Liver Disease Diagnosis-Applied Exosomes
Liver Disease Diagnosis-Applied Exosomes service uses high-purity exosome extraction and analysis to deeply explore the exosome content molecules, and combines proteomics, transcriptomics, metabolomics and other technologies to reveal the molecular mechanisms related to liver disease and assist in the development of biomarkers for liver disease diagnosis.
Liver diseases—such as viral hepatitis, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)—continue to pose a significant global health burden due to their high mortality rates. However, current diagnostic methods often suffer from limitations including invasiveness, low sensitivity, and inability to detect early-stage disease. In recent years, exosomes have emerged as a powerful tool in liquid biopsy. With their tissue-specific origin, high molecular stability, and detectability, exosomes have become ideal carriers for exploring biomarkers, pathological mechanisms, and therapeutic targets in liver disease research.
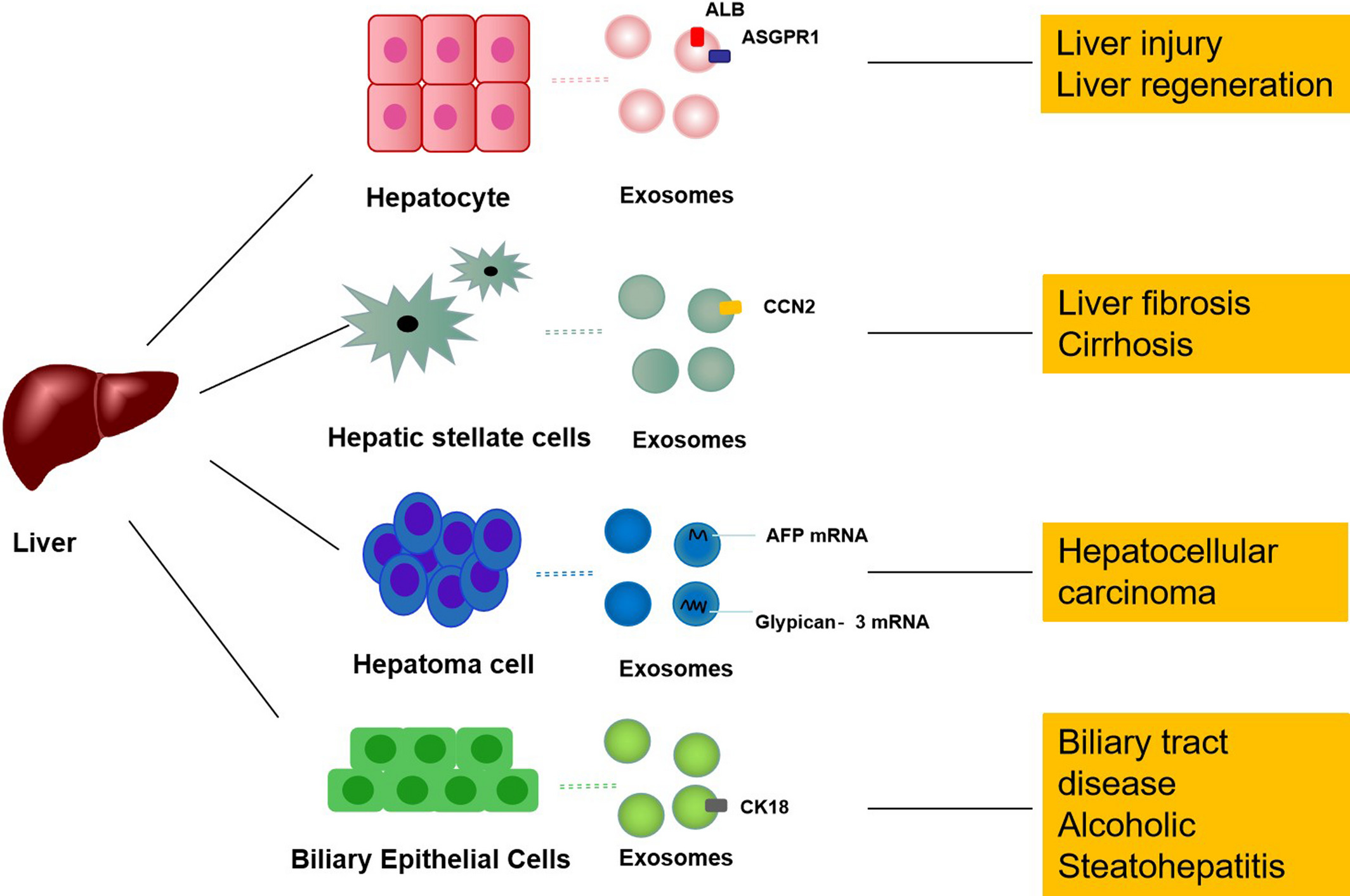
Jiao Y. et al. Cell Mol Med. 2021.
