Tissue Exosome Isolation Service
- Enhancing the understanding and treatment of complex diseases through targeted tissue and extracellular analysis.
- Further analyzing tissue-derived exosomes to identify novel biomarkers for precision medicine.
- Revealing characteristics of tumor-derived or host cell-derived exosomes.
- Facilitating other downstream analytical and detection applications.
Tissue Exosome Isolation Service refers to the isolation of exosomes from tissue cells or tissue fluids, enabling the study of specific tissue molecular characteristics and tissue-specific pathological processes.
Exosomes are nanoscale vesicles with a diameter of approximately 30-150 nm, widely present in extracellular fluids, including blood, urine, saliva, and cell culture media. They originate through the endocytic process of multivesicular bodies (MVBs) and play a crucial role in intercellular signaling. In recent years, exosomes have garnered significant attention in medical and biological research due to their ability to carry diverse biomolecules, including proteins, RNA, DNA, and lipids. These biomolecules make exosomes promising biomarkers for disease diagnosis and potential therapeutic agents.
Tissues serve as unique experimental samples in life sciences research, providing a more accurate reflection of complex biological processes and molecular mechanisms within living organisms. Tissue samples retain cell-cell interactions and tissue-specific molecular features within the physiological environment, which is critical for studying cellular heterogeneity, tissue-specific responses, and localized disease progression.
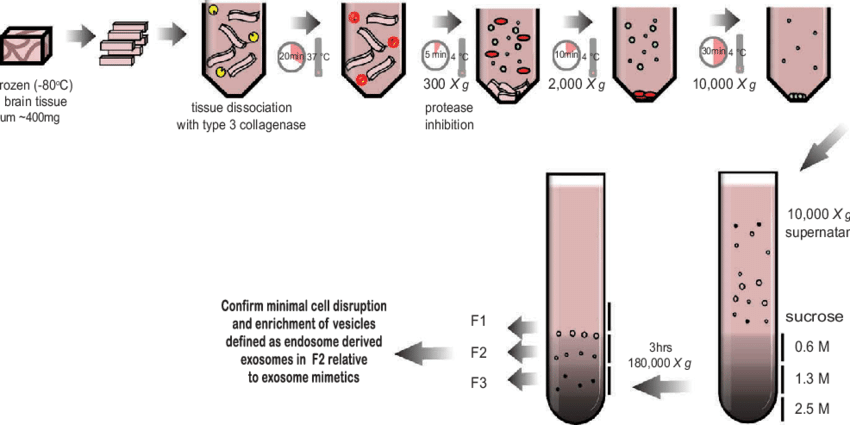
Vella L J. et al. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles. 2017.
Figure 1. Schematic of the exosome isolation protocol from solid brain tissue.
Tissue exosomes are exosomes derived from specific tissues, reflecting the molecular characteristics of the originating tissue. They can carry tissue-specific proteins, RNA, lipids, and other biomolecules. For example, exosomes derived from tumor tissues are often enriched with tumor-associated proteins, RNA molecules, and specific surface markers. The isolation and study of tissue exosomes provide new insights into the molecular characteristics of tissues and the underlying mechanisms of tissue-related diseases.
MtoZ Biolabs offers Tissue Exosome Isolation Service along with exosome analysis after isolation, enabling the discovery of early disease markers, intercellular communication mechanisms, and pathological changes associated with tissue-related diseases.
Technical Principles
Examples of Traditional Tissue Exosome Isolation Techniques and Principles:
1. Ultracentrifugation: This is the most widely used method for exosome isolation. It separates exosomes from other cellular secretions based on differences in size, shape, and density. This method is simple and efficient; however, it may co-precipitate other small particles, leading to lower purity.
2. Density Gradient Centrifugation: This technique separates exosomes by layering substances with different densities and applying centrifugal force, allowing exosomes to be fractionated based on their density differences. While it improves exosome purity, it is time-consuming.
3. Immunoaffinity Capture: This method uses specific antibodies to bind to exosomal surface markers (such as CD9, CD63, and CD81) for selective enrichment. It significantly enhances the specificity and sensitivity of exosome isolation, making it ideal for analyzing specific exosome subtypes. However, it has lower efficiency, and exosomal bioactivity may be affected by salt concentration, which can be a limitation for downstream experiments.
4. Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC): SEC isolates exosomes based on molecular size differences. The molecular weight differences between exosomes and other small molecules enable effective separation. This method typically yields high-purity exosome preparations, but the efficiency may be influenced by sample complexity and other factors.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
In addition to traditional exosome isolation methods such as ultracentrifugation, immunoaffinity capture, and density gradient centrifugation, MtoZ Biolabs' Tissue Exosome Isolation Service also offers optimized approaches for isolating all extracellular vesicles (EVs), including exosomes, from tissues. These advanced methods cater to diverse research needs, ensuring high-quality and comprehensive extracellular vesicle analysis.
Applications
FAQ
Q. How Can Tissue Exosome Analysis be Integrated with Clinical Samples to Support Precision Medicine?
Integrating tissue exosome analysis with clinical samples to support precision medicine involves the following key steps:
Sample Collection and Processing: Clinical samples (such as blood, urine, or tissue specimens) are combined with exosome isolation techniques. Methods like ultracentrifugation, immunoaffinity capture, and size exclusion chromatography are used to obtain high-purity tissue-derived exosomes.
Biomarker Screening and Validation: Exosomal contents, including proteins, RNA (miRNA, mRNA), and DNA, are analyzed to identify biomarkers associated with specific diseases. These biomarkers are validated through clinical trials to assess sensitivity, specificity, and performance in patient cohorts, ensuring their feasibility for early disease diagnosis and prognosis assessment.
