Labeled Exosomal Proteomic Detection Service
Labeled exosomal proteomic detection is a service based on labeled protein quantification technology for exosomal proteomics analysis, aimed at high-throughput, precise quantification and differential analysis of proteins in exosomes. This technique applies specific chemical tags to proteins from different samples, followed by high-resolution mass spectrometry for combined detection, allowing the analysis of protein types, abundances, and changes across multiple exosome samples. This reveals the molecular mechanisms of exosomes in various physiological or pathological states.
The labeled exosomal proteomic detection service is widely applied in fields such as cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, metabolic diseases, and immune diseases. It is especially useful for screening disease-related exosomal protein biomarkers, investigating the role of exosomes in disease progression, and evaluating the effects of exosomal drug delivery. Through labeling quantification methods, it provides highly sensitive, accurate, and comparable detection data across batch samples, offering strong support for disease mechanism research, clinical diagnosis, and the development of novel therapeutic strategies.
Services at MtoZ Biolabs
Based on high-resolution mass spectrometry platforms (such as Orbitrap, Q-Exactive series) and combined with labeling quantification technology, MtoZ Biolabs offers the labeled exosomal proteomic detection service for high-throughput, precise quantification of exosome proteins. The service includes exosome protein extraction, labeling, enzymatic digestion, separation, mass spectrometry analysis, and data analysis, ensuring highly sensitive, high-resolution protein identification and quantification data. Ultimately, the service provides exosome protein identification tables, abundance differential analysis, functional annotation, and pathway enrichment analysis reports, supporting research needs in disease mechanisms, biomarker discovery, and drug development.
Service Advantages
1. High-throughput Quantitative Analysis
Using multiplex labeling technology, this service supports the simultaneous analysis of multiple samples, improving detection efficiency and reducing batch-to-batch variation.
2. Comprehensive Protein Coverage
Systematically analyzing the abundant membrane proteins, transport proteins, and functional proteins within exosomes, this service reveals their roles in disease and cell communication.
3. Rich Data Analysis
Providing detailed protein identification, abundance changes, functional annotations, and pathway enrichment data, this service supports mechanism research and biomarker screening.
4. Professional Customization Service
Based on client needs, flexible labeling strategies and analysis plans are designed to meet various research and application goals.
Applications
1. Disease Biomarker Screening
By quantitatively analyzing exosomal proteins, specific biomarkers related to cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, metabolic disorders, and more can be identified for early diagnosis and prognosis evaluation.
2. Disease Mechanism Research
The labeled exosomal proteomic detection service systematically analyzes differential expression of exosomal proteins, revealing their roles in disease onset, progression, immune regulation, cell communication, and other biological processes.
3. Drug Targets and Efficacy Evaluation
By analyzing the changes in the exosomal proteome before and after drug treatment, potential drug targets can be identified, and the impact of the drug on exosome secretion and function can be evaluated.
4. Exosome Engineering and Delivery System Validation
The labeled exosomal proteomic detection service can be used to assess the protein composition of engineered or functionalized exosomes, validating the effectiveness and molecular composition of exosome-based drug delivery systems.
Case Study
1. High-performance Chemical Isotope Labeling Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry for Exosome Metabolomics
This study aims to develop an exosome metabolomics analysis method based on high-performance chemical isotope labeling liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (CIL LC-MS) to improve the detection sensitivity and coverage of metabolites in exosomes. The research targets exosomes secreted by human cells, which were extracted through ultracentrifugation and subjected to metabolomics analysis. The method involves using chemical isotope labeling to specifically derivatize metabolites within exosomes, enhancing their ionization efficiency. This is followed by separation and precise detection using a high-resolution liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry system. The results show that this method effectively identifies and quantifies a large number of exosomal metabolites, significantly enhancing the detection capability of low-abundance molecules and distinguishing the metabolic features of exosomes from different sources. The conclusion indicates that chemical isotope labeling technology provides a high-sensitivity and high-accuracy detection solution for exosome metabolomics, contributing to a deeper understanding of the role of exosomal metabolites in disease mechanisms and biomarker discovery, thus advancing exosome research toward precision medicine and clinical application.
