Targeting Tumors and Microenvironment of Multi-antibody-modified Exosome Service
- Construction of precision-targeted drug delivery systems for cancer
- Remodeling of the tumor immune microenvironment (TME)
- Development of CAF-targeted nanodelivery systems
- Optimization of combination immunotherapy platforms (e.g., in synergy with ICB or CAR-T)
- Personalized exosome carrier development for pharmacodynamic evaluation or preclinical studies
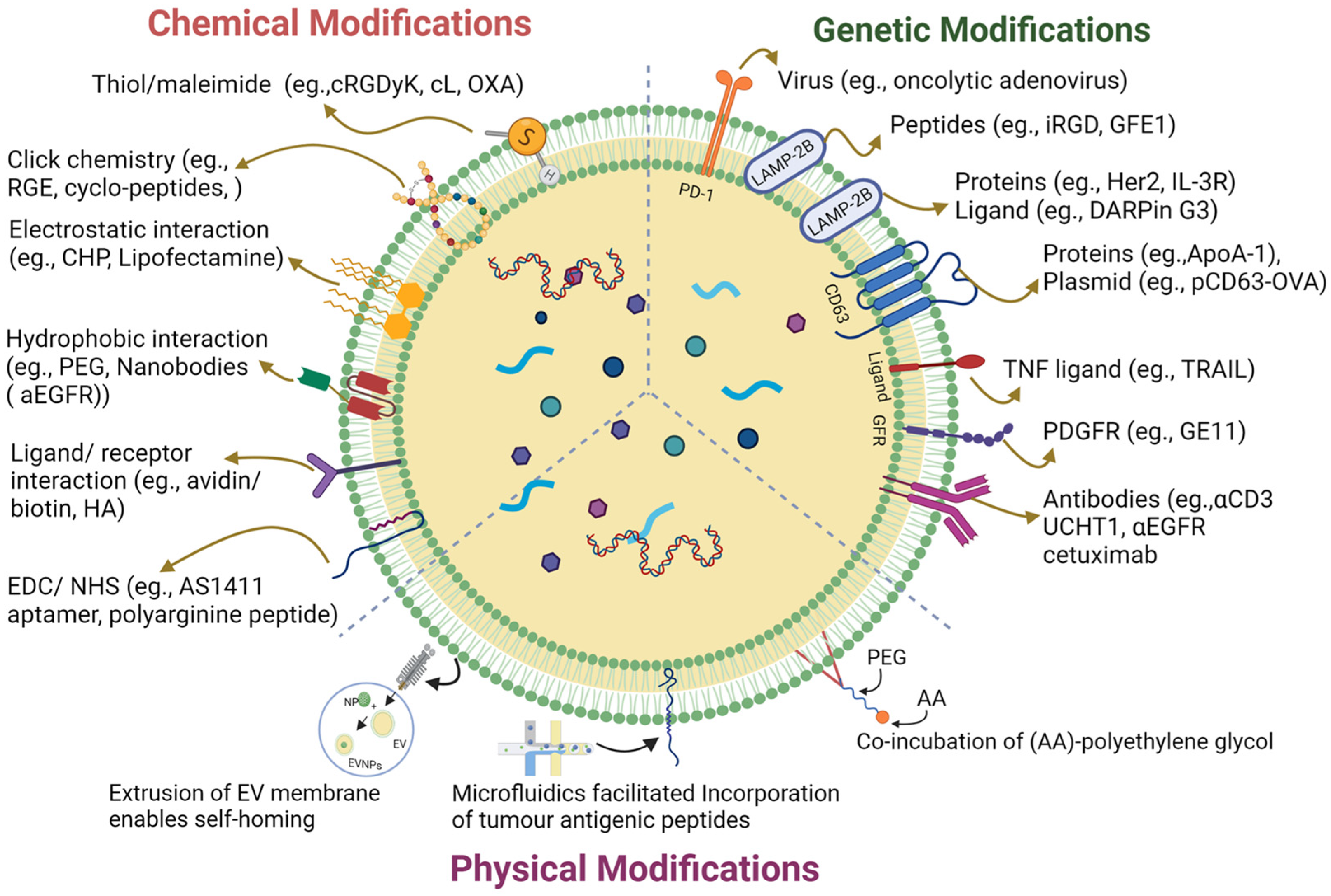
Targeting Tumors and Microenvironment of Multi-antibody-modified Exosome Service is designed to enhance the targeting specificity and therapeutic efficacy of exosomes in complex tumor settings by displaying multiple specific antibodies on the exosome surface to simultaneously target tumor cells and their surrounding microenvironment.
