Vaccine Development Service
- Surface modification (ligand conjugation, lipid bilayer engineering, or antibody decoration for targeted delivery)
- Cargo loading (genetic engineering, electroporation, sonication, or passive incubation for antigen, mRNA, siRNA, or protein encapsulation)
- Proteomics: Identification of exosomal proteins via LC-MS/MS and label-free quantification
- Lipidomics: Characterization of exosomal lipids via high-resolution MS and chromatography
- Metabolomics: Profiling of exosome-associated metabolites for immunomodulatory functions
- Transcriptomics: RNA-seq and small RNA-seq to analyze exosomal mRNA, miRNA, lncRNA, and circRNA
Vaccination remains a cornerstone of modern medicine, effectively preventing and controlling infectious diseases, cancers, and other chronic conditions. As global health challenges evolve, so does the demand for innovative vaccine technologies that offer enhanced safety, efficacy, and specificity. Exosome-based vaccines have emerged as a revolutionary approach that leverages the natural properties of exosomes—nanoscale extracellular vesicles secreted by cells—to deliver antigens and stimulate potent immune responses. Unlike traditional vaccines that often rely on live attenuated viruses, inactivated pathogens, or synthetic particles, exosome-based vaccines offer a natural, biocompatible platform for precise antigen presentation, significantly reducing the risk of adverse immune reactions. By harnessing exosomes' intrinsic ability to carry proteins, RNAs, and lipids, these vaccines can effectively mimic native immune interactions and deliver targeted immune stimulation. MtoZ Biolabs introduces a Vaccine Development Service that focuses on cutting-edge exosome-based vaccine development solutions. From early-stage antigen discovery to preclinical validation, MtoZ Biolabs provides end-to-end services to accelerate the development of therapeutic and preventive vaccines for cancer, infectious diseases, and emerging pathogens.
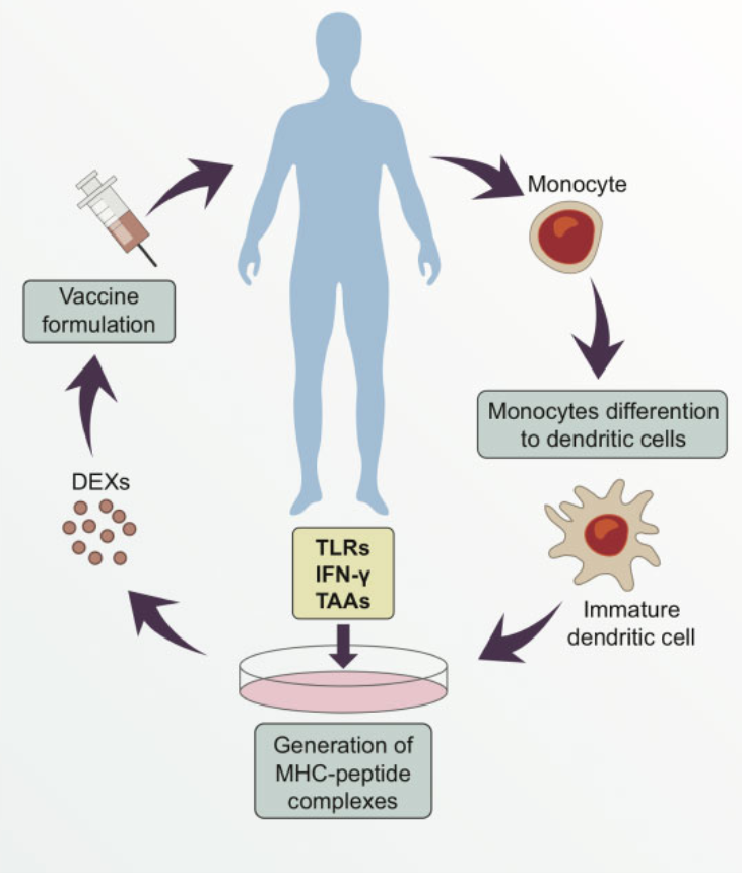
Figure 1. Simplified Illustration of a Personalized Vaccine using Exosomes Derived from Dendritic Cells (DEXs)
Key Features of Exosome-Based Vaccines
1. Natural Nanocarriers for Antigen Delivery
Exosomes are naturally occurring nanoscale vesicles capable of delivering a wide range of biomolecules, including proteins, peptides, nucleic acids, and lipids. Their biocompatible and membrane-enclosed structure protects vaccine antigens from enzymatic degradation and enhances delivery efficiency to target cells.