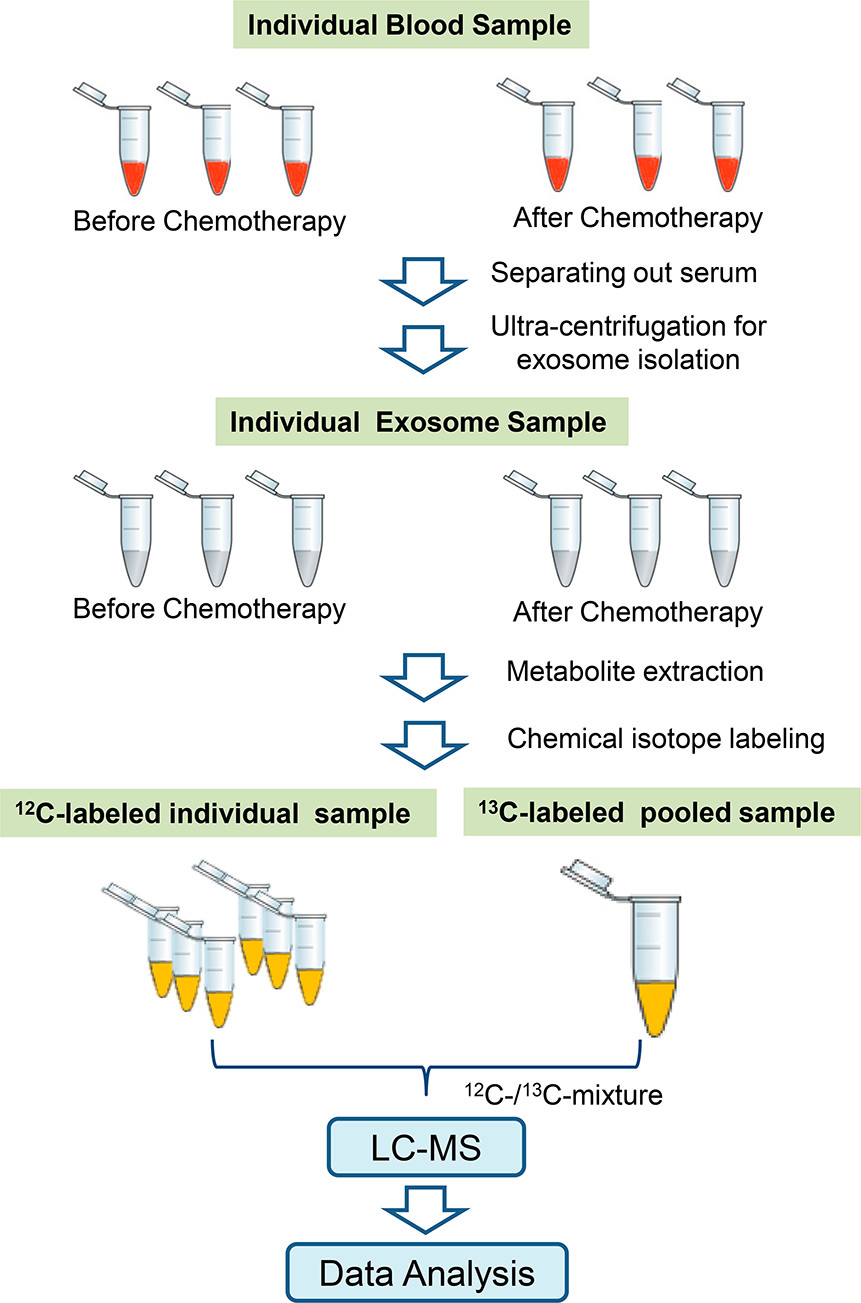
Luo, X. et al. Analytical Chemistry, 2018.
Figure 1. Workflow for Exosome Metabolomics Based on CIL nLC-MS.
2. Redefining the Breast Cancer Exosome Proteome by Tandem Mass Tag Quantitative Proteomics and Multivariate Cluster Analysis
This study aims to systematically analyze the protein composition of breast cancer-related exosomes using Tandem Mass Tag (TMT) quantitative proteomics and multivariate cluster analysis, to redefine the proteomic characteristics of breast cancer exosomes. The research focuses on exosomes secreted by different subtypes of breast cancer cell lines. Exosomes were extracted using ultracentrifugation, and their morphology and marker proteins were confirmed by transmission electron microscopy and Western blotting. TMT labeling combined with high-resolution mass spectrometry was then used for high-throughput quantitative analysis of the exosomal proteins, followed by multivariate statistical and cluster analysis to explore the expression features and potential functions of exosomal proteins in different breast cancer subtypes. The results show that breast cancer exosomes are enriched with a range of specific proteins related to cell adhesion, signal transduction, and immune regulation, and that there are significant differences in the exosomal protein expression across different breast cancer subtypes. This reveals the association between exosomal proteins and subtype-specific mechanisms of breast cancer. The conclusion emphasizes that TMT quantitative proteomics combined with cluster analysis provides a systematic approach for in-depth study of the breast cancer exosome proteome, aiding in the discovery of potential diagnostic and therapeutic targets and advancing the development of precision medicine in breast cancer.
