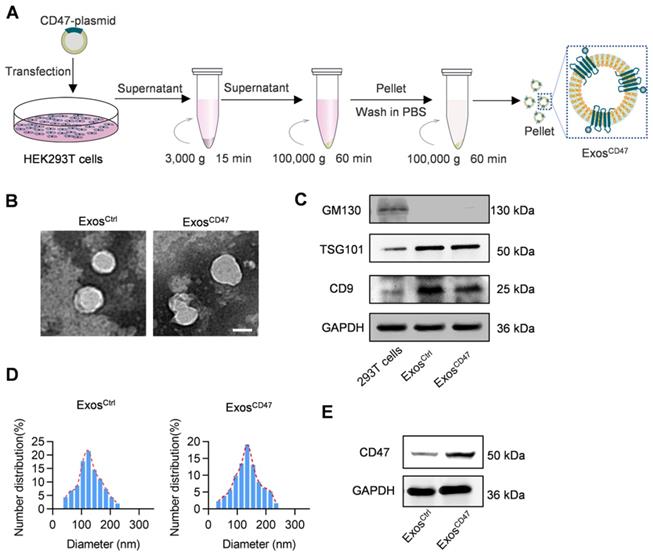
Du, J B. et al. Theranostics, 2021.
Figure 2. Preparation and Characterization of ExosCD47.
2. Construction of Exosomes that Overexpress CD47 and Evaluation of Their Immune Escape
This study aims to construct CD47-overexpressing exosomes and evaluate their immune evasion capability to enhance exosomal stability in vivo and reduce macrophage-mediated phagocytosis. The study subjects include engineered CD47-overexpressing exosomes and unmodified natural exosomes. By comparing their phagocytosis rates and circulation times, the immune regulatory effects of CD47 modification are analyzed. The research employs genetic engineering techniques to overexpress CD47 in exosome-producing cells, ensuring its stable integration into the exosomal membrane during secretion. Various analytical methods, including transmission electron microscopy (TEM), nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA), flow cytometry (FACS), and in vivo mouse studies, are used to assess particle size, morphology, CD47 expression levels, and immune evasion ability. The results indicate that CD47 modification significantly reduces macrophage phagocytosis, prolongs exosomal circulation time, and enhances drug delivery efficiency. The study concludes that CD47-modified exosomes effectively improve immune evasion, making them promising biotherapeutic tools and providing new strategies for cancer immunotherapy, precision drug delivery, and stem cell research.
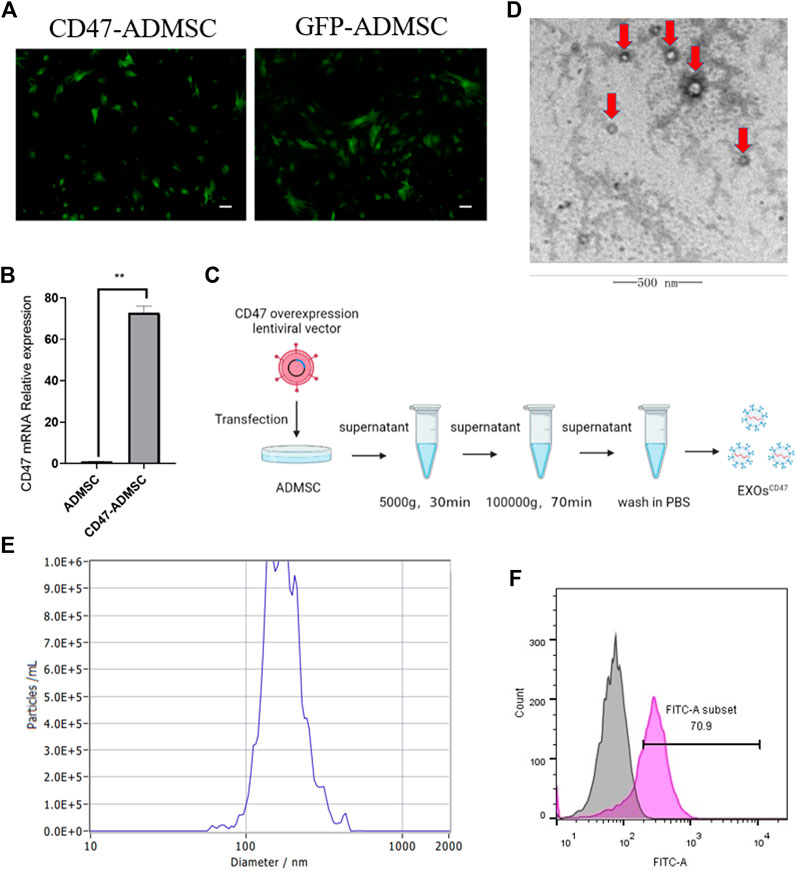
Ben, X Y. et al. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2022.
Figure 3. Development and Characterization of ExosomesCD47.
FAQ
Q1: Why Is it Necessary to Modify CD47 on Exosomes?
A1: CD47 is a transmembrane glycoprotein that interacts with signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα) to transmit a “don’t eat me” signal to the immune system, thereby inhibiting macrophage-mediated phagocytosis of exosomes. Unmodified exosomes, upon entering the body, are rapidly cleared by the reticuloendothelial system (RES), leading to a short circulation time and reduced efficacy as delivery vehicles. By modifying CD47 on the exosomal membrane, immune clearance can be effectively reduced, enhancing exosome stability and delivery efficiency. This modification significantly improves exosome applications in tumor immunotherapy, stem cell therapy, and precision drug delivery.
Q2: What Are the Methods for Preparing CD47-Modified Exosomes?
A2: There are two main approaches: genetic engineering modification and chemical modification.
Genetic engineering modification: CD47 is overexpressed in exosome-producing cells, allowing its natural integration into the exosomal membrane during exosome secretion. This method ensures stable CD47 expression while maintaining its biological function.
Chemical modification: CD47 molecules are directly conjugated onto the surface of purified exosomes using conjugation techniques or bio-orthogonal chemistry. This approach is suitable for post-isolation modifications of exosomes without requiring genetic manipulation of source cells.
How to order?