2. Intrinsic Immunomodulatory Properties
Exosomes inherently contain immunologically active components such as MHC molecules, heat shock proteins, and adhesion molecules, which enable them to mimic natural antigen presentation and stimulate both innate and adaptive immune responses without requiring synthetic adjuvants.
3. Enhanced Targeting and Cellular Uptake
Exosomes can be engineered to express targeting ligands or antibodies on their surface, facilitating selective delivery to dendritic cells (DCs), lymph nodes, or specific tissues. Their natural ability to fuse with recipient cells enhances antigen uptake and processing.
4. Reduced Risk of Adverse Reactions
As endogenous vesicles, exosomes demonstrate excellent biocompatibility and low immunogenicity, reducing the risk of severe immune responses and toxicity commonly associated with synthetic nanoparticles or viral vectors.
Service at MtoZ Biolabs
MtoZ Biolabs offers a full suite of exosome-based vaccine development services, leveraging cutting-edge multi-omics and bioengineering technologies to accelerate the discovery, characterization, and optimization of exosome-based immunotherapies. Our expertise in exosome isolation, purification, characterization, engineering, and functional analysis provides a robust platform for vaccine research and development.
Our services include:
1. Exosome Isolation and Purification
Using ultracentrifugation, size-exclusion chromatography (SEC), microfluidics technology, and immunoaffinity capture, we ensure high-purity exosome isolation from diverse sources such as cell cultures, biological fluids, and engineered cells.
