Capillary Flow Porometry Analysis Service
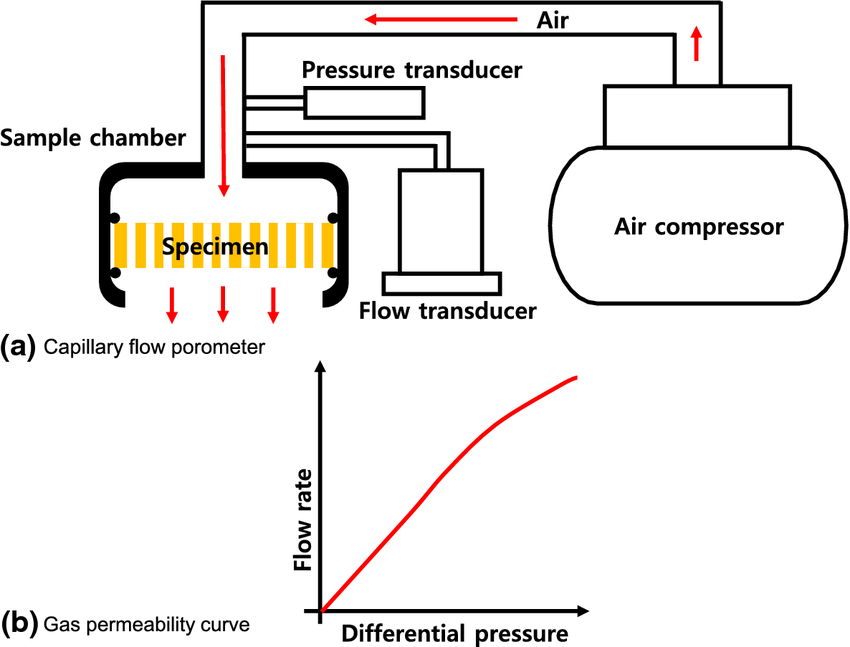
Capillary flow porometry is a precise analytical technique used to measure pore size distribution, pore structure, and permeability of porous materials. Its basic principle is to displace the liquid that completely wets the sample with an inert gas. As the gas pressure gradually increases and breaks through the capillary pores, the liquid is expelled, and flow channels are formed. By recording the relationship between pressure and gas flow rate, parameters such as maximum pore size, minimum pore size, and average pore size can be obtained. This method is characterized by simple operation, high sensitivity, and a wide range of applications. It is widely used to analyze the pore size distribution and permeability characteristics of sheet membranes, hollow fiber tubes, and biological porous matrices, supporting structural studies and functional evaluations of biological samples.
Jang, E. et al. Wood Science and Technology, 2021.
Figure 1. Schematic Diagram of Capillary Flow Porometer and Gas Permeability Curve
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Based on a high-performance capillary flow porometer, MtoZ Biolabs has launched a capillary flow porometry analysis service that can real-time monitor the flow and pressure changes of porous materials during the gas displacement process, thereby accurately analyzing key pore size parameters. This service can be used to characterize the pore structure and permeability of samples such as cell membranes, filtration membranes, and biological porous matrices. The final output data include complete pressure–flow curves, pore size distribution charts, and quantitative parameter reports, providing researchers with reliable pore structure characterization and functional evaluation support.
Analysis Workflow
1. Sample Preparation
Perform wetting treatment on the sample to be tested, ensuring the liquid fully fills the pores to provide stable conditions for subsequent gas displacement.
2. Gas Pressurization
Gradually increase the inert gas pressure to overcome the capillary action of the liquid in the pores, starting from the largest pore size and progressively opening the channels.
3. Flow Monitoring
Record in real time the changes in gas flow under different pressures, capturing key signals during the pore-opening process.
4. Data Acquisition
Obtain pressure–flow curves and the corresponding pore size distribution data, including average pore size, pore size range, and permeability parameters.
5. Result Analysis
Fit and analyze the data using models, outputting pore size distribution graphs and quantitative results to reveal the pore structure characteristics of the sample.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Type
Applicable to filter membranes, thin films, porous materials, and biologically related matrices. Samples must be representative and uniform to ensure the reliability of pore size measurements.
2. Sample Purity
It is recommended to remove impurities, moisture, or contaminants to avoid interference with gas flow and pore size signal analysis during pressurization.
3. Sample Storage
Samples should be stored in a dry, dark, and appropriate temperature environment to prevent moisture absorption or structural changes from affecting pore characteristics.
4. Sample Transportation
Use sealed containers during transportation, and apply moisture-proof or cold-chain conditions if necessary to ensure that samples remain intact and stable before reaching the testing platform.
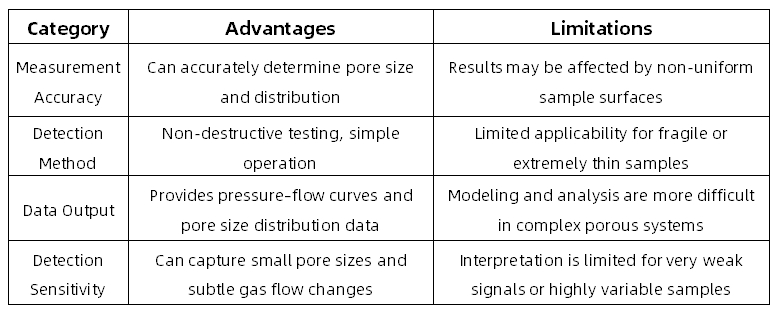
Advantages and Limitations
Applications
1. Cell and Biomembrane Studies
By analyzing the pore size distribution and permeability characteristics of samples such as cell membranes and artificial biomembranes, this method helps study structural integrity and functional performance.
2. Filtration and Separation Performance Evaluation
Capillary flow porometry analysis service can be used to detect the pore structure of filter membranes or porous matrices, supporting their application in the filtration and separation of biological samples.
3. Quality and Stability Control
Through monitoring pore size and flow data, it supports the evaluation of the consistency and reliability of biological samples and related materials in experiments or applications.
4. Biomaterial Characterization
Capillary flow porometry analysis service can be applied to the pore size characterization of tissue engineering scaffolds, nano-porous materials, and other biologically related materials to assess their suitability and performance.
FAQs
Q1: Will the Testing Damage the Sample?
A1: This method is generally a non-destructive test and does not alter the overall structure of the sample. However, some fragile or extremely thin samples may undergo deformation during pressurization, so prior evaluation is necessary.
Q2: What Factors May Affect the Accuracy of the Results?
A2: Sample non-uniformity, insufficient wetting, the presence of impurities, or gas leakage may all lead to abnormal signals or data deviations. Therefore, strict sample preparation is crucial.
Q3: What Are the Advantages Compared with Other Pore Size Analysis Methods?
A3: Capillary flow porometry is simple to operate and can monitor gas flow changes in real time, providing more intuitive pore size distribution data, especially suitable for detecting pores from the micrometer to nanometer scale.
How to order?







