3-Hydroxytyramine Analysis Service
- Highly Efficient Sample Recovery and Processing
- Accurate and Reliable Detection and Quantification
- Capability to Handle Various Sample Types
- Customized Data Analysis Services
- Rapid Service Response and Cost-Effectiveness
- Neurological Research
- Drug Development
- Clinical Diagnostics
- Behavioural Studies
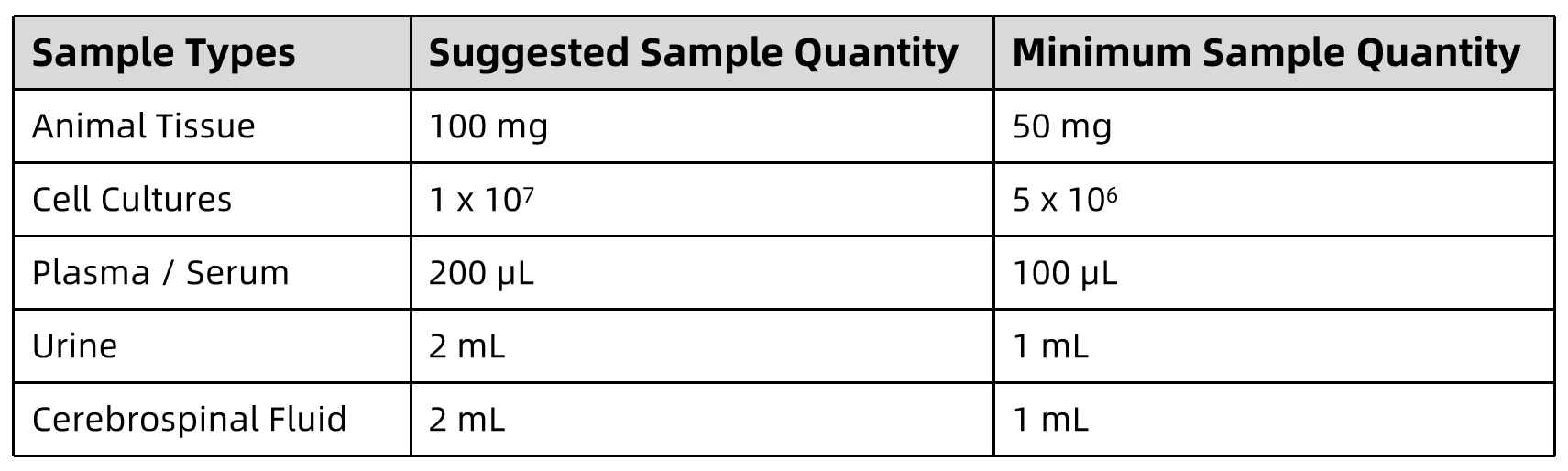
- Samples should be stored at -80℃ and shipped with dry ice.
- We recommend providing at least 3 samples of similar conditions for each type of sample.
- Other sample types, please contact us for more details.
3-Hydroxytyramine, commonly known as dopamine, is a crucial catecholamine neurotransmitter in the brain. Its chemical structure consists of a benzene ring with two hydroxyl groups at the 3- and 4-positions and an ethylamine side chain, making it a 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine. Dopamine is synthesized primarily in neurons from the amino acid tyrosine through a two-step enzymatic pathway. First, tyrosine is hydroxylated to form L-DOPA (L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine) by the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase. Subsequently, L-DOPA is decarboxylated by dopa decarboxylase (DDC) to produce dopamine.
Dopamine plays a central role in regulating motor control, reward-seeking behavior, mood, and various physiological processes, including cardiovascular and endocrine functions. Beyond its role in neurotransmission, dopamine serves as a precursor for other catecholamines such as norepinephrine and epinephrine, further extending its metabolic significance. The degradation of dopamine involves several pathways, primarily through enzymes such as monoamine oxidase (MAO) and catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT), leading to metabolites like homovanillic acid (HVA) and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC), which are often studied to understand dopamine turnover and metabolism.
