Multi-specific Antibody-modified Exosome Engineering Services
Multi-specific Antibody-modified Exosome Engineering Services integrate multi-specific antibodies with exosomes to develop innovative drug delivery systems with enhanced targeting and immunomodulatory functions. The service covers the full workflow—from exosome isolation and purification to antibody modification and functional validation—supporting clients in advancing multi-specific antibody drug research and applications based on exosomes.
Exosomes are nano-sized vesicles secreted by cells that mediate intercellular material and information exchange. With the growing applications of exosomes in drug delivery and immunotherapy, enhancing their targeting and functional specificity has become a major research focus. Multi-specific antibodies—capable of simultaneously recognizing multiple targets or epitopes—exhibit superior immunomodulatory and targeting potential. Through engineering approaches, these antibodies can be modified onto the exosome surface to enable simultaneous recognition and binding of multiple targets, significantly improving exosomal targeting efficiency, transmembrane penetration, and therapeutic efficacy. This modification can be achieved either by genetically engineering the exosome-producing cells or by chemically modifying the exosomes directly.
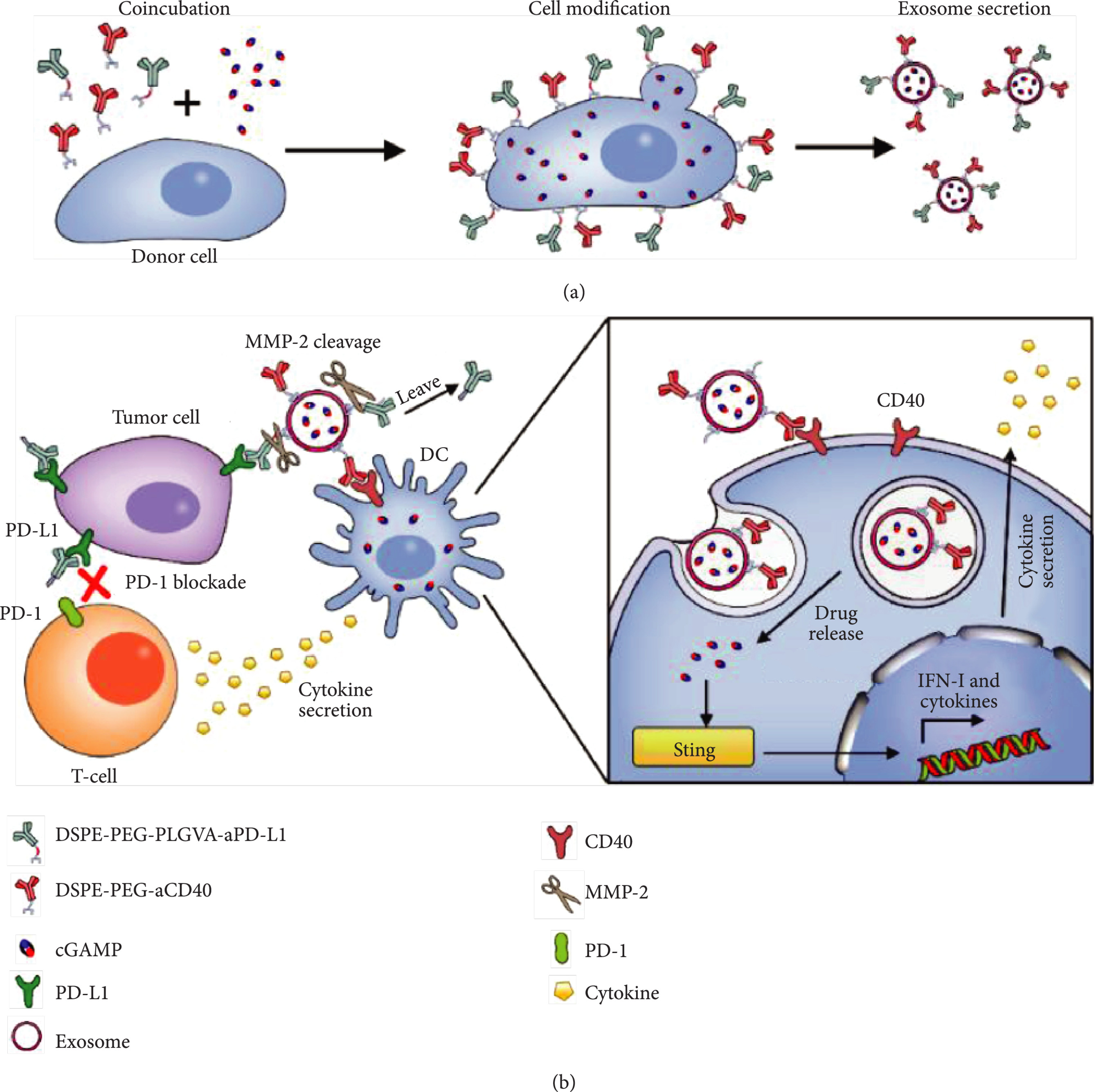
Fan Y. et al. Cancer Immunotherapy. 2021.
