Virus Infections Diagnosis-Applied Exosomes
Exosomes are nanoscale extracellular vesicles (30-150 nm) released by cells. They carry proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, and other molecules that reflect the physiological or pathological state of their parent cells. Exosomes play a pivotal role in intercellular communication and disease pathogenesis. In viral infections, exosomes encapsulate viral components (e.g., proteins, genomic fragments) and host-derived molecules altered by infection, offering a non-invasive window into viral activity and host immune responses. MtoZ Biolabs specializes in providing integrated Virus Infections Diagnosis-Applied Exosomes services, combining advanced exosome isolation, characterization, and multi-omics profiling to decode infection-related biomarkers and advance your viral infection diagnostics research.
Exosomes play a dual role in viral infections, acting as both vehicles for viral dissemination and mediators of host immune responses. During infection, viruses hijack the host exosome biogenesis machinery to package viral components—such as genomic RNA, proteins (e.g., SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoproteins), and microRNAs—into exosomes. These virus-modified exosomes facilitate immune evasion by masking viral antigens, enable long-distance spread of infection to uninfected cells, and modulate recipient cell environments to favor viral replication. Conversely, host cells also release exosomes containing antiviral miRNAs, cytokines (e.g., interferons), and stress-response proteins to counteract infection, alert neighboring cells, and recruit immune defenses.
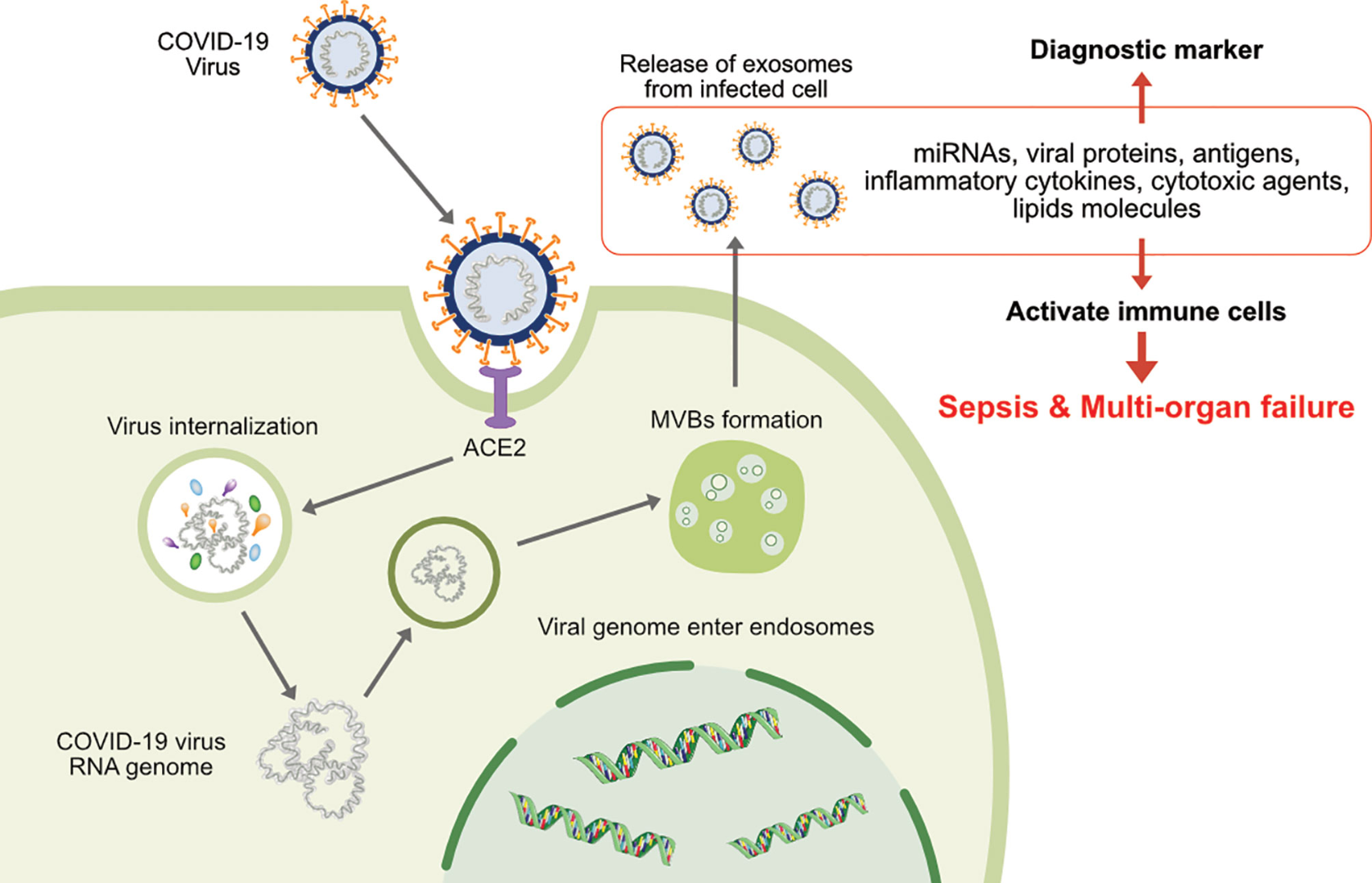
Figure 1. The Dual Function of Exosomes in Virus Infections
The diagnostic potential of exosomes lies in their ability to capture real-time molecular signatures of infection. For instance, exosomal viral proteins or RNA can indicate active replication, while host-derived exosomal biomarkers (e.g., cytokines, stress-response proteins) reveal systemic immune activation. Unlike traditional diagnostic methods reliant on direct pathogen detection or invasive biopsies, exosome-based approaches enable early, sensitive, and longitudinal monitoring of viral infections through easily accessible biofluids like blood or urine.
Service at MtoZ Biolabs