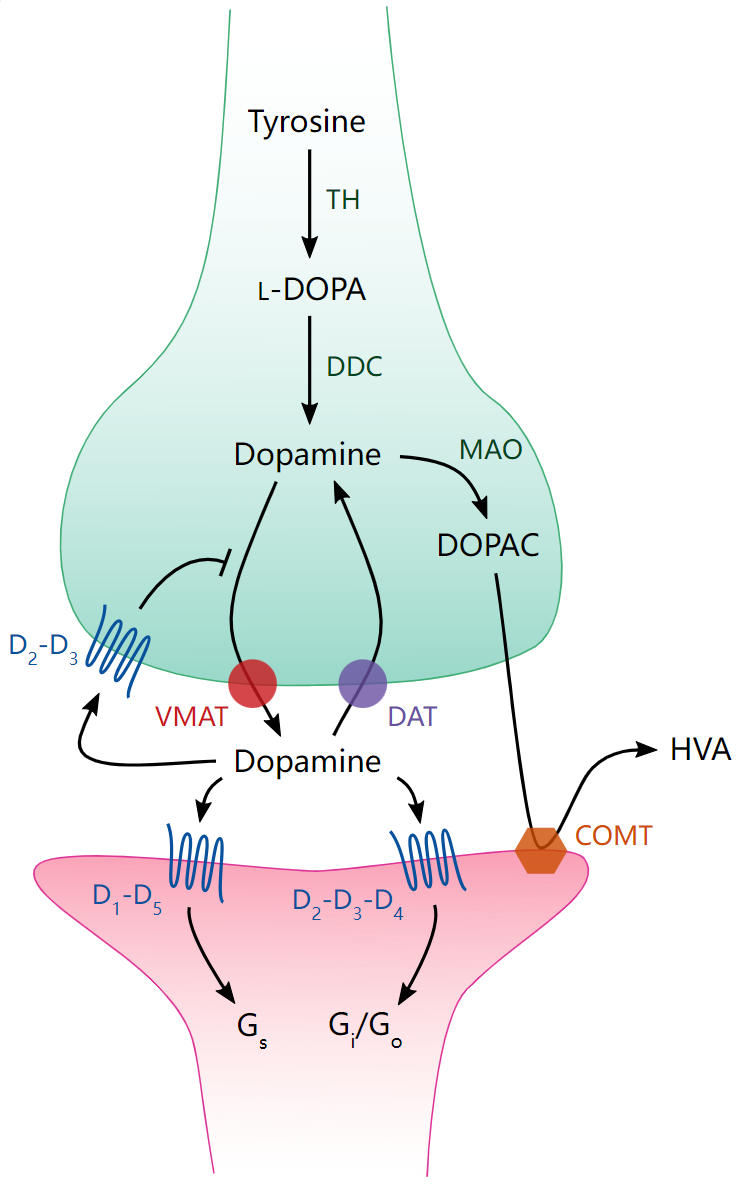
Figure 1. Dopamine Processing in A Synapse
The study of dopamine and its metabolic pathways is critical due to its involvement in several neurological and psychiatric disorders, including Parkinson's disease, schizophrenia, and addiction. Dopamine dysfunction has been linked to neurodegenerative conditions where dopamine-producing neurons degenerate, leading to movement disorders and cognitive decline. Therefore, accurate measurement and analysis of dopamine levels and its related metabolites can provide valuable insights into disease mechanisms, therapeutic targets, and overall brain health.
At MtoZ Biolabs, our team of experts in mass spectrometry and metabolomics is equipped to provide accurate, reproducible, and reliable 3-Hydroxytyramine analysis service. We can help you determine the concentration of 3-Hydroxytyramine in a variety of sample types, providing valuable insights for your research projects.
Analysis Workflow
1. Sample Preparation: Biological samples are collected and prepared according to standard protocols.
2. Metabolite Extraction: Extraction of 3-Hydroxytyramine from the provided samples.
3. Instrumental Analysis: Utilization of advanced mass spectrometry for the analysis.
4. Data Processing and Interpretation: Comprehensive data analysis by our team of experts.
5. Report: Detailed report of the analysis and findings will be provided.
Service Advantages
Applications
Our 3-Hydroxytyramine analysis service can be applied in a wide range of fields:
Sample Submission Requirements
Deliverables
1. Experimental Procedures
2. Relevant Liquid Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry Parameters
3. Detailed Information on 3-Hydroxytyramine
4. Raw Data
5. Custom Analysis Report
We look forward to serving your research needs. Please feel free to contact us for more information or to request a quote.
How to order?







