N-Terminal PTM Analysis Service
N-terminal PTM analysis is a detection technique focused on analyzing post-translational modifications (PTMs) at the N-terminus of proteins. The N-terminus refers to the starting end of the amino acid sequence and often serves as a regulatory site for various biological processes, playing a critical role in protein stability, subcellular localization, half-life, and functional execution. This service utilizes high-resolution mass spectrometry to perform targeted analysis of N-terminal sequences, accurately identifying modifications such as acetylation, formylation, and methylation, while distinguishing between native N-termini and those arising from cleavage or translation products, thereby elucidating the regulatory mechanisms of these modifications on protein function and fate.
The N-terminal PTM analysis service is widely applied in protein function studies, signal transduction pathway analysis, protein degradation mechanism research, and biomarker discovery. It is particularly suitable for investigating key scientific questions related to translational regulation, protein stability control, and disease pathogenesis associated with N-terminal modifications.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Based on a high-resolution mass spectrometry platform, the N-terminal PTM analysis service launched by MtoZ Biolabs focuses on the precise characterization of post-translational modifications at the protein N-terminus. This service employs optimized sample preparation and N-terminal enrichment strategies, combined with advanced LC-MS/MS workflows, to systematically analyze various modification types such as acetylation, formylation, and methylation at the N-terminus. By enabling highly sensitive detection and accurate localization of modified peptides, the service delivers high-confidence modification spectra and sequence information, providing essential data support for protein function studies and regulatory mechanism investigations.
Analysis Workflow
1. Protein Extraction and Digestion
Proteins are extracted from cells, tissues, or body fluids, followed by reduction and alkylation, then enzymatically digested into peptides while preserving N-terminal information.
2. N-terminal Peptide Enrichment
Chemical labeling or selective capture strategies are employed to enrich N-terminal peptides and eliminate internal peptide background.
3. High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry Detection
Enriched samples are analyzed using advanced LC-MS/MS systems (such as Orbitrap Fusion Lumos) for high-sensitivity detection.
4. Data Analysis and PTM Identification
N-terminal modification types and specific modification sites are identified through database searching and customized algorithms.
5. Result Compilation and Report Delivery
Modification spectra, sequence localization, and annotation reports are provided to support functional studies and downstream applications.
Sample Submission Suggestions
1. Sample Types
Compatible with a wide range of sample types, including cells, tissues, serum/plasma, body fluids, and purified proteins.
2. Sample Purity
Samples should be free of high concentrations of salts, glycerol, SDS, or other components that may interfere with enzymatic digestion or mass spectrometry analysis.
3. Sample Transport
Samples must be stored at -80 °C and shipped on dry ice to ensure stability and integrity during transport.
Service Advantages
1. High-Resolution Detection Platform
Powered by high-end mass spectrometry platforms such as the Orbitrap Fusion Lumos, enabling highly sensitive and accurate detection of low-abundance N-terminal modified peptides to ensure data quality.
2. Dedicated N-terminal Enrichment Strategy
Utilizes well-established chemical labeling and selective capture methods to effectively enrich N-terminal peptides, significantly reducing background interference and enhancing modification site detection rates.
3. Comprehensive Modification Coverage
Capable of identifying multiple types of N-terminal post-translational modifications, including acetylation, formylation, and methylation, to meet the diverse needs of various research directions.
4. Customized One-Stop Service
Offers flexible, end-to-end solutions from experimental design, sample processing, and mass spectrometry analysis to data annotation, tailored to different sample types and research objectives.
Applications
1. Protein Function Studies
N-terminal PTM analysis service can be used to investigate how N-terminal modifications affect protein stability, localization, and functional regulation, supporting protein annotation and mechanistic studies.
2. Translation and Degradation Mechanism Research
By identifying the N-terminal start sites and modification patterns of nascent peptides, this service helps elucidate the roles of N-termini in translation initiation control and protein degradation pathways.
3. Signal Pathway and Disease Mechanism Analysis
N-terminal PTM analysis service enables the study of dynamic N-terminal modifications in key signaling pathways, offering insights into regulatory mechanisms in cancer, autophagy, and neurodegenerative diseases.