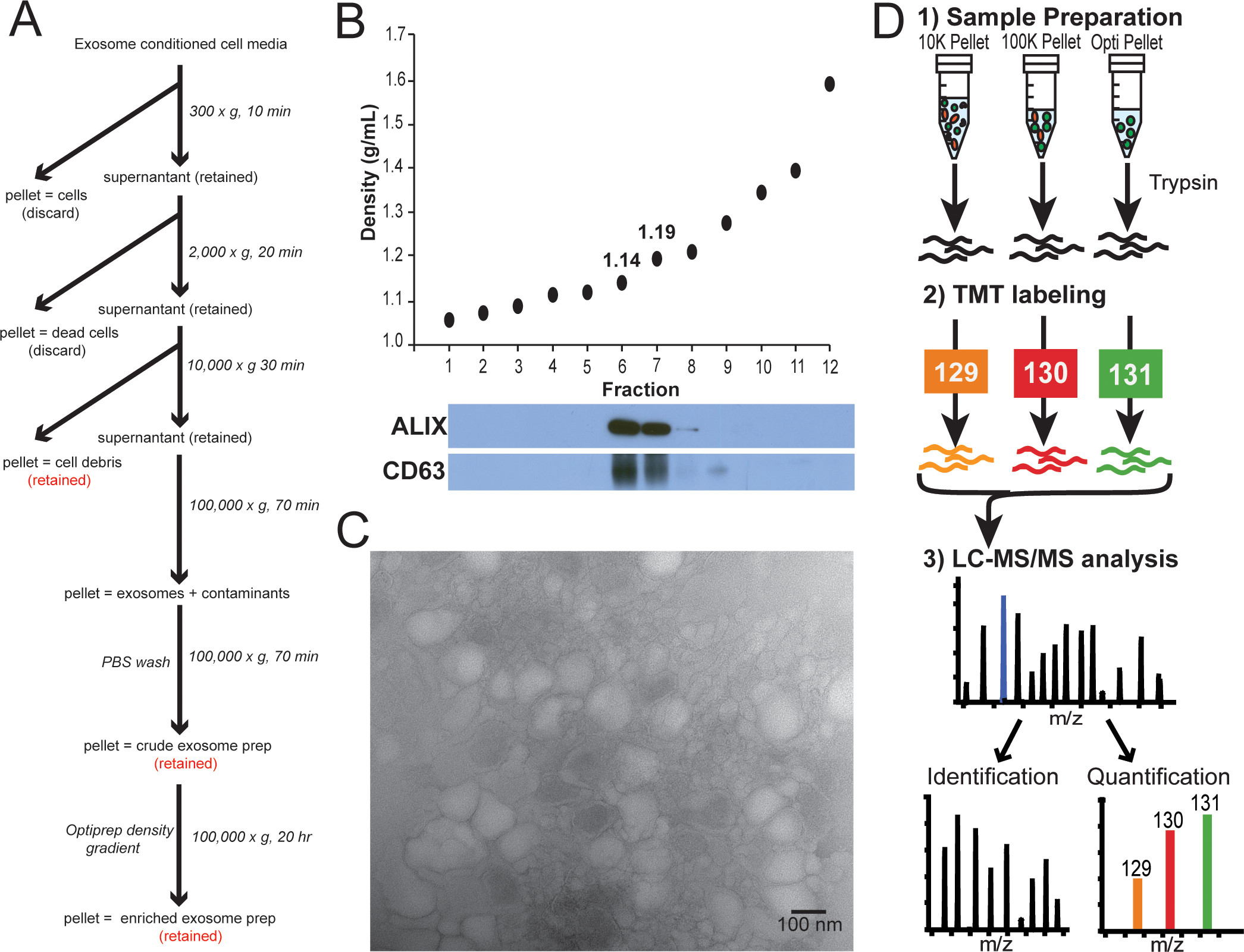
Clark, D J. Analytical Chemistry, 2015.
Figure 2. Overview of Exosome Isolation, Characterization, and TMT-Labeling Strategy to Elucidate Exosomal Protein Enrichment.
FAQ
Q1: What Is the Difference between Labeled Exosomal Proteomic Detection and Traditional Exosome Protein Detection Methods?
A1: Labeled Exosomal Proteomic Detection uses isotopic or chemical labeling methods combined with high-resolution mass spectrometry for precise quantification, allowing direct comparison between different samples. The sensitivity and quantification accuracy are much higher than traditional methods.
Q2: How to Ensure the Accuracy and Reproducibility of the Detection Data?
A2: We use standardized procedures throughout the protein extraction, labeling, and mass spectrometry detection process. We are equipped with high-resolution mass spectrometry platforms (such as Orbitrap, Q-Exactive, etc.), and implement technical replicates and quality control standards (such as internal standards and QC samples) to ensure high accuracy and good reproducibility of the data.
How to order?







