Protein Sequencing by Edman Degradation Service
Protein Sequencing by Edman Degradation Service utilizes Edman degradation technology to determine the N-terminal sequence of proteins. The N-terminal sequence of a protein not only enables rapid identification of the protein's type and origin, as well as verification of its accuracy, but also plays a crucial role in drug development, protein function analysis, and disease mechanism research. Protein sequencing by Edman degradation is a classic protein N-terminal sequencing method, which is still playing an irreplaceable role in proteomics research because of its high accuracy and reliability. Leveraging an advanced Edman sequencing system, MtoZ Biolabs offers Protein Sequencing by Edman Degradation Service to determine N-terminal sequence information of proteins. With a specialized protein loading system, we can accurately sequence up to 60-70 N-terminal amino acids.
Analysis Workflow
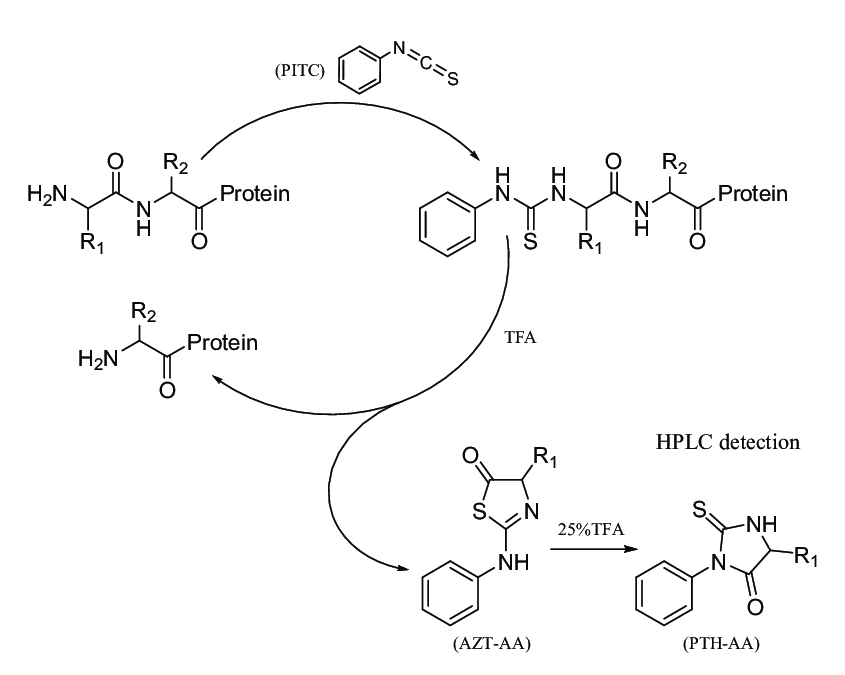
Yang W. et al. Molecules. 2021.
Sample Preparation
Proteins are purified or separated via electrophoresis and transferred onto a PVDF membrane to ensure high purity.
N-terminal Amino Acid Derivatization
PITC reacts with the N-terminal amino acid, generating a phenylthiocarbamoyl (PTC)-amino acid derivative.
Chemical Degradation
Under acidic conditions, the N-terminal PTC-amino acid is selectively cleaved, forming a phenylthiohydantoin (PTH)-amino acid.
Separation and Identification
The PTH-amino acids are separated and identified using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).
Sequence Deduction
Based on the amino acid identified in each degradation cycle, the N-terminal sequence of the protein is progressively deduced.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry (MS) Services Provider, provides advanced proteomics, metabolomics, and biopharmaceutical analysis services to researchers in biochemistry, biotechnology, and biopharmaceutical fields. Our ultimate aim is to provide more rapid, high-throughput, and cost-effective analysis, with exceptional data quality and minimal sample consumption. MtoZ Biolabs provides protein sequencing by Edman degradation service to determine the N-terminal sequence of non-blocked proteins. Additionally, we offer mass spectrometry analysis for blocked and modified N-terminal proteins to ensure seamless N-terminal sequencing services.
Applications
Antibody Engineering
Protein sequencing by Edman degradation service can precisely determine antibody N-terminal sequences to optimize structure and function.
Drug Development
Identify the amino acid sequences of therapeutic protein drugs to ensure quality and consistency.
Biomarker Discovery
Reveal potential disease biomarkers through sequence information.
Protein Function Research
Explore structure-function relationships of proteins through sequence data.
Proteomics
Combine with mass spectrometry for high-throughput protein identification and functional studies.
FAQ
Q. How to Address the Issue of N-terminal Blockage in Edman Degradation Sequencing?
In some proteins, the N-terminal amino acids may be blocked by acetylation, formylation, or other post-translational modifications, preventing Edman degradation from determining the N-terminal sequence. The following strategies can address this issue:
1. Preliminary Detection of N-terminal Blockage
Before performing Edman degradation, techniques such as LC-MS/MS or Western Blot can be used to preliminarily detect whether the protein's N-terminus is modified. If blockage is detected, Edman degradation may not proceed directly.
