Advantages and Disadvantages of Untargeted Metabolomics
-
Sample pretreatment (including extraction, protein removal, and derivatization);
-
High-resolution mass spectrometric analysis;
-
Data preprocessing (peak detection, alignment, and normalization);
-
Multivariate statistical analysis and pattern recognition;
-
Metabolite identification and metabolic pathway enrichment analysis.
In life science research, metabolomics serves as a critical bridge between genotype and phenotype. As the final downstream products of biological processes, metabolites most directly reflect the integrated responses of cells, tissues, or whole organisms to genetic regulation, environmental stimuli, and disease states. Among current analytical strategies, untargeted metabolomics, characterized by broad analytical coverage and a high potential for novel discovery, has been widely applied in disease mechanism investigation, studies of drug modes of action, nutritional metabolism, and environmental toxicology.
Definition and Core Technologies of Untargeted Metabolomics
Untargeted metabolomics refers to a comprehensive analytical strategy that aims to detect and analyze as many metabolites as possible within a sample without predefining specific target compounds. Rather than focusing on a single class of metabolites, this approach relies on high-resolution mass spectrometry platforms (such as Orbitrap or time-of-flight analyzers) coupled with chromatographic separation techniques (including LC-MS and GC-MS) to generate global metabolic profiles.
The core workflow typically includes:
At MtoZ Biolabs, untargeted metabolomics solutions are developed based on high-resolution mass spectrometry platforms, such as the Thermo Orbitrap Exploris series, in combination with internally optimized metabolite databases. These solutions offer broad metabolite coverage and high analytical reproducibility, supporting the extraction of biologically meaningful metabolic signals from complex biological matrices.
Advantages of Untargeted Metabolomics
1. Comprehensive Metabolite Coverage for Mechanism Exploration
Because untargeted strategies do not depend on predefined metabolite lists, they enable the simultaneous detection of both known and previously uncharacterized metabolites. This feature provides substantial opportunities for novel mechanism discovery and disease biomarker identification.
2. Strong Data-Driven Discovery Capability
By integrating multivariate statistical approaches, such as PCA and PLS-DA, with machine learning algorithms, untargeted metabolomics enables the extraction of potential biomarkers and metabolic patterns from high-dimensional datasets. This approach is particularly suitable for exploratory studies in which clear biological hypotheses have not yet been established.
3. Broad Applicability Across Species and Sample Types
Untargeted metabolomics demonstrates strong adaptability across diverse sample types, including serum, urine, tissues, cells, as well as plant and animal samples. Owing to its platform versatility, this strategy is well suited for constructing global metabolic landscapes and for comparative metabolic analyses across different species.
4. Support for Downstream Targeted Validation and Pathway Expansion
Untargeted metabolomics is commonly employed as an initial discovery tool, after which targeted quantitative techniques, such as MRM, can be applied to validate key metabolites. Furthermore, metabolic pathway enrichment analyses can provide mechanistic insights and guide subsequent functional experiments.
Disadvantages and Challenges of Untargeted Metabolomics
1. Challenges in Qualitative Identification: Unknown Metabolites Remain a Major Bottleneck
Despite significant advances in mass spectrometry, the identification of a large number of unknown spectral features remains challenging. Current metabolite databases have limited coverage, and structural elucidation often depends on comparison with authentic standards or manual interpretation of fragmentation spectra, which can constrain data interpretation in certain studies.
2. Relatively Limited Quantitative Accuracy
In contrast to targeted metabolomics, which employs internal standard calibration and clearly defined linear quantitative ranges, untargeted metabolomics is more susceptible to signal drift and matrix effects. As a result, absolute quantification is generally limited, and comparative analyses are typically based on relative abundance.
3. High Requirements for Batch Effect Control and Reproducibility
Untargeted metabolomics places stringent demands on instrument stability and consistency in sample preparation. Batch-to-batch variability can significantly influence analytical outcomes, necessitating the use of quality control samples, signal correction strategies, and rigorous experimental design to minimize technical variation.
4. Complex Data Processing and High Analytical Demands
The large data volume, high dimensionality, and complexity of preprocessing and statistical workflows require substantial expertise in data analysis. Researchers often need strong bioinformatics capabilities or professional analytical platforms to ensure reliable data interpretation.
Research Scenarios Suitable for Untargeted Metabolomics
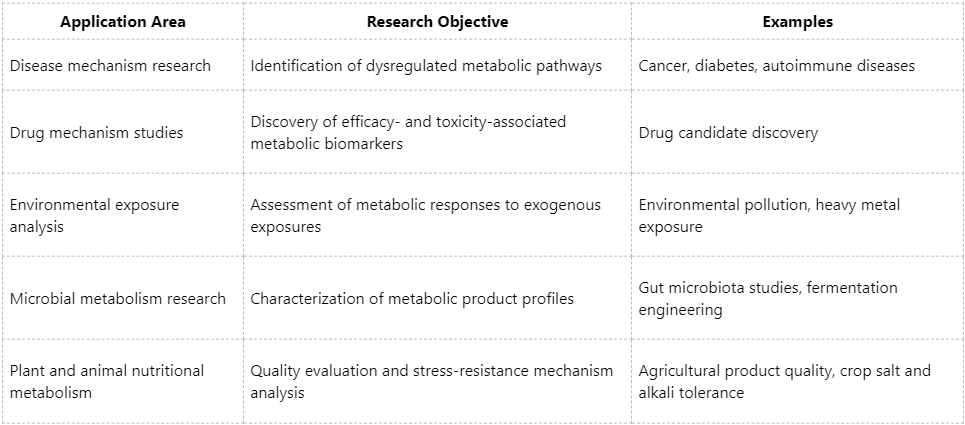
With its unbiased and high-throughput analytical characteristics, untargeted metabolomics provides a powerful approach for capturing the global metabolic landscape in life science research. It represents not only a key tool for biomarker discovery but also an essential strategy for understanding biological system complexity. Nevertheless, as no analytical technology is without limitations, the application of untargeted metabolomics should be carefully balanced against research objectives, sample characteristics, and budget considerations. In practice, it is often most effective when applied as an exploratory approach in combination with targeted quantitative strategies, enabling deeper mechanistic investigation and functional validation. MtoZ Biolabs has more than a decade of experience in mass spectrometry-based omics analysis and operates a well-established untargeted metabolomics platform supported by extensive project experience and a professional bioinformatics team. Beyond data acquisition, MtoZ Biolabs emphasizes the transformation of metabolomics data into scientifically rigorous and publishable research outcomes. We welcome inquiries for complimentary experimental design consultation and project evaluation, ensuring that metabolomics data effectively support defined research goals.
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
How to order?