MtoZ Biolabs offers Virus Infections Diagnosis-Applied Exosomes services to support exosome-based biomarker discovery and diagnostic development for viral infections. We provide high-purity exosome isolation from clinical samples using ultracentrifugation, SEC, and immunoaffinity methods, ensuring specificity and minimal contamination. Our comprehensive analysis includes exosomal proteomics, total RNA-seq, miRNA-seq, lncRNA-seq, and circRNA-seq, enabling detailed profiling of exosomal cargo linked to viral pathogenesis. These services facilitate non-invasive diagnosis, disease monitoring, and host-virus interaction studies.
MtoZ Biolabs delivers customized, end-to-end solutions tailored to client-specific viral models, including but not limited to HBV, HCV, HIV, SARS-CoV-2, EBV, CMV, and other emerging pathogens, addressing key challenges in virus diagnostics, from sample preparation to data analysis and interpretation. If you are interested in our Virus Infections Diagnosis-Applied Exosomes service, please feel free to contact us. Our technical specialists are available to provide a free business assessment.
Service Advantages
✔️Cutting-Edge Multi-Omics Platforms: Leverage high-sensitivity mass spectrometry and integrated lipidomics/transcriptomics workflows to achieve deep, unbiased profiling of exosomal cargo.
✔️End-to-End Expertise: From exosome isolation to biomarker validation, our PhD-led team ensures rigorous, publication-ready results aligned with clinical diagnostic standards.
✔️Rapid Turnaround: Streamlined workflows deliver actionable data quickly, accelerating research and therapeutic decision-making.
✔️Customizable Solutions: Tailored services adapt to diverse pathogens, sample types, and research goals.
Applications
Our Exosome-Based Viral Infection Diagnostics services empower groundbreaking research and clinical applications, including:
1. Early Detection of Viral Infections
Identify asymptomatic or pre-symptomatic carriers through sensitive detection of exosome-encapsulated viral proteins (e.g., SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid) or host-derived biomarkers.
2. Therapeutic Efficacy Monitoring
Track dynamic changes in exosomal viral load or immune-modulatory proteins to evaluate drug or vaccine impacts.
3. Biomarker Discovery for Vaccine Development
Uncover exosomal antigens or immune-activating molecules (e.g., MHC complexes) to guide antiviral vaccine design.
4. Mechanistic Insights into Viral Pathogenesis
Decipher host-pathogen interactions via multi-omics integration.