Based on the exosome engineering modification platform, MtoZ Biolabs provides Multi-specific Antibody-modified Exosome Engineering Services to precisely modify multiple antibody functional modules onto the surface of exosomes, constructing a new nanocarrier system with intelligent recognition, active targeting and immune activation capabilities. Provide integrated solutions for targeted therapy, immune activation, and drug delivery, and help promote efficient scientific research and transformation.
Analysis Workflow
MtoZ Biolabs offers a flexible and customizable workflow for Multi-specific Antibody-modified Exosome Engineering Services:
1. Multi-Specific Antibody Modification & Exosome Isolation and Purification
Genetic engineering method: Transfect plasmids encoding multi-specific antibody-membrane protein fusion genes into exosome-producing cells, enabling the secreted exosomes to display multi-specific antibodies on their surface. Exosomes are then isolated and purified from cell culture supernatants or biological fluids.
Chemical modification method: Isolate and purify exosomes from culture media or body fluids. Use click chemistry or PEG-mediated approaches to directly conjugate pre-prepared multi-specific antibodies onto the exosome membrane surface.
2. Characterization of Modified Exosomes
Utilize techniques such as Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA), Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS), and Western blot to comprehensively evaluate particle size, morphology, surface charge, and antibody display, ensuring quality and consistency.
3. Functional Validation (optional)
Assess the biological functions of modified exosomes in vitro and in vivo, including target cell binding ability and immune modulation effects.
Applications
Tumor-targeted therapy
Enable precise recognition of multiple antigens on tumor cell surfaces to enhance delivery of drugs, nucleic acids, or immune regulators.
Immune modulation and vaccine development
Develop exosome-based vaccines capable of activating multiple immune cell types, enhancing anti-tumor responses or protective immunity against infectious diseases.
Multi-target intervention for complex diseases
Simultaneously target multiple pathological pathways (e.g., inflammation, immune evasion, cell proliferation) for combined therapeutic effects.
Cross-physiological barrier delivery
Improve exosome enrichment in hard-to-reach tissues (e.g., brain, liver), enhancing drug efficacy and safety.
Service Advantages
1. High-specificity targeting: Supports recognition of up to three antigens, suitable for complex tumor microenvironments.
2. Flexible modification strategies: Offers both genetic engineering and chemical conjugation methods to fit various project needs.
3. Comprehensive data output: Includes full exosome characterization, modification validation, and functional assessment.
4. One-Time-Charge: Our pricing is transparent, with no hidden fees or additional costs.
FAQ
Q. What are the advantages of using multi-specific antibodies to modify exosomes?
Enhanced targeting: Exosomes modified with multiple antibodies can simultaneously bind to different cell types or molecules, increasing specificity and efficacy.
Multifunctionality: With tailored antibody combinations, engineered exosomes can address a wide range of diseases.
Reduced off-target effects: Precise targeting reduces side effects compared to conventional therapies.
Q. Do modified exosomes retain typical markers like CD63 and CD9? Are there significant changes in size or charge?
We conduct comprehensive quality control post-modification, including NTA (size), zeta potential analysis, TEM (morphology), and Western blot (CD9/CD63/TSG101). With rational antibody design and modification strategies (e.g., transmembrane fusion or surface coupling), exosomes maintain structural integrity and stable marker expression, preserving their functional delivery capabilities.