Exosomes are nanoscale vesicles secreted by cells through exocytosis and are widely present in bodily fluids such as plasma, bile, and urine. They play essential roles in intercellular communication, as well as the regulation of metabolism and immune functions. Studies have shown that damaged hepatocytes release large quantities of exosomes, which are involved in key pathological processes of liver injury, fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Therefore, analyzing exosomal alterations under disease conditions—combined with high-throughput omics technologies and bioinformatics—can facilitate the identification of early diagnostic biomarkers, disease classification and staging indicators, and potential therapeutic targets, while also enabling the construction of disease-associated signaling networks and pathological models.
Leveraging high-purity exosome isolation techniques and multi-omics platforms, MtoZ Biolabs offers a comprehensive Liver Disease Diagnosis-Applied Exosomes service covering the entire workflow from sample processing, exosome extraction and characterization, molecular profiling of exosomal cargo to bioinformatic interpretation, providing robust support for both basic research and translational medicine.
Analysis Workflow
The primary workflow of the Liver Disease Diagnosis-Applied Exosomes service is as follows:
1. Exosome Isolation and Quality Control
Multiple techniques are employed to isolate high-purity exosomes, followed by rigorous quality assessment.
2. Extraction of Target Biomolecules
Target molecules are extracted from exosomes based on project-specific requirements.
3. Biomarker Detection
Proteomics, metabolomics, or high-throughput sequencing is used to analyze the extracted biomolecules.
4. Data Analysis and Reporting
Comprehensive data processing and bioinformatics analysis are conducted, including the identification of disease-associated biomarkers and functional interpretation. A detailed experimental report is provided.
Applications
Examples of applications for the Liver Disease Diagnosis-Applied Exosomes service include:
Early Non-Invasive Diagnosis of Liver Cancer
Identification of plasma- or urine-derived exosomal miRNAs, lncRNAs, or proteins closely associated with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) to support early screening and dynamic monitoring.
Monitoring the Progression of Hepatitis and Liver Fibrosis
Characterization of exosomes from chronic HBV/HCV patients to uncover key pathways involved in fibrosis progression, immune regulation, and inflammation.
Drug Response and Therapeutic Outcome Prediction
Assessment of exosomal cargo alterations before and after targeted or antiviral therapy to aid in therapeutic stratification and personalized treatment decisions.
FAQ
Q. Which sample types are most suitable for exosome analysis in liver-related diseases?
For liver disease research, serum and plasma are the most commonly used sample types due to their accessibility and ability to broadly reflect exosome release from liver cells. For studies requiring closer insight into the local disease microenvironment, exosomes derived from bile, urine, or liver biopsy fluid offer high specificity—particularly valuable for investigating changes in biliary diseases, liver fibrosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. MtoZ Biolabs supports a wide range of biofluid samples and provides tailored extraction strategies to ensure both exosome purity and representativeness.
Q. Are the extraction and omics analyses of exosomal cargo sensitive enough?
For transcriptomic profiling, we use high-efficiency RNA extraction reagents and small RNA library construction protocols, enabling the capture of low-abundance molecules such as miRNAs and lncRNAs. For proteomic analysis, we utilize high-resolution mass spectrometry platforms (e.g., Orbitrap) for both label-free and TMT-based quantification, achieving sensitivity down to the picogram level. Targeted validation services such as qPCR and Western blot are also available to ensure reproducibility and reliability in both research and clinical translation.
Case Study
In this study, exosomes were isolated from the plasma of patients with various stages of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV)-related liver disease, including chronic hepatitis B, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Standard characterization was performed using transmission electron microscopy (TEM), nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA), and Western blotting. High-resolution LC-MS/MS was subsequently used to analyze the exosomal proteome. The results revealed that several proteins (such as CO9, LBP, VWF, and SVEP1) exhibited stage-specific expression patterns, with VWF and KV311 showing significant differences between cirrhosis and HCC stages. These findings suggest that plasma exosomal protein profiles may serve as a potential biomarker source for staging and diagnosing chronic HBV-related liver diseases.