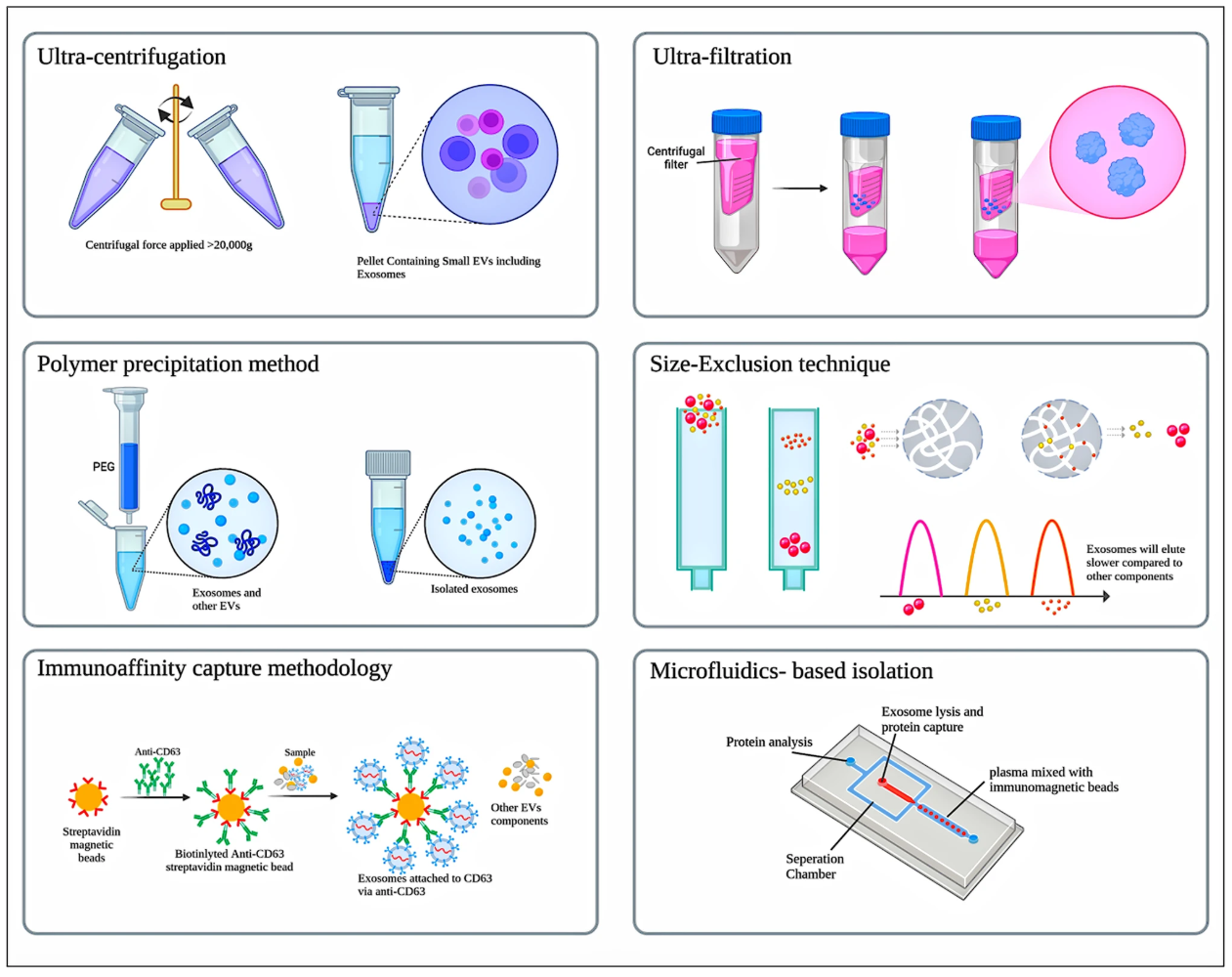
Figure 2. Different Isolation Techniques of Exosomes
2. Exosome Characterization
MtoZ Biolabs applies transmission electron microscopy (TEM), nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA), dynamic light scattering (DLS), and flow cytometry to assess exosome morphology, size distribution, and surface markers, ensuring vaccine-grade quality.
3. Exosome Biomarker Profiling
We provide precise quantification and identification of exosomal biomarkers using Western blotting, ELISA, mass spectrometry (MS)-based proteomics, and RNA sequencing, helping to validate exosome-based immunogenic cargo for vaccine development.
4. Exosome Engineering
Our advanced bioengineering solutions allow the modification of exosomes to enhance antigen presentation and immune response:
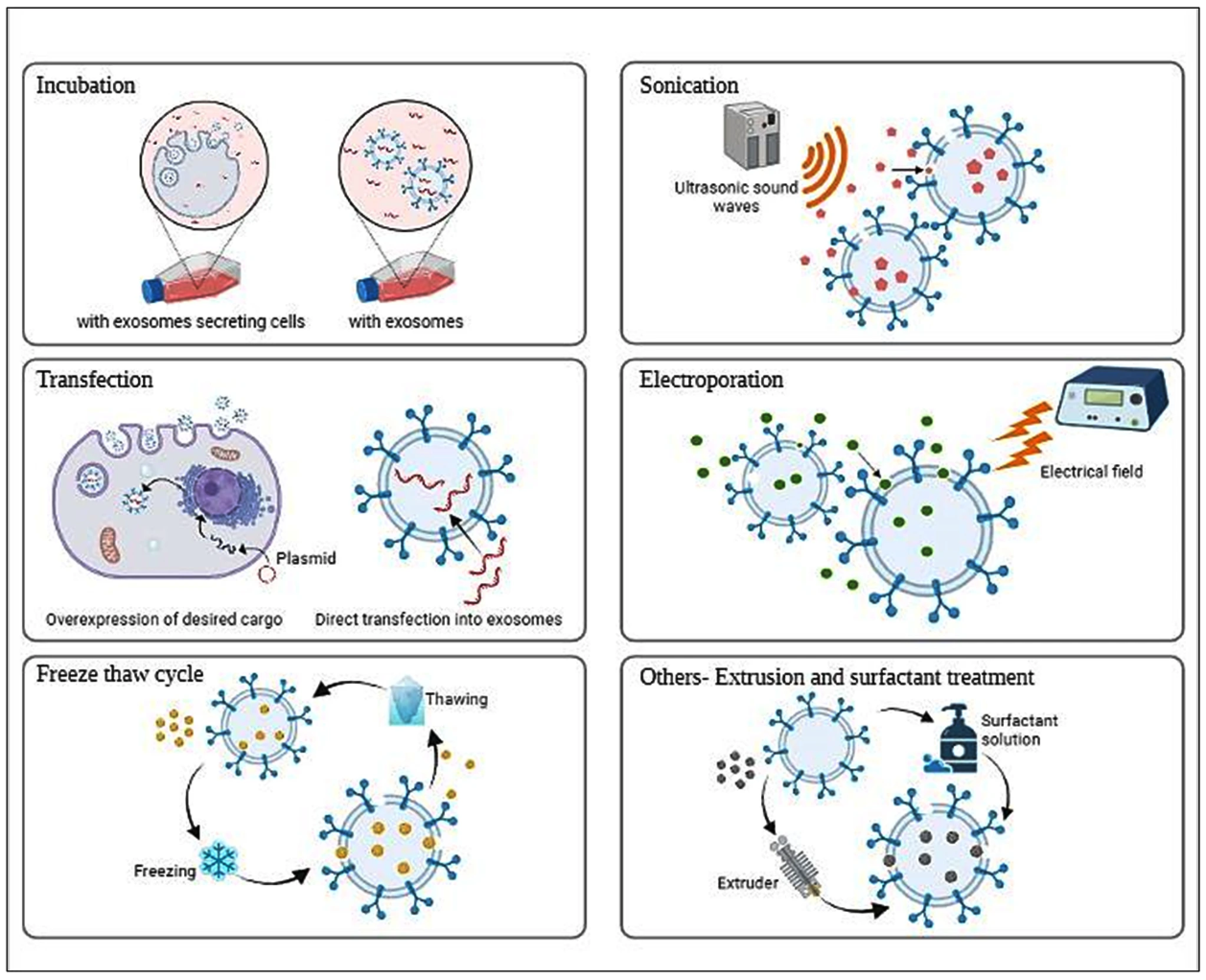
Figure 3. Different Methods of Loading Cargo into Exosomes
5. Multi-Omics Analysis of Exosomes
We offer a comprehensive multi-omics approach to study exosomal composition and function:
6. Functional Assessment of Exosomes
We conduct in vitro and in vivo functional studies to assess exosome-induced immune responses and therapeutic efficacy
Why Choose MtoZ Biolabs?
☑️Advanced Platform: MtoZ Biolabs' advanced exosome vaccine development platform combines proteomics, transcriptomics, and lipidomics to systematically isolate and characterize exosome vaccines and guarantee high-quality, reproducible results.