4. Biomarker and Target Discovery
By identifying disease-associated N-terminal modification signatures, this service supports the development of novel diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
Case Study
1. Natural Monoclonal Antibody B4-IgM Recognizes Post-Translational Modification of Acetylated N-Terminal Methionine
This study aims to investigate the molecular basis by which the natural monoclonal antibody B4-IgM recognizes its antigen, focusing on antigenic epitopes exposed during cell apoptosis. Using proteomic screening, mass spectrometry analysis, and mutational validation, the authors discovered that B4-IgM specifically recognizes a distinct N-terminal post-translational modification composed of an acetylated N-terminal methionine followed by either aspartic acid or glutamic acid. The study shows that this modification is widely present in endogenous proteins across various cell types and becomes more accessible on the cell surface during apoptosis or necrosis. The findings highlight the critical role of N-terminal acetylation in natural immune recognition and reveal the molecular mechanism by which natural IgM initiates immune responses through recognition of specific N-terminal modification patterns, providing new structural insights into innate immunity mediated by natural antibodies.
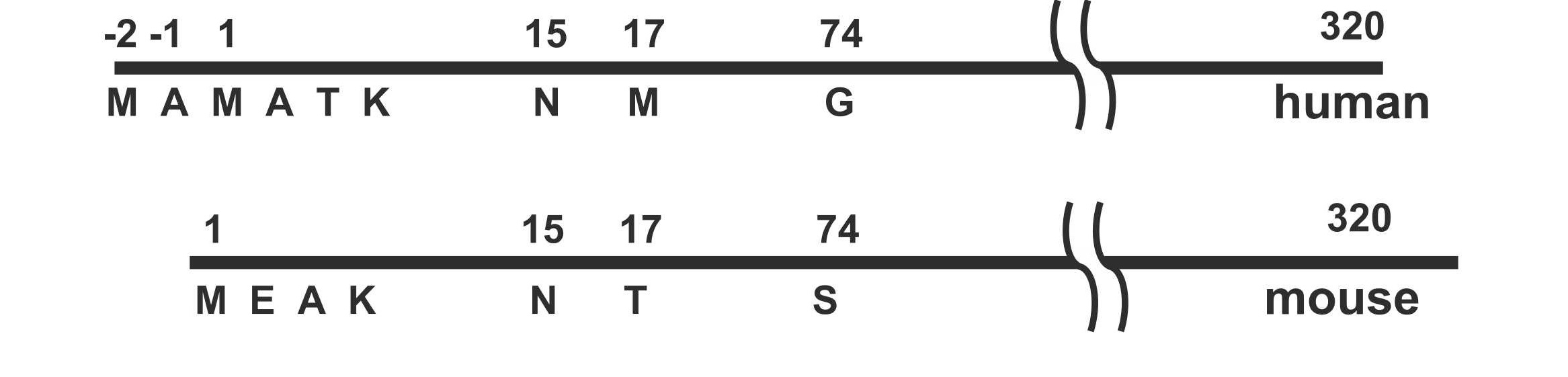
Kulik,L. et al. Molecular Immunology, 2023.
Figure 1. Representative Diagram Showing N-Terminal Amino Acid Differences in Human and Mouse An4 Proteins.
2. New Roles for Old Modifications: Emerging Roles of N-Terminal Post-Translational Modifications in Development and Disease
This study provides a comprehensive overview of the emerging roles of N-terminal post-translational modifications (N-terminal PTMs) in developmental regulation and disease pathogenesis, covering common modification types such as acetylation, deformylation, and methylation. Based on recent literature and mechanistic studies, the authors explore the essential roles of these modifications in regulating protein stability, localization, interactions, and degradation signaling. The study highlights that N-terminal PTMs exhibit high dynamism and functional specificity during processes such as embryonic development, nervous system formation, immune regulation, and tumor progression, and their dysregulation is closely associated with various diseases. The conclusion emphasizes that N-terminal modifications are not merely byproducts of co-translational processes, but active regulatory elements involved in determining cell fate and mediating signal transduction, offering significant value for biomedical research and clinical translation.