Tumor heterogeneity and the complex immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME) are major obstacles limiting the effectiveness of cancer therapies. Traditional targeting strategies often focus solely on tumor cells while overlooking the collaborative influence of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), immunosuppressive factors, and stromal barriers. Exosomes are nanoscale vesicles secreted by cells that mediate intercellular communication. Due to their natural biocompatibility and low immunogenicity, they are considered promising carriers in cancer therapy. Within the TME, exosomes play critical roles in regulating immune responses, promoting angiogenesis, and facilitating tumor metastasis. By employing engineering strategies to decorate the exosome membrane with multiple specific antibodies, these modified exosomes can simultaneously recognize and bind to multiple targets in both tumor cells and the microenvironment—such as tumor-associated antigens and immunosuppressive molecules—enhancing drug accumulation at the tumor site, modulating the immune milieu, and ultimately improving therapeutic outcomes.
Johnson V. et al. Cancers. 2023.
Leveraging advanced multi-antibody surface modification and drug delivery engineering technologies, MtoZ Biolabs offers the Targeting Tumors and Microenvironment of Multi-antibody-modified Exosome Service enabling the co-modification of exosome surfaces with antibodies targeting both tumor cell markers and microenvironmental targets. This dual-targeting strategy allows exosomes to simultaneously recognize tumor cells and their immune/stromal microenvironment, providing an integrated approach for precise therapeutic delivery and tumor microenvironment modulation in anti-cancer treatment.
Analysis Workflow
MtoZ Biolabs can provide the following customized processes according to different research needs:
1. Modification Strategy Design
Surface Conjugation: PEG-linkers, click chemistry, or other chemical conjugation strategies.
Genetic Engineering Fusion: Antibody-Fc/CD63/Lamp2b fusion proteins for membrane display.
2. Exosome Preparation and Purification
Multiple cell sources supported (HEK293, immune cells, MSCs, etc.).
Purification methods include ultracentrifugation, SEC, and density gradient centrifugation.
3. Cargo Loading (Optional)
Encapsulation of drugs, siRNA, miRNA, STING agonists, and more.
Evaluation of encapsulation efficiency and cargo stability.
4. Characterization and Functional Validation
Quality and modification verification via NTA, TEM, Western blot, flow cytometry.
Optional in vitro testing: targeting binding assays, penetration analysis, immunoactivation or cytotoxicity evaluation.
Applications
Targeting Tumors and Microenvironment of Multi-antibody-modified Exosome Service is applicable to the following research and translational areas:
Service Advantages
Multi-antibody co-modification for precise recognition of tumor–microenvironment complexes.
Flexible choice between non-covalent conjugation or genetic expression modification to preserve antibody activity and membrane integrity.
Supports combinatorial loading of drugs, nucleic acids, and immunostimulants.
High-stability, high-specificity platform compatible with both in vitro and in vivo validations.
Full-process experimental support and standardized report delivery.
FAQ
Q. Do you Use Genetic Fusion or Non-Covalent Conjugation for Antibody Modification? Which is more Suitable for Stable Delivery in Complex Tumor Microenvironments?
Both options are available, and the choice depends on the experimental objective:
Genetic fusion (e.g., antibody fused to CD63 or Lamp2b) is ideal for constructing stable, batch-consistent carriers suitable for long-term studies or in vivo experiments.
Non-covalent conjugation (e.g., PEG linkers, self-assembling tags) is better suited for flexible, rapid multi-antibody decoration or for screening applications.
For delivery in complex TME, non-covalent strategies are recommended due to their tunable antibody density and spatial conformation, which enhance tumor penetration and immune activation.
Q. Does Multi-Antibody Modification Compromise Exosome Membrane Integrity or Natural Delivery Properties?
When properly designed and optimized, multi-antibody modification does not disrupt the exosome membrane. MtoZ Biolabs uses TEM, DLS, and NTA to assess particle size, morphology, and membrane integrity, along with flow cytometry and Western blotting to confirm marker expression (e.g., CD63, CD81). These steps ensure that the exosomes retain their native delivery capacity and biological function.
How to order?