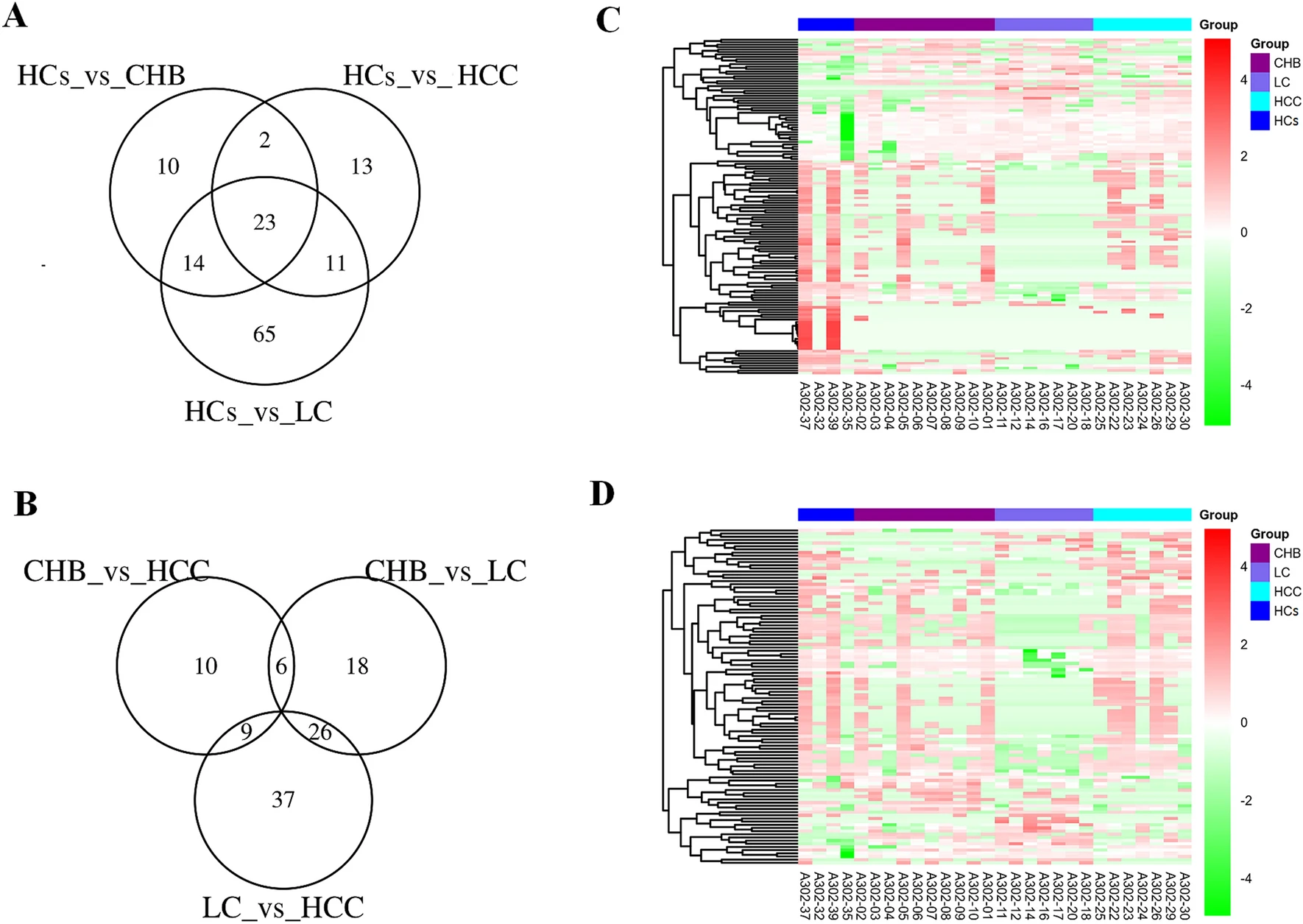
Ye B. et al. Sci Rep. 2022.
How to order?