Case Study
In this study, exosomes were co-modified with anti-PD-L1 and anti-CD40 antibodies. Anti-PD-L1 blocked tumor immune evasion, while anti-CD40 activated dendritic cells, creating a dual mechanism of immune activation and checkpoint inhibition. Additionally, the exosome core was loaded with the STING agonist cGAMP to enhance innate immunity. Results showed the dual-targeted exosome system significantly improved T-cell activation and tumor cell clearance in vitro and effectively suppressed tumor growth in a murine model, demonstrating the strong potential of multi-specific antibody-modified exosomes in combination immunotherapy.
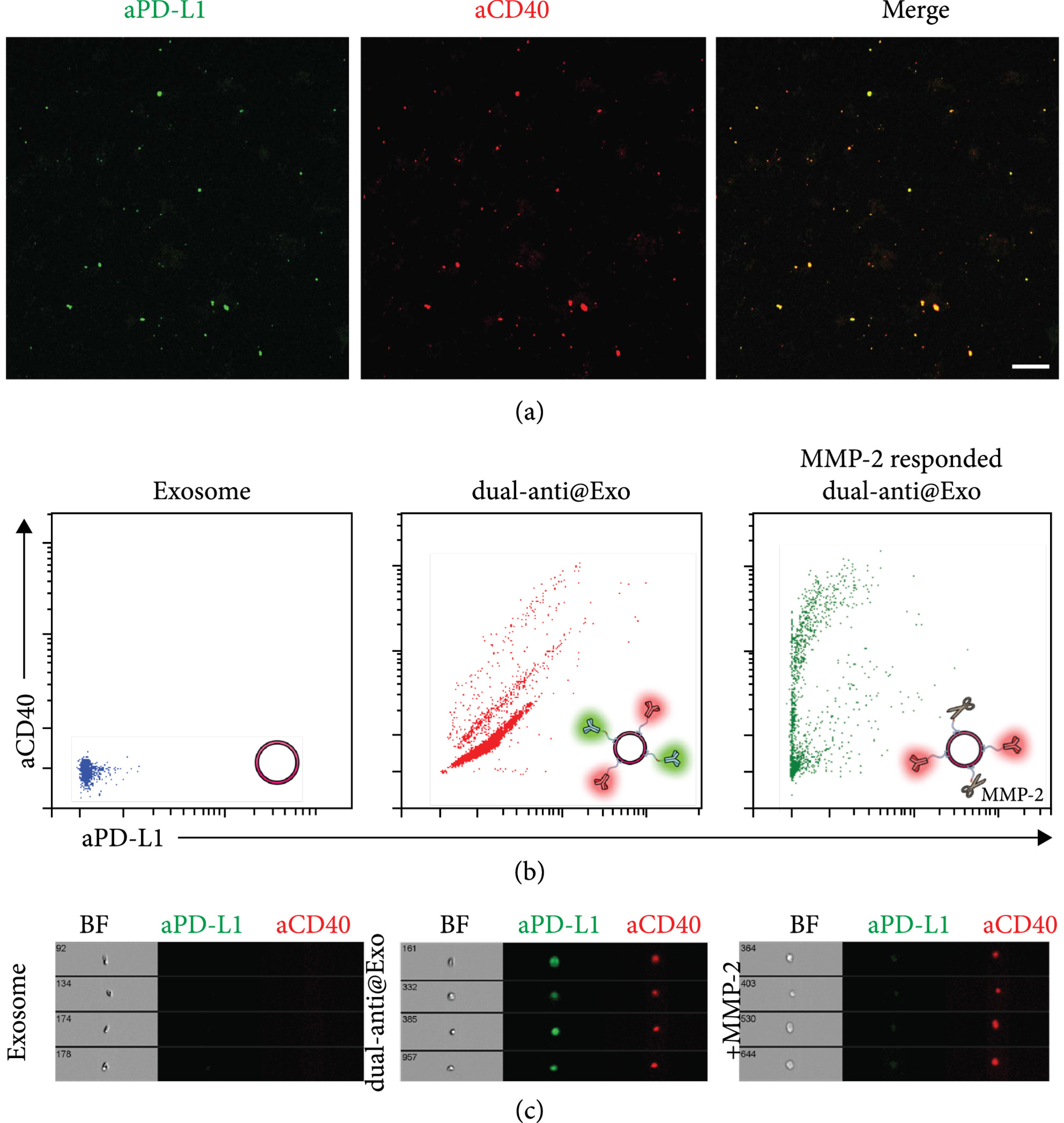
Fan Y. et al. Cancer Immunotherapy. 2021.
How to order?