☑️Highly Experienced Team: A multidisciplinary team with extensive expertise in exosome biology, immunology, and vaccine development guides each project from conception to delivery.
☑️End-to-End Service Solutions: From exosome isolation and engineering to preclinical validation, MtoZ Biolabs offers fully customizable, one-stop solutions tailored to client needs.
☑️Transparent and Competitive Pricing: MtoZ Biolabs offers clear pricing with no hidden costs, providing cost-effective, high-value solutions to accelerate vaccine development.
Applications
1. Cancer Immunotherapy
Exosome vaccines loaded with tumor-specific antigens (TSAs) and tumor-associated antigens (TAAs) can induce robust anti-tumor T cell responses. Applicable for melanoma, breast cancer, lung cancer, colorectal cancer, glioblastoma, and more.
2. Infectious Disease Vaccines
Exosome-based vaccines presenting viral or bacterial antigens offer promising solutions for COVID-19, influenza, HIV, hepatitis, and emerging pathogens by stimulating both innate and adaptive immunity.
3. Personalized and Neoantigen Vaccines
Patient-derived exosomes carrying neoantigens for personalized cancer vaccines. Ideal for tumors with high mutational burden and heterogeneity.
4. Autoimmune and Tolerance Induction
Engineered exosomes carrying autoantigens or immunomodulatory molecules for autoimmune diseases (e.g., multiple sclerosis, type 1 diabetes).
5. Regenerative Medicine and Anti-inflammatory Therapies
Exosomes engineered to modulate immune responses for wound healing, cardiovascular disease, and neuroinflammation.