Guiding Precision Treatment Strategies: Tissue exosome analysis can reveal molecular biomarkers linked to drug response, enabling the development of personalized treatment plans for individual patients. For instance, the expression patterns of exosomal miRNAs or proteins may indicate drug efficacy or resistance, helping clinicians select the most suitable therapeutic approach.
Monitoring Treatment Efficacy and Disease Progression: Regular analysis of exosomal biomarkers in patient biofluids allows real-time monitoring of treatment outcomes, disease progression, and recurrence risk. This enables dynamic disease management and supports personalized therapeutic adjustments.
By following these steps, tissue exosome analysis not only strengthens early disease diagnosis but also aids in developing precise treatment strategies, advancing the field of precision medicine.
Case Study
This study utilized ultracentrifugation to isolate exosomes from perivascular adipose tissue (PVAT) surrounding the uterine blood vessels of pregnant mice to investigate the role of exosomes in intercellular communication, particularly the interaction between uterine vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) and PVAT. The results demonstrated that exosomes secreted by PVAT surrounding the uterine blood vessels can transfer molecules such as miRNAs, facilitating the functional regulation of vascular smooth muscle cells. This process plays a critical role in regulating uterine blood flow and pregnancy-related physiological changes during gestation.
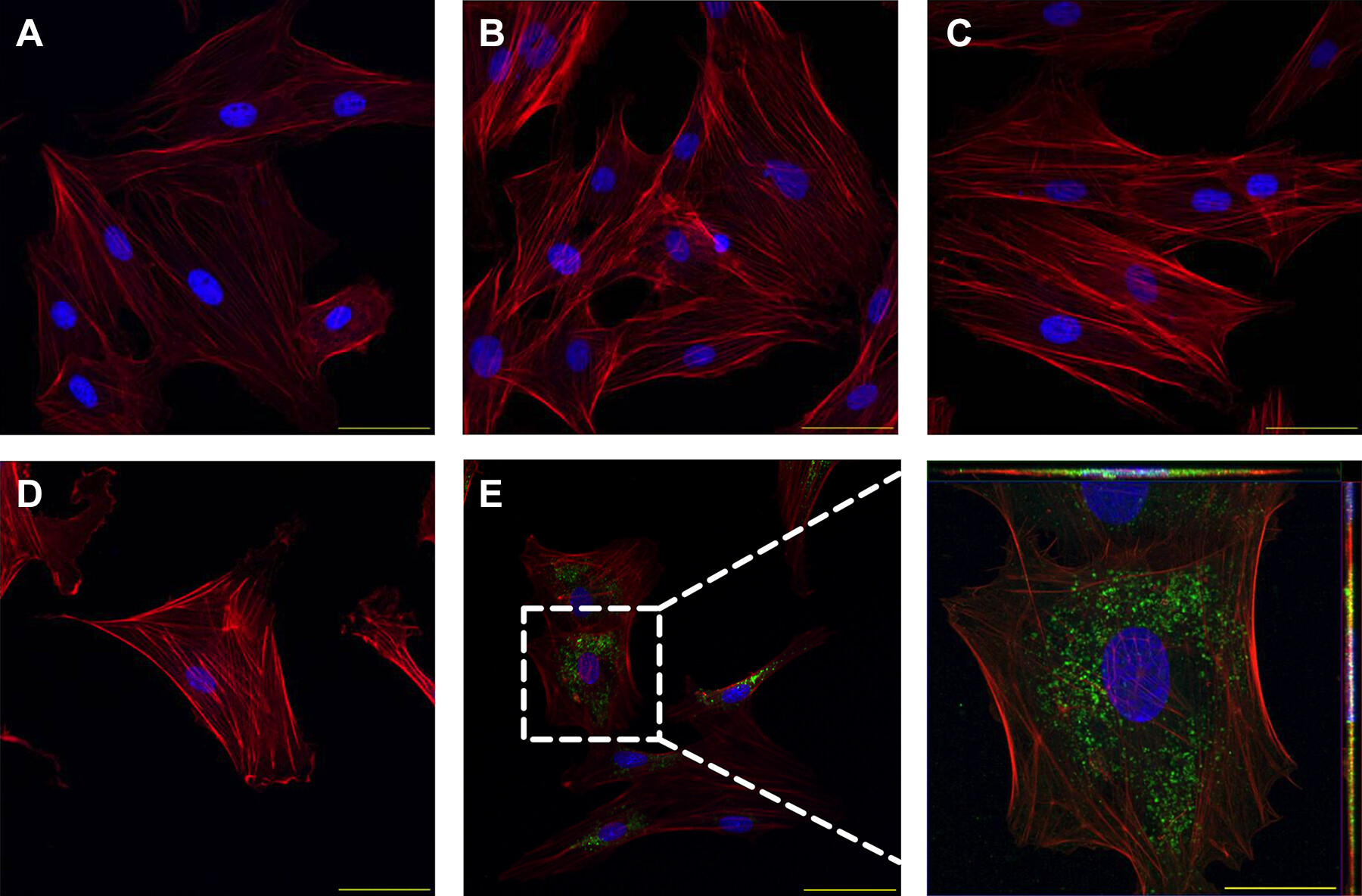
Osikoya O. et al. Am J Physiol-Heart C. 2022.
Figure 2. Trafficking of uterine perivascular adipose tissue-derived exosome-like vesicles into adjacent uterine vascular smooth muscle cells in a pregnant rat.
How to order?