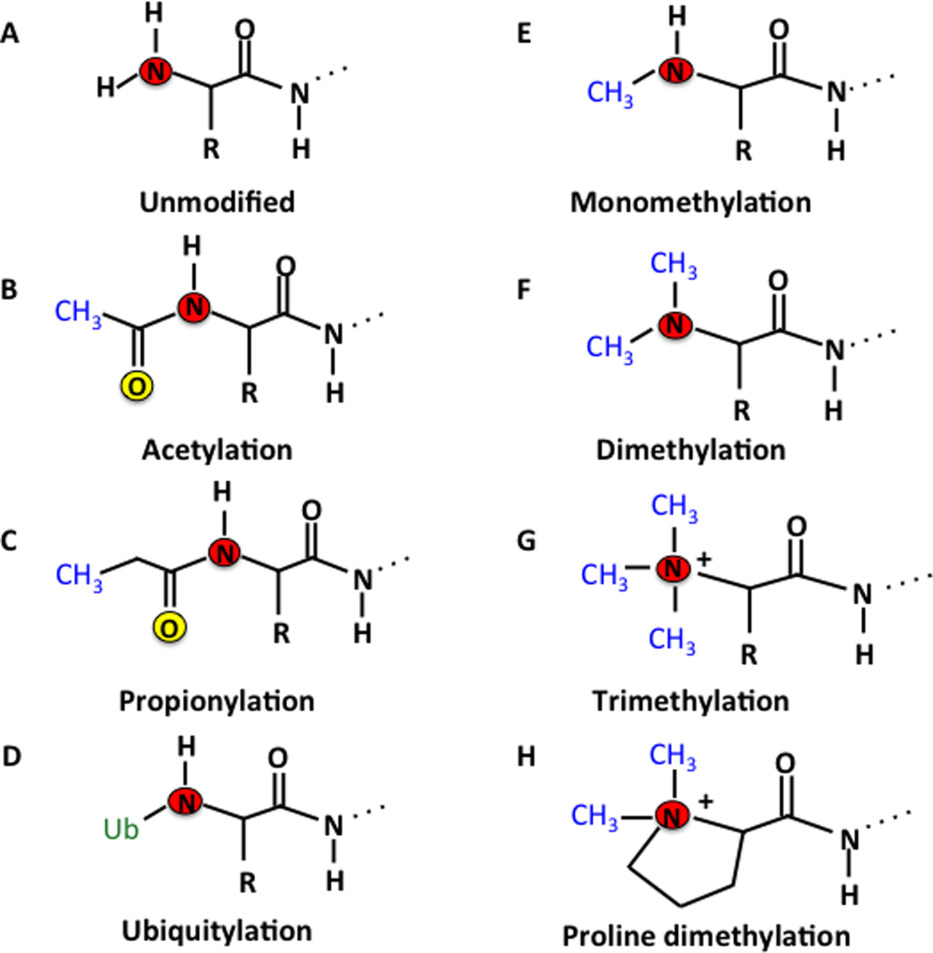
Tooley, J G. et al. Protein Science, 2014.
Figure 2. Diagram of N-Terminal PTM.
FAQ
Q1: What Types of Samples Are Suitable for the N-Terminal PTM Analysis Service?
A1: This service is applicable to various sample types, including cells, tissues, serum/plasma, body fluids, and purified proteins. It is especially recommended for projects focusing on translation initiation or protein degradation mechanisms, where total protein yield exceeds 100 µg. MtoZ Biolabs also provides sample-specific preprocessing optimization to ensure efficient enrichment and reliable mass spectrometry detection.
Q2: Is Customized Analysis Supported?
A2: Yes. MtoZ Biolabs offers flexible, customized services tailored to the specific needs of each project. This includes adjustments to sample handling protocols, enrichment strategies, and database search parameters. We also provide early-stage technical consultation and experimental design support to ensure clear analytical goals and high usability of results.
Deliverables
1. Comprehensive Experimental Details
2. Materials, Instruments, and Methods
3. Data Analysis, Preprocessing, and Estimation
4. Bioinformatics Analysis
5. Raw Data Files
How to order?