Case Study
Exosome-Based Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 Infection
In this study, a proteomic approach was utilized to analyze exosomes isolated from the plasma of COVID-19 patients and healthy volunteers. The aim was to determine if exosomes could serve as carriers for virus-induced soluble mediators that might trigger cytokine storms and tissue damage, a hallmark of severe COVID-19 infections. The results revealed that two proteins, tenascin-C (TNC) and fibrinogen-β (FGB), were highly abundant in the exosomes of COVID-19 patients. Both of these proteins are known to stimulate pro-inflammatory cytokines through the Nuclear Factor-κB (NF-κB) pathway. Further examination showed that when hepatocytes were exposed to exosomes from COVID-19 patients, there was a significant increase in pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and C-C motif chemokine ligand 5 (CCL5), compared to the exposure to exosomes from healthy subjects. The findings underscore the potential of exosome-based diagnostics for identifying viral infections and understanding their impact on distant organs. Through this approach, MtoZ Biolabs can offer advanced diagnostic solutions by utilizing exosome profiling for identifying viral infection biomarkers and providing insights into their inflammatory pathways.
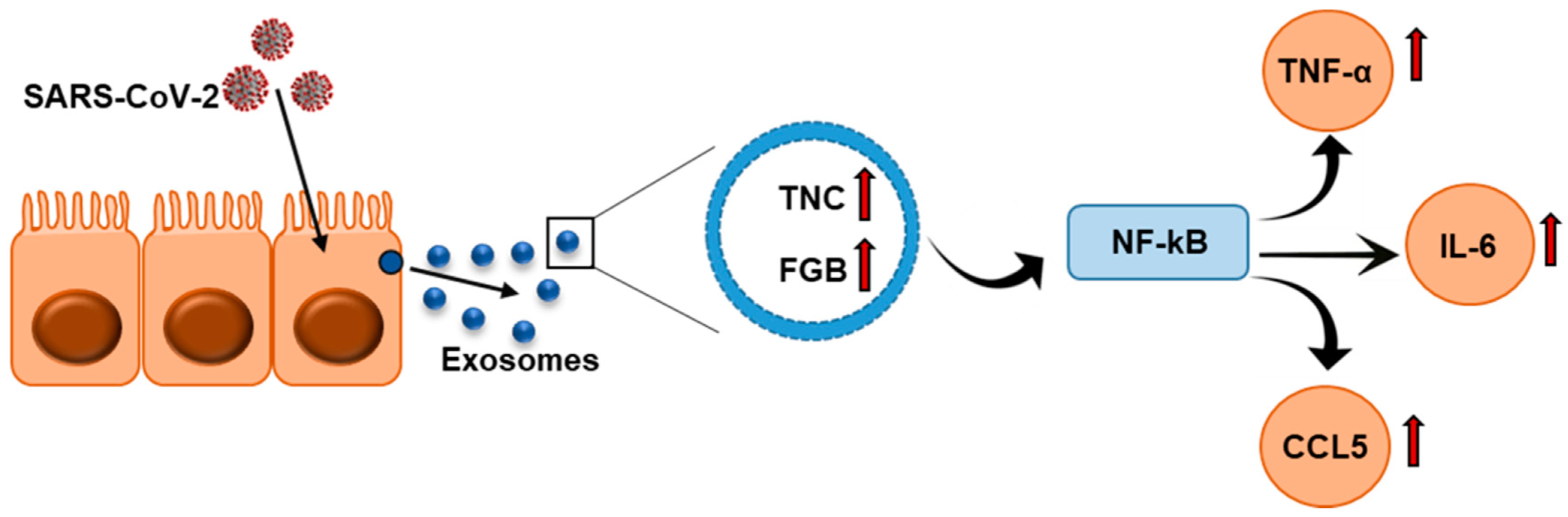
Figure 2. Schematic Representation Shows Exosomes Secreted from SARS-CoV-2-Infected Cells are Enriched with TNC and FGB Triggering TNF-α, IL-6, and CCL5 Production in Hepatocytes via NF-κB Signaling
FAQ
Q: Can exosome-based diagnostics identify viral infections in asymptomatic individuals?
Yes, exosome-based diagnostics can potentially identify viral infections in asymptomatic individuals. Exosomes carry viral particles, proteins, and RNA from infected cells, which can serve as early indicators of infection before clinical symptoms appear. By analyzing the molecular cargo of exosomes, such as viral RNA or specific proteins, it is possible to detect viral presence and monitor infection at early stages, even in asymptomatic individuals. This approach offers a non-invasive, sensitive, and rapid method for early detection, aiding in timely intervention and disease management.
How to order?