Case Study
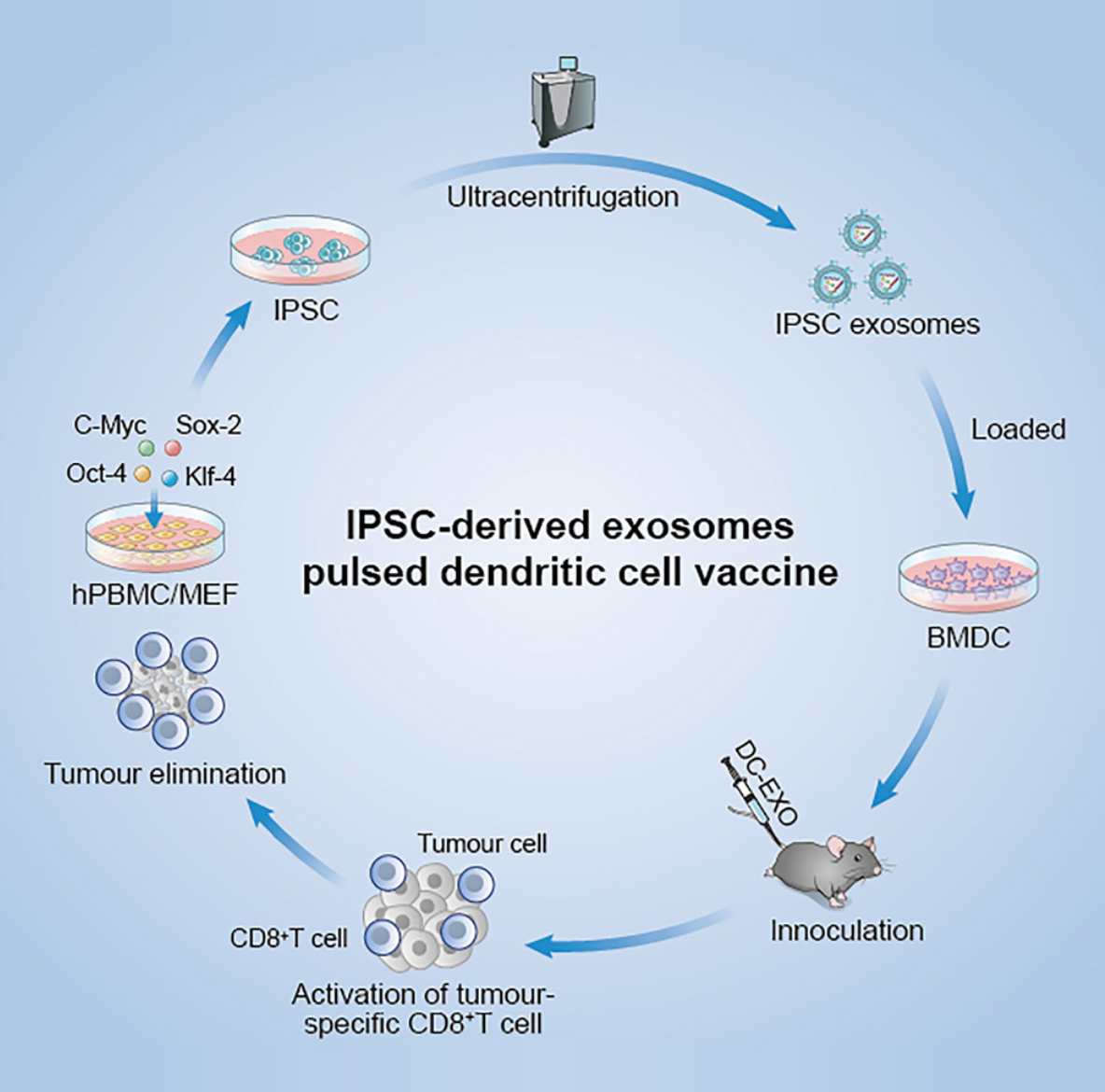
Development of iPSC-Derived Exosome-Based Tumor Vaccines for Melanoma Immunotherapy
A study explored the use of induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived exosomes as a novel vaccine platform to induce robust antitumor immunity against melanoma. iPSCs naturally express a wide array of tumor-associated antigens (TAAs), making them an attractive source for cancer vaccines. However, traditional iPSC-based vaccines face critical challenges, including tumorigenicity risks and inefficient targeting of immune organs. To overcome these issues, researchers isolated exosomes from iPSCs and used them to pulse dendritic cells (DCs), generating a DC + iPSC-exosome vaccine. This strategy leveraged the exosome's intrinsic ability to present antigens in a safe, cell-free format, enhancing biocompatibility and immune accessibility. In murine melanoma models, the DC + exosome vaccine effectively stimulated T cell responses, inhibited tumor growth and metastasis, and induced long-lasting immune memory capable of preventing tumor rechallenge—all without inducing adverse effects in healthy tissues. This case highlights the potential of tumor-derived and stem cell-derived exosome vaccines in personalized cancer immunotherapy. MtoZ Biolabs offers comprehensive support for developing such exosome-based vaccines, including exosome isolation, engineering, multi-omics profiling, and functional validation, providing a one-stop solution from discovery to preclinical studies.
Contact us to explore tailored solutions for your research. Our technical specialists are available to provide a free business assessment.
How to order?