2. Chemical or Enzymatic De-modification
For acetylation, deacetylase enzymes can be employed to remove the acetyl group. For formylation, acid hydrolysis or specific chemical reagents can be used to remove the formyl group. If chemical treatment is not feasible, specific proteases such as trypsin or Lys-C can cleave the protein, generating new peptide fragments that expose a free N-terminal residue suitable for Edman degradation.
3. Combined with Mass Spectrometry
If N-terminal modifications cannot be effectively removed, Edman degradation can be combined with mass spectrometry. Mass spectrometry can identify the types of N-terminal modifications and assist in deducing sequence information.
Deliverables
1. Comprehensive Experimental Details
2. Materials, Instruments, and Methods
3. Total Ion Chromatogram & Quality Control Assessment (project-dependent)
4. Data Analysis, Preprocessing, and Estimation (project-dependent)
5. Bioinformatics Analysis
6. Raw Data Files
Case Study
Using Edman Degradation Technology, the amino acid sequence of the degraded ATG16L1 protein in macrophages was analyzed, and the degradation site was identified at Aspartic Acid 495 (D495). This finding revealed the specific cleavage mechanism of ATG16L1 protein during Entamoeba histolytica infection.
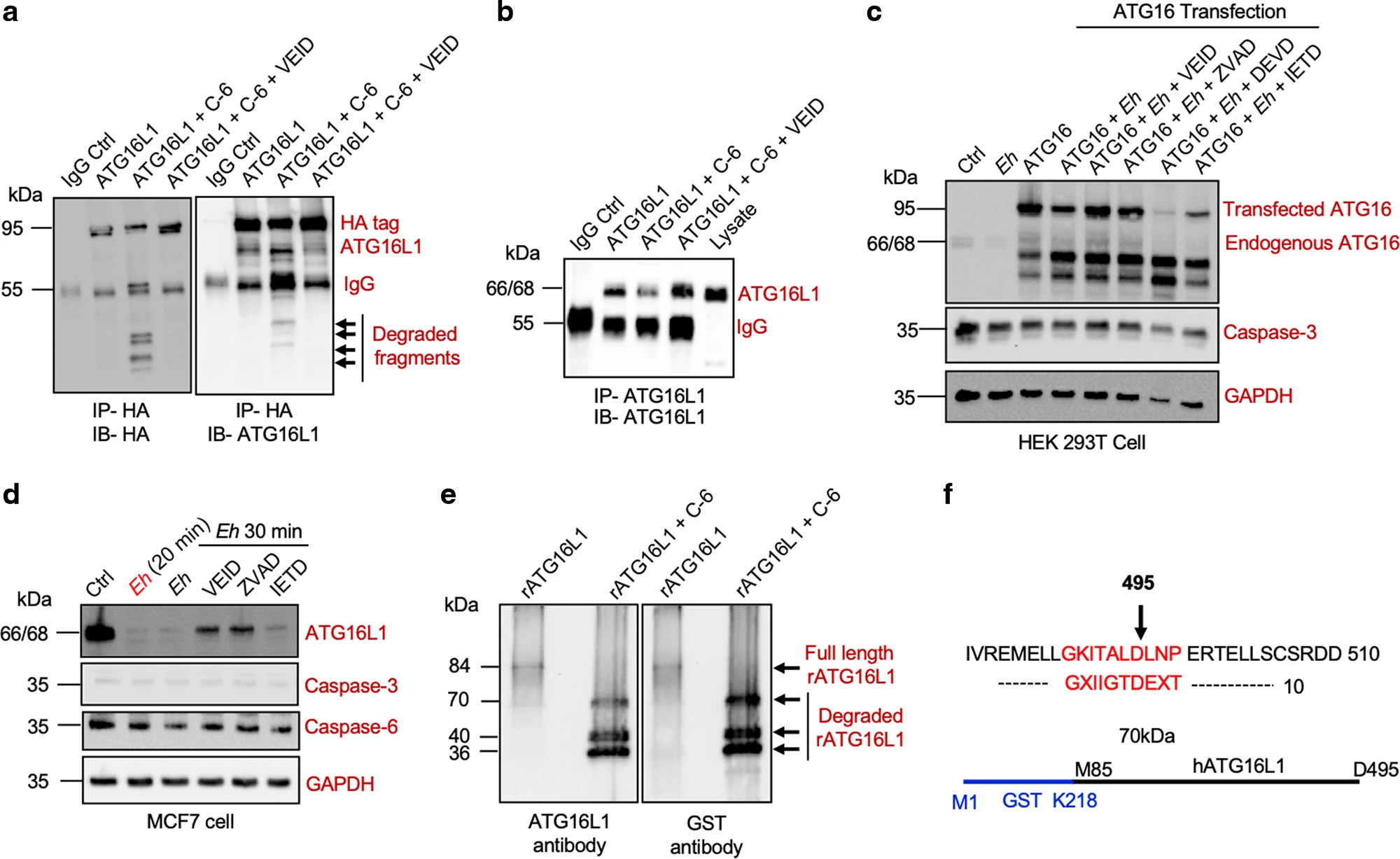
Begum S. et al. Mucosal immunology. 2021.
MtoZ Biolabs, an integrated chromatography and mass spectrometry (MS) services provider.
Related Services
How to order?







